
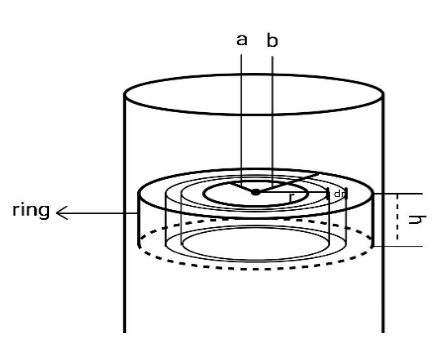
In the middle of a long solenoid there is a coaxial ring of square cross-section, made of conductive material with resistivity $\rho $. The thickness of the ring is equal to $h$, its inside and outside radii are equal to $'a'$ and $'b'$ respectively. What is the current induced in a radial width $(dr)$, where the magnetic field varies with time as $B = \beta t$?
(A) $\dfrac{{h(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }}$
(B) $\dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{4\rho }}$
(C) $\dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{\rho }$
(D) \[\dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }}\]

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: The cylinder is the solenoid. The EMF induced in the circular strip of radius $r$ will be given by Faraday's Law. Now after finding the EMF induced, the current induced will be $\dfrac{E}{R}$, where $E$ is the EMF induced and $R$ is the resistance offered by the strip. Here, the current will pass through the rectangular cross section area of length $h$ and width $dr$.
Complete step by step answer:
The EMF induced will be $E = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$, where $\phi $ is the flux given as $\phi = {\mathbf{B}}.{\mathbf{A}}$. Here, the magnetic field $B$ is parallel to the axis of the solenoid, and the area vector of the circular strip is also in the same direction which is in the upward direction parallel to the axis of the cylinder. Therefore the angle between the magnetic field and the area vector will be zero.
Hence,
$
{\mathbf{B}}.{\mathbf{A}} = BA\cos 0^\circ \\
{\mathbf{B}}.{\mathbf{A}} = BA \\ $
Now, $\phi = \beta t\pi {r^2}$
$
E = - \dfrac{{d(\beta t\pi {r^2})}}{{dt}} \\
\Rightarrow E = - \beta \pi {r^2}\dfrac{{d(t)}}{{dt}} \\ $
$r$ is constant because we are looking for the circular strip only.
The EMF induced will be $E = - \beta \pi {r^2}$
Now, the resistance offered by the strip will be $R = \rho \dfrac{l}{A}$.
$R = \rho \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{{h(dr)}}$.
Therefore, the current will be given by $i = \dfrac{E}{R}$
$
i = - \dfrac{{\beta \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{{h(dr)}}}} \\
\therefore i = - \dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }} \\ $
Here the current came out to be negative, meaning the direction of the current will be in the opposite direction of the current flowing in the solenoid. The magnitude of the current will be \[\dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }}\].Hence, the current induced in a radial width $(dr)$ will be \[\dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The current induced flows in the direction in which it opposes the effect of the magnetic flux. If the flux is increasing, the current will be induced in such a direction that will reduce the flux.If the flux is decreasing, the current will be induced in such a direction that will increase the flux.
Complete step by step answer:
The EMF induced will be $E = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$, where $\phi $ is the flux given as $\phi = {\mathbf{B}}.{\mathbf{A}}$. Here, the magnetic field $B$ is parallel to the axis of the solenoid, and the area vector of the circular strip is also in the same direction which is in the upward direction parallel to the axis of the cylinder. Therefore the angle between the magnetic field and the area vector will be zero.
Hence,
$
{\mathbf{B}}.{\mathbf{A}} = BA\cos 0^\circ \\
{\mathbf{B}}.{\mathbf{A}} = BA \\ $
Now, $\phi = \beta t\pi {r^2}$
$
E = - \dfrac{{d(\beta t\pi {r^2})}}{{dt}} \\
\Rightarrow E = - \beta \pi {r^2}\dfrac{{d(t)}}{{dt}} \\ $
$r$ is constant because we are looking for the circular strip only.
The EMF induced will be $E = - \beta \pi {r^2}$
Now, the resistance offered by the strip will be $R = \rho \dfrac{l}{A}$.
$R = \rho \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{{h(dr)}}$.
Therefore, the current will be given by $i = \dfrac{E}{R}$
$
i = - \dfrac{{\beta \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{{h(dr)}}}} \\
\therefore i = - \dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }} \\ $
Here the current came out to be negative, meaning the direction of the current will be in the opposite direction of the current flowing in the solenoid. The magnitude of the current will be \[\dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }}\].Hence, the current induced in a radial width $(dr)$ will be \[\dfrac{{hr(dr)\beta }}{{2\rho }}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The current induced flows in the direction in which it opposes the effect of the magnetic flux. If the flux is increasing, the current will be induced in such a direction that will reduce the flux.If the flux is decreasing, the current will be induced in such a direction that will increase the flux.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




