
In the projection of point \[P(\mathop p\limits^ \to )\]on the plane\[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\] is the points \[S(\mathop s\limits^ \to )\], then
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: The projection of a point is its shadow on the plane or central projection.
If C is a point, called the centre of projection then the projection of a point P different from C onto a plane that does not contain C is the interaction of the line CP with the plane.
Complete step-by- step solution:
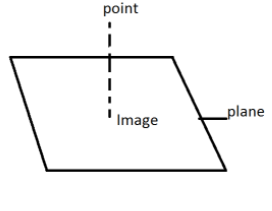
Let us draw a plane and the projection of point \[P(\mathop p\limits^ \to )\]on the plane is \[\mathop s\limits^ \to \].
The intersection is \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As the line is normal to the plane i.e. perpendicular to the plane and vector \[\mathop P\limits^ \to \] is passing through the plane and parallel to \[\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[E{q^n}\] of such a line is\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow p + \lambda \overrightarrow n ……...(1)\]
Given, \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q........(2)\]
As the line is passing through the plane, then the equation (1) will be satisfying equation (2) and that point \[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop s\limits^ \to \]
Substituting equation (1) in (2), we get:
$\Rightarrow$ \[(\mathop p\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to )\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
To find the value of \[\lambda \], simplify the above term then we get it as
\[ \Rightarrow \mathop p\limits^ \to . \mathop n\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As \[\left[ {\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n = {{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}} \right]\] , we get:
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda {\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2} = q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = \dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}}\]______ (3) {On RHS \[{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2}\] will be in division as it was multiplication on LHS}
Now using equation (3) in (1), we get:
\[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
We know that\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow s \], hence:
\[\mathop s\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
Note: Two planes are parallel if they have the same normal vector (i.e. their normal vectors are parallel). If two planes are not parallel, then they intersect in a line.If any line passes through a plane then it always satisfies the equation of that plane.
If C is a point, called the centre of projection then the projection of a point P different from C onto a plane that does not contain C is the interaction of the line CP with the plane.

Complete step-by- step solution:

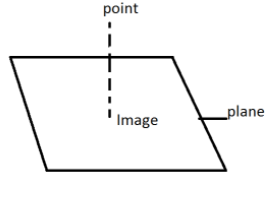
Let us draw a plane and the projection of point \[P(\mathop p\limits^ \to )\]on the plane is \[\mathop s\limits^ \to \].
The intersection is \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As the line is normal to the plane i.e. perpendicular to the plane and vector \[\mathop P\limits^ \to \] is passing through the plane and parallel to \[\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[E{q^n}\] of such a line is\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow p + \lambda \overrightarrow n ……...(1)\]
Given, \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q........(2)\]
As the line is passing through the plane, then the equation (1) will be satisfying equation (2) and that point \[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop s\limits^ \to \]
Substituting equation (1) in (2), we get:
$\Rightarrow$ \[(\mathop p\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to )\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
To find the value of \[\lambda \], simplify the above term then we get it as
\[ \Rightarrow \mathop p\limits^ \to . \mathop n\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As \[\left[ {\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n = {{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}} \right]\] , we get:
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda {\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2} = q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = \dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}}\]______ (3) {On RHS \[{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2}\] will be in division as it was multiplication on LHS}
Now using equation (3) in (1), we get:
\[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
We know that\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow s \], hence:
\[\mathop s\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
Note: Two planes are parallel if they have the same normal vector (i.e. their normal vectors are parallel). If two planes are not parallel, then they intersect in a line.If any line passes through a plane then it always satisfies the equation of that plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




