
In the right angled triangle, the length of the perpendicular and the base are 8cm and 15 cm respectively. Find the length of its hypotenuse.
Answer
628.2k+ views
Hint: Because the given triangle is a right-angled triangle therefore, this question can be solved by applying Pythagoras theorem to the given triangle, which is stated as in any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs of the right triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
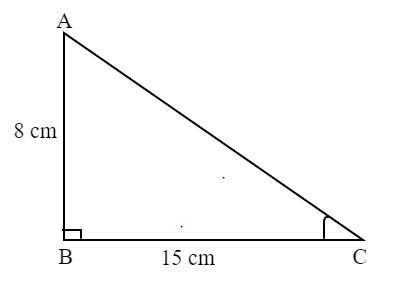
Take the triangle as ABC. Let the length of perpendicular be AB= 8cm and the length of the base be BC=15 cm and the hypotenuse to be determine is AC
The Pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs of the right triangle.
Then, because the given triangle ABC is a right-angled triangle therefore, we can apply Pythagoras theorem on the three sides of the triangle AB, BC, and AC.
By Pythagoras theorem, we have
\[AC{}^\text{2}=AB{}^\text{2}+BC{}^\text{2}\]
Substituting the values of length of perpendicular AB= 8cm and the length of the base BC=15 cm, we get \[AC{}^\text{2}=15{}^\text{2}+8{}^\text{2}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow AC{}^\text{2}=225+64 \\
& \\
& \Rightarrow AC{}^\text{2}=\text{ }289 \\
& \\
& \Rightarrow AC\text{ }={{(289)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}=\text{ }17 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we get the length of the hypotenuse AC =17, which is the required answer
Note: The possibility of error in the question would be applying Pythagoras theorem in the wrong way, that is using hypotenuse on the wrong side of the expression, which will give an incorrect solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Take the triangle as ABC. Let the length of perpendicular be AB= 8cm and the length of the base be BC=15 cm and the hypotenuse to be determine is AC
The Pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs of the right triangle.
Then, because the given triangle ABC is a right-angled triangle therefore, we can apply Pythagoras theorem on the three sides of the triangle AB, BC, and AC.
By Pythagoras theorem, we have
\[AC{}^\text{2}=AB{}^\text{2}+BC{}^\text{2}\]
Substituting the values of length of perpendicular AB= 8cm and the length of the base BC=15 cm, we get \[AC{}^\text{2}=15{}^\text{2}+8{}^\text{2}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow AC{}^\text{2}=225+64 \\
& \\
& \Rightarrow AC{}^\text{2}=\text{ }289 \\
& \\
& \Rightarrow AC\text{ }={{(289)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}=\text{ }17 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we get the length of the hypotenuse AC =17, which is the required answer
Note: The possibility of error in the question would be applying Pythagoras theorem in the wrong way, that is using hypotenuse on the wrong side of the expression, which will give an incorrect solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




