
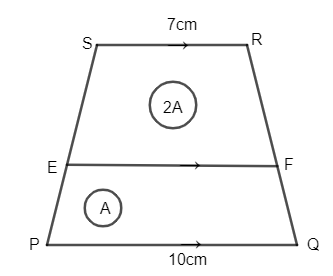
In the given figure the area of trapezium PQFE is half of the area of trapezium EFRS. If $\text{SR}\parallel \text{EF}\parallel \text{PQ}$ and SR and PQ is 7 cm and 10 cm respectively, then EF $\text{=?}$
(a)9cm
(b)$\sqrt{83}cm$
(c)$4\sqrt{6}cm$
(d)$\sqrt{87}cm$

Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint: We have been given the areas of the trapezium. Find the height of both the trapezium and the length of EF as $\left( SR+K \right)$ , where K is a constant. Thus, area of EFRS $=2\times $ area of PQFE. Equate the value using trapezoidal. Find and then substitute it in EF to find the length of EF.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the figure where PQRS is trapezium. We have been given the area of trapezium EFRS and PQFE in the figure. We get three values from the figure.
The area of trapezium PQFE \[=\] A
The area of trapezium EFRS \[=\] 2A
Thus, total area of trapezium PQRS \[=\] area of trapezium PQEF + area of trapezium EFRS
\[=A+2A=3A\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of trapezium PQRS \[=\] 3A.
We know that Area of trapezium is given by the formula,
Area $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b \right)h$
We have been told that $\text{SR}\parallel \text{EF}\parallel \text{PQ}$ . And the length of the sides SR and PQ. Let us take the height of the trapezium as H.
We know $PQ=10cm$ and $SR=7cm$
$\therefore $ Area of trapezium PQRS $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( PQ+SR \right)H$
We found the area of 3A.
$\therefore 3A=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 10+7 \right)H$
$\therefore 3A=\dfrac{17}{2}H$
The height of the trapezium is directly proportional to the decrease in the difference between the length of parallel sides.
Let us consider the length of EF \[=SR+K\]
\[\therefore EF=7+K\]
The height of trapezium EFRS \[=\dfrac{KH}{3}\]
Height of trapezium PQEF \[=\dfrac{\left( PQ-SR-K \right)H}{3}\]
\[=\dfrac{\left( 10+7+K \right)H}{3}=\dfrac{\left( 3-K \right)H}{3}\]
$\therefore $ height of trapezium PQEF \[=\dfrac{\left( 3-K \right)H}{3}\]
$\therefore $ Area of EFRS $=2\times $ area of PQEF
Area of EFRS $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{KH}{3} \right)\left( SR+EF \right)$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{KH}{3} \right)\left( 7+7+K \right)=\left( \dfrac{KH}{6} \right)\left( 14+K \right)$
Area of PQEF $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{\left( 3-K \right)H}{3} \right)\left( PQ+EF \right)$
\[=\dfrac{1}{6}\left( 3-K \right)H\left( 10+7+K \right)=\dfrac{\left( 17+K \right)\left( 3-K \right)H}{6}\]
$\therefore $ area of EFRS $=2\times $ area of PQEF
Substitute the value in above and simplify it
$a\left( \dfrac{KH}{6} \right)\left( 14+K \right)=\dfrac{\left( 17+K \right)\left( 3-K \right)H}{6}\times 2$
Let us simplify the above, cancel out $\dfrac{H}{6}$ on LHS and RHS.
$K\left( 14+K \right)=2\left( 17+K \right)\left( 3-K \right)$
$14K+{{K}^{2}}=2\left[ 51-17K+3K+{{K}^{2}} \right]$
$3{{K}^{2}}+42K-102=0$
The above epression is similar to the general quadratic expression $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ , where it is K in place of x. Thus, comparing we get, $a=3,b=+42,c=-102$ .
