
In the process of ATP synthesis, oligomycin and DCCD act at which place in the figure:
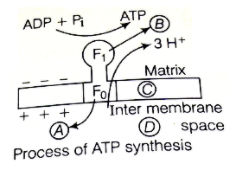
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for cells driving them to perform their functions. The formation of ATP is mediated by ATP synthase.
Complete answer:
To arrive at a solution, the process of ATP synthesis is to be studied. ATP is formed in the mitochondria by the oxidative phosphorylation of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) with a release of protons as follows:
\[ADP + Pi + 3{H^ + } \leftrightarrow ATP + H2O + 3{H^ + }\]
However, this reaction is energetically unfavourable to produce ATP. To overcome this, the ATP synthase couples this process along with the electrochemical gradient formed across the inner membrane and mitochondrial matrix during cellular respiration. This is possible by ATP synthase because of the two units in it, namely: \[F0\], an integral membrane protein complex which acts as a channel to protons and \[F1\], a peripheral membrane protein complex which contains the binding site for the ATP synthesis. The passage of protons through \[F0\] triggers the catalysis of ADP to ATP.
Oligomycin and N, \[N'\]-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) are ATP synthase inhibitors. They act on the \[F0\] subunit of ATP synthase, inhibiting ATP synthesis.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Oligomycin is a natural compound secreted by Streptomyces. They inhibit ATP synthesis by blocking the flow of protons. But they cannot completely block the flow due to the diffusion of protons through uncoupling protein. This phenomenon is known as proton leak.
DCCD is an inorganic compound. The ATP synthase has a rotatory mechanism for its production. DCCD causes steric hindrance to the rotating \[F0\] subunit, which halts the synthesis.
Complete answer:
To arrive at a solution, the process of ATP synthesis is to be studied. ATP is formed in the mitochondria by the oxidative phosphorylation of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) with a release of protons as follows:
\[ADP + Pi + 3{H^ + } \leftrightarrow ATP + H2O + 3{H^ + }\]
However, this reaction is energetically unfavourable to produce ATP. To overcome this, the ATP synthase couples this process along with the electrochemical gradient formed across the inner membrane and mitochondrial matrix during cellular respiration. This is possible by ATP synthase because of the two units in it, namely: \[F0\], an integral membrane protein complex which acts as a channel to protons and \[F1\], a peripheral membrane protein complex which contains the binding site for the ATP synthesis. The passage of protons through \[F0\] triggers the catalysis of ADP to ATP.
Oligomycin and N, \[N'\]-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) are ATP synthase inhibitors. They act on the \[F0\] subunit of ATP synthase, inhibiting ATP synthesis.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Oligomycin is a natural compound secreted by Streptomyces. They inhibit ATP synthesis by blocking the flow of protons. But they cannot completely block the flow due to the diffusion of protons through uncoupling protein. This phenomenon is known as proton leak.
DCCD is an inorganic compound. The ATP synthase has a rotatory mechanism for its production. DCCD causes steric hindrance to the rotating \[F0\] subunit, which halts the synthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




