
In the normal expiration, the diaphragm is –
A) Arched
B) Flattened
C) Not involved
D) Perforated
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint:During the process of expiration, the intercostal muscles along with the diaphragm acquire their relaxed states. The diaphragm relaxes in order to decrease the volume of the thoracic chamber.
Complete Answer:
To understand this concept, we need to study the mechanism involved in breathing. There are two basic steps of this mechanism which are inspiration and expiration. Atmospheric air is drawn into the lungs during inspiration while in expiration, alveolar air is released outside. A pressure gradient is formed between the lungs and the environment in order to exchange gases. Inspiration occurs when the intrapulmonary pressure, i.e. the pressure inside lungs is less than that of the atmosphere. This produced a negative pressure inside the lungs with respect to the atmosphere. Similarly, when intrapulmonary pressure is higher than that of the atmosphere, expiration occurs as the pressure gradient inside the lungs is higher with respect with the environment. This change of gradient occurs due to activity of diaphragm and intercostal muscles, both internal as well as external intercostal muscles. For inspiration, diaphragm contracts and the external intercostal muscles lift up the ribs along with sternum due to contraction, thereby increasing the volume of the thoracic chamber in both antero-posterior and dorsi-ventral axes. This increases the pulmonary volume which decreases the intrapulmonary pressure and results in inspiration. The relaxation of intercostal muscles and diaphragm returns sternum to its normal position, decreasing the volume of the thoracic chamber which results in an increased intrapulmonary pressure, finally resulting in expiration.
Thus, the correct answer is option ‘A’. Arched.
Note:The contraction in muscles causes inspiration while their relaxation results in expiration. The diaphragm remains arched in its relaxed state while expands due to contraction.
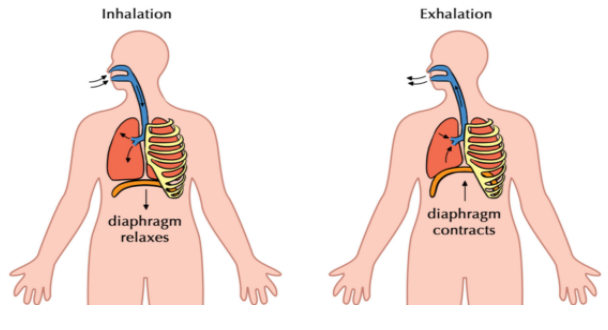
Complete Answer:
To understand this concept, we need to study the mechanism involved in breathing. There are two basic steps of this mechanism which are inspiration and expiration. Atmospheric air is drawn into the lungs during inspiration while in expiration, alveolar air is released outside. A pressure gradient is formed between the lungs and the environment in order to exchange gases. Inspiration occurs when the intrapulmonary pressure, i.e. the pressure inside lungs is less than that of the atmosphere. This produced a negative pressure inside the lungs with respect to the atmosphere. Similarly, when intrapulmonary pressure is higher than that of the atmosphere, expiration occurs as the pressure gradient inside the lungs is higher with respect with the environment. This change of gradient occurs due to activity of diaphragm and intercostal muscles, both internal as well as external intercostal muscles. For inspiration, diaphragm contracts and the external intercostal muscles lift up the ribs along with sternum due to contraction, thereby increasing the volume of the thoracic chamber in both antero-posterior and dorsi-ventral axes. This increases the pulmonary volume which decreases the intrapulmonary pressure and results in inspiration. The relaxation of intercostal muscles and diaphragm returns sternum to its normal position, decreasing the volume of the thoracic chamber which results in an increased intrapulmonary pressure, finally resulting in expiration.
Thus, the correct answer is option ‘A’. Arched.
Note:The contraction in muscles causes inspiration while their relaxation results in expiration. The diaphragm remains arched in its relaxed state while expands due to contraction.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




