
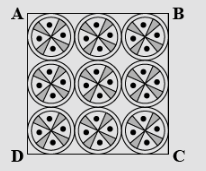
In the given figure on a square handkerchief, nine circular designs each of radius $7cm$ are made. Find the area of the remaining of the handkerchief.

Answer
621.9k+ views
Hint: Find the relation between the radius of the circle and the side of the square and then calculate the required areas.
Let the radius of the circle is $r$ and the side of the square handkerchief is $S$. The radius is given in the question. So, we have:
$ \Rightarrow r = 7cm$
As we can see from the figure, each side of the square is completely covered by three circles.
Thus the side of the square will be the sum of the lengths of the diameter of these three circles. But the circles are of equal diameters, then we have:
$
\Rightarrow s = 2r + 2r + 2r, \\
\Rightarrow s = 2(7) + 2(7) + 2(7) \\
\Rightarrow s = 14 + 14 + 14, \\
\Rightarrow s = 42 \\
$
Thus the side of the square is $42 cm$ . And we know the formula for the area of square which is ${s^2}$. So we have:
$
\Rightarrow {A_{square}} = {s^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{square}} = {\left( {42} \right)^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{square}} = 1764c{m^2} \\
$
Area of circle is $\pi {r^2}$. And there are $9$ circles in the square. So, the total area of all the circles is:
$
\Rightarrow {A_{circles}} = 9\pi {r^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{circles}} = 9 \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( 7 \right)^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{circles}} = 1386c{m^2}. \\
$
Therefore, the area of the remaining part of the handkerchief is:
$
\Rightarrow {A_{remaining}} = {A_{square}} - {A_{circles}}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{remaining}} = 1764 - 1386, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{remaining}} = 378c{m^2}. \\
$
Thus, the area of the remaining portion of the handkerchief is $378c{m^2}$.
Note: In such cases, when one of the standard geometrical figures is inscribed in another standard figure, finding the relation between the sides of both the figures is the key point to solve the question.
Let the radius of the circle is $r$ and the side of the square handkerchief is $S$. The radius is given in the question. So, we have:
$ \Rightarrow r = 7cm$
As we can see from the figure, each side of the square is completely covered by three circles.
Thus the side of the square will be the sum of the lengths of the diameter of these three circles. But the circles are of equal diameters, then we have:
$
\Rightarrow s = 2r + 2r + 2r, \\
\Rightarrow s = 2(7) + 2(7) + 2(7) \\
\Rightarrow s = 14 + 14 + 14, \\
\Rightarrow s = 42 \\
$
Thus the side of the square is $42 cm$ . And we know the formula for the area of square which is ${s^2}$. So we have:
$
\Rightarrow {A_{square}} = {s^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{square}} = {\left( {42} \right)^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{square}} = 1764c{m^2} \\
$
Area of circle is $\pi {r^2}$. And there are $9$ circles in the square. So, the total area of all the circles is:
$
\Rightarrow {A_{circles}} = 9\pi {r^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{circles}} = 9 \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( 7 \right)^2}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{circles}} = 1386c{m^2}. \\
$
Therefore, the area of the remaining part of the handkerchief is:
$
\Rightarrow {A_{remaining}} = {A_{square}} - {A_{circles}}, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{remaining}} = 1764 - 1386, \\
\Rightarrow {A_{remaining}} = 378c{m^2}. \\
$
Thus, the area of the remaining portion of the handkerchief is $378c{m^2}$.
Note: In such cases, when one of the standard geometrical figures is inscribed in another standard figure, finding the relation between the sides of both the figures is the key point to solve the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




