
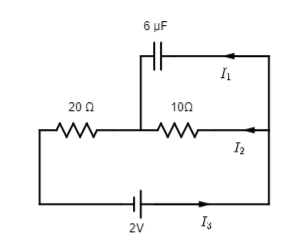
In the steady-state, find the charge on the capacitor shown in the figure
A) $4\mu C$
B) $5\mu C$
C) $6\mu C$
D) None

Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: We can find the \[{R_{equivalent}}\] as the two resistances are connected in series which helps us to find the current flowing through the circuit. This current will help us to find the voltage across the $10\Omega $resistance. After finding the voltage, we can use the formula \[Q = CV\].
Formula used:
\[{R_{series}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\] (when the resistance are in series)
\[V = iR\]( where \[V\] is the voltage across the circuit, $i$ be the current in the circuit and \[R\] be the resistance)
\[Q = CV\](where \[Q\] is the charge of the capacitor, \[V\] be the voltage across the capacitor and \[C\] be the capacitance of the capacitor)
Complete step by step answer:
We have given a circuit in a steady-state condition. We know that in steady-state conditions no current flows through the capacitor.
In the figure, there are two resistances (${R_1} = 10\Omega $ and ${R_2} = 20\Omega $ ) connected in series. So, the equivalent resistance (\[{R_{equivalent}}\])will be-
\[{R_{equivalent}} = 10 + 20 = 30\Omega \]
In the given figure, the potential difference ($V = 2V$ )is connected in the circuit. So, the current($i$ ) flow through the circuit is given as-
\[i = \dfrac{2}{{30}}{\text{ }}A\]
(Where \[i = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{equivalent}}}}\])
Now, the voltage drop across the \[10\Omega \] resistance is given as,
${V^{'}} = iR $
$\Rightarrow {V^{'}} = \dfrac{2}{{30}} \times 10$
$\Rightarrow {V^{'}} = \dfrac{2}{3}{\text{ }}V $
Which is equal to the voltage across the capacitor.
According to the figure, the charge in the capacitor of capacitance $C = 6\mu C$ will be given as,
\[Q = C{V^{'}}\]
$Q = 6 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times \dfrac{2}{3} $
$ \Rightarrow Q = 2 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 2 $
$ \Rightarrow Q = 4 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
$ \Rightarrow Q = 4\mu C $
($1\mu C = {10^{ - 6}}C$ )
Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
In steady-state conditions no current flows through the capacitor. The voltage across the $10\Omega $ resistance is equal to the voltage across the $C = 6\mu C$ capacitance.
Formula used:
\[{R_{series}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\] (when the resistance are in series)
\[V = iR\]( where \[V\] is the voltage across the circuit, $i$ be the current in the circuit and \[R\] be the resistance)
\[Q = CV\](where \[Q\] is the charge of the capacitor, \[V\] be the voltage across the capacitor and \[C\] be the capacitance of the capacitor)
Complete step by step answer:
We have given a circuit in a steady-state condition. We know that in steady-state conditions no current flows through the capacitor.
In the figure, there are two resistances (${R_1} = 10\Omega $ and ${R_2} = 20\Omega $ ) connected in series. So, the equivalent resistance (\[{R_{equivalent}}\])will be-
\[{R_{equivalent}} = 10 + 20 = 30\Omega \]
In the given figure, the potential difference ($V = 2V$ )is connected in the circuit. So, the current($i$ ) flow through the circuit is given as-
\[i = \dfrac{2}{{30}}{\text{ }}A\]
(Where \[i = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{equivalent}}}}\])
Now, the voltage drop across the \[10\Omega \] resistance is given as,
${V^{'}} = iR $
$\Rightarrow {V^{'}} = \dfrac{2}{{30}} \times 10$
$\Rightarrow {V^{'}} = \dfrac{2}{3}{\text{ }}V $
Which is equal to the voltage across the capacitor.
According to the figure, the charge in the capacitor of capacitance $C = 6\mu C$ will be given as,
\[Q = C{V^{'}}\]
$Q = 6 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times \dfrac{2}{3} $
$ \Rightarrow Q = 2 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 2 $
$ \Rightarrow Q = 4 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
$ \Rightarrow Q = 4\mu C $
($1\mu C = {10^{ - 6}}C$ )
Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
In steady-state conditions no current flows through the capacitor. The voltage across the $10\Omega $ resistance is equal to the voltage across the $C = 6\mu C$ capacitance.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