Now put three values in quadratic formula,
$K=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left( +42 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -42 \right)}^{2}}+4\times 3\times 102}}{2\times 3}$
$=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{1764+1224}}{6}=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{2988}}{6}=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{36\times 83}}{6}$
$=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{{{6}^{2}}\times 83}}{6}$
$=\dfrac{-42\pm 6\sqrt{83}}{6}$
$=-7\pm \sqrt{83}$
Thus, let us take the positive value K $=-7+\sqrt{83}$
$\therefore EF=7+K$
$=7-7+\sqrt{83}=\sqrt{83}$
Hence, the length of EF $=\sqrt{83}cm$
$\therefore $ Option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Assume the length of EF as $\left( 7+K \right)$ . If you miss this step, then the entire solution becomes complex. After then, find the value of K. Don’t forget to put it in the expression of EF.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the figure where PQRS is trapezium. We have been given the area of trapezium EFRS and PQFE in the figure. We get three values from the figure.
The area of trapezium PQFE \[=\] A
The area of trapezium EFRS \[=\] 2A
Thus, total area of trapezium PQRS \[=\] area of trapezium PQEF + area of trapezium EFRS
\[=A+2A=3A\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of trapezium PQRS \[=\] 3A.
We know that Area of trapezium is given by the formula,
Area $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b \right)h$
We have been told that $\text{SR}\parallel \text{EF}\parallel \text{PQ}$ . And the length of the sides SR and PQ. Let us take the height of the trapezium as H.
We know $PQ=10cm$ and $SR=7cm$
$\therefore $ Area of trapezium PQRS $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( PQ+SR \right)H$
We found the area of 3A.
$\therefore 3A=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 10+7 \right)H$
$\therefore 3A=\dfrac{17}{2}H$
The height of the trapezium is directly proportional to the decrease in the difference between the length of parallel sides.
Let us consider the length of EF \[=SR+K\]
\[\therefore EF=7+K\]
The height of trapezium EFRS \[=\dfrac{KH}{3}\]
Height of trapezium PQEF \[=\dfrac{\left( PQ-SR-K \right)H}{3}\]
\[=\dfrac{\left( 10+7+K \right)H}{3}=\dfrac{\left( 3-K \right)H}{3}\]
$\therefore $ height of trapezium PQEF \[=\dfrac{\left( 3-K \right)H}{3}\]
$\therefore $ Area of EFRS $=2\times $ area of PQEF
Area of EFRS $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{KH}{3} \right)\left( SR+EF \right)$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{KH}{3} \right)\left( 7+7+K \right)=\left( \dfrac{KH}{6} \right)\left( 14+K \right)$
Area of PQEF $=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{\left( 3-K \right)H}{3} \right)\left( PQ+EF \right)$
\[=\dfrac{1}{6}\left( 3-K \right)H\left( 10+7+K \right)=\dfrac{\left( 17+K \right)\left( 3-K \right)H}{6}\]
$\therefore $ area of EFRS $=2\times $ area of PQEF
Substitute the value in above and simplify it
$a\left( \dfrac{KH}{6} \right)\left( 14+K \right)=\dfrac{\left( 17+K \right)\left( 3-K \right)H}{6}\times 2$
Let us simplify the above, cancel out $\dfrac{H}{6}$ on LHS and RHS.
$K\left( 14+K \right)=2\left( 17+K \right)\left( 3-K \right)$
$14K+{{K}^{2}}=2\left[ 51-17K+3K+{{K}^{2}} \right]$
$3{{K}^{2}}+42K-102=0$
The above epression is similar to the general quadratic expression $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ , where it is K in place of x. Thus, comparing we get, $a=3,b=+42,c=-102$ .
Now put three values in quadratic formula,
$K=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left( +42 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -42 \right)}^{2}}+4\times 3\times 102}}{2\times 3}$
$=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{1764+1224}}{6}=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{2988}}{6}=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{36\times 83}}{6}$
$=\dfrac{-42\pm \sqrt{{{6}^{2}}\times 83}}{6}$
$=\dfrac{-42\pm 6\sqrt{83}}{6}$
$=-7\pm \sqrt{83}$
Thus, let us take the positive value K $=-7+\sqrt{83}$
$\therefore EF=7+K$
$=7-7+\sqrt{83}=\sqrt{83}$
Hence, the length of EF $=\sqrt{83}cm$
$\therefore $ Option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Assume the length of EF as $\left( 7+K \right)$ . If you miss this step, then the entire solution becomes complex. After then, find the value of K. Don’t forget to put it in the expression of EF.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




