
In the structure given below, how many heteroatoms are present?


Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:
Heteroatoms are defined as the atoms other than carbon and hydrogen in a given compound. There are limited number of hetero atom in a compound. In a compound there cannot be more than three heteroatoms.
Complete answer:
-Heteroatoms are non hydrogen or non carbon atoms that have replaced carbon or hydrogen in the molecular structure.
-These atoms will have lesser or greater attraction for the electrons than the carbon atom.
-The bond that is present between carbon and the heteroatom is polar in nature.
-Heteroatoms affect the reactivity of the organic molecule.
-The examples of heteroatoms are: oxygen, nitrogen, bromine, chlorine, sulphur, phosphorus, iodine, lithium and magnesium.
-In the diagram given below:
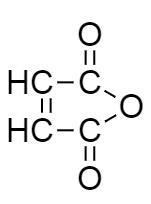
There is only one heteroatom present in a compound and that is oxygen.
Therefore, the compound given in the diagram consists of only one heteroatom.
Additional information:
Example of a compound which consists of two heteroatoms and that is acetamide.
The structure of acetamide is given below as follows:
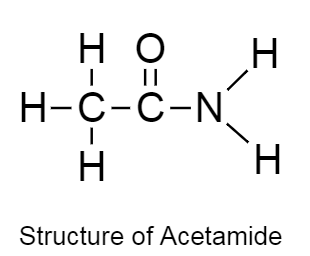
In the given structure there are two heteroatoms present namely: oxygen and nitrogen.
Likewise , we can identify heteroatoms on the basis of the molecular formula also.
Note:The polarity between carbon and oxygen bonds depends on the electron attracting properties of these atoms. For example if there are 2 oxygen atoms in a compound, it will still be considered as one heteroatom because we are only supposed to know which atom is there and not the number of the same heteroatom in a compound.
Heteroatoms are defined as the atoms other than carbon and hydrogen in a given compound. There are limited number of hetero atom in a compound. In a compound there cannot be more than three heteroatoms.
Complete answer:
-Heteroatoms are non hydrogen or non carbon atoms that have replaced carbon or hydrogen in the molecular structure.
-These atoms will have lesser or greater attraction for the electrons than the carbon atom.
-The bond that is present between carbon and the heteroatom is polar in nature.
-Heteroatoms affect the reactivity of the organic molecule.
-The examples of heteroatoms are: oxygen, nitrogen, bromine, chlorine, sulphur, phosphorus, iodine, lithium and magnesium.
-In the diagram given below:

There is only one heteroatom present in a compound and that is oxygen.
Therefore, the compound given in the diagram consists of only one heteroatom.
Additional information:
Example of a compound which consists of two heteroatoms and that is acetamide.
The structure of acetamide is given below as follows:

In the given structure there are two heteroatoms present namely: oxygen and nitrogen.
Likewise , we can identify heteroatoms on the basis of the molecular formula also.
Note:The polarity between carbon and oxygen bonds depends on the electron attracting properties of these atoms. For example if there are 2 oxygen atoms in a compound, it will still be considered as one heteroatom because we are only supposed to know which atom is there and not the number of the same heteroatom in a compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




