
In the Northern Hemisphere, how do winds rotate in a low pressure area? What about in a high pressure area?
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: In the Northern Hemisphere, the winds rotate in a low pressure area in an anticlockwise swirl of winds which the air flows inwards, however, in high pressure area the air moves outward and rotates in clockwise swirl of winds due to coriolis effect.
Complete answer:
The figure below shows the low pressure area and high pressure area in the northern hemisphere of the earth. The red arrows show that in low pressure area air moves inward in anticlockwise direction and the blue arrows shows in high pressure area air moves outward in clockwise direction.
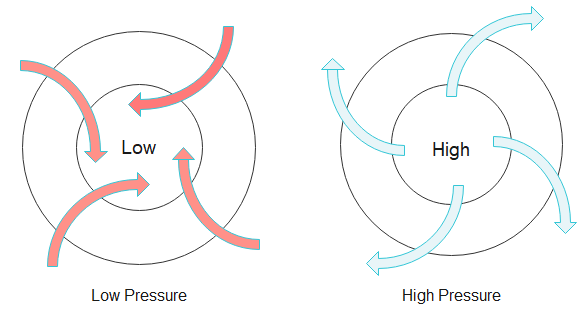
In the Northern Hemisphere, air is deflected towards the right due to Coriolis force, this phenomenon is called the Coriolis effect. Coriolis force is a fictional force which acts on the earth because of its rotation about its axis. Coriolis force is normally quite small, it becomes more relevant when considering motion of large objects over huge time intervals like the rotation of the earth.
Coriolis force is given by,
$F=-2m(\omega \times r)$ …(i)
Where, m is mass of earth, $\omega $ is angular velocity of earth and v is velocity of object (air).
In a low pressure area, in the low region where the air pressure is lower than the surroundings, air moves inwards (anticlockwise) as air is deflected towards the right due to Coriolis effect. This causes cyclones in the low pressure areas.
In a high pressure area, where the pressure is higher than the surroundings, air moves outwards (clockwise) as air is deflected towards the right due to Coriolis effect. This causes anticyclones in the high pressure areas.
Additional Information:
In the southern hemisphere, as air is deflected towards the left due to Coriolis effect. Thus, wind blows in anticlockwise direction in a high pressure area and wind blows in clockwise direction in a low pressure area.
Note:
Students should not be confused by the movement of air in high and low pressure areas in the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere. It is important to remember the concept of Coriolis effect and formula of Coriolis force given by equation (i) above.
Complete answer:
The figure below shows the low pressure area and high pressure area in the northern hemisphere of the earth. The red arrows show that in low pressure area air moves inward in anticlockwise direction and the blue arrows shows in high pressure area air moves outward in clockwise direction.

In the Northern Hemisphere, air is deflected towards the right due to Coriolis force, this phenomenon is called the Coriolis effect. Coriolis force is a fictional force which acts on the earth because of its rotation about its axis. Coriolis force is normally quite small, it becomes more relevant when considering motion of large objects over huge time intervals like the rotation of the earth.
Coriolis force is given by,
$F=-2m(\omega \times r)$ …(i)
Where, m is mass of earth, $\omega $ is angular velocity of earth and v is velocity of object (air).
In a low pressure area, in the low region where the air pressure is lower than the surroundings, air moves inwards (anticlockwise) as air is deflected towards the right due to Coriolis effect. This causes cyclones in the low pressure areas.
In a high pressure area, where the pressure is higher than the surroundings, air moves outwards (clockwise) as air is deflected towards the right due to Coriolis effect. This causes anticyclones in the high pressure areas.
Additional Information:
In the southern hemisphere, as air is deflected towards the left due to Coriolis effect. Thus, wind blows in anticlockwise direction in a high pressure area and wind blows in clockwise direction in a low pressure area.
Note:
Students should not be confused by the movement of air in high and low pressure areas in the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere. It is important to remember the concept of Coriolis effect and formula of Coriolis force given by equation (i) above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




