
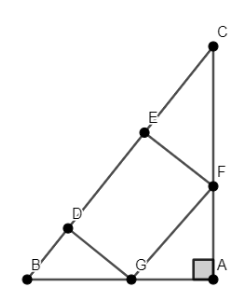
In the given figure, DEFG is a square and \[\angle BAC={{90}^{\circ }}\]. Show that \[D{{E}^{2}}=BD\times EC\].

Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint: Prove that $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta ECF$ are similar using AA (Angle – Angle) Property. Use the fact that the ratio of corresponding sides of similar triangles is equal. Rearrange the terms to prove the given expression.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We have $\Delta ABC$ with a square DEFG inscribed in it such that \[\angle BAC={{90}^{\circ }}\]. We have to prove that \[D{{E}^{2}}=BD\times EC\].
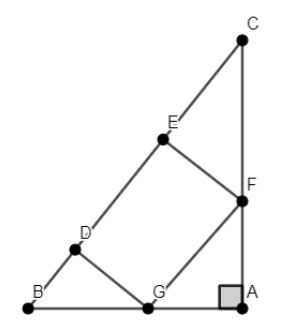
We will prove that $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta ECF$ are similar.
As DEFG is a square, each angle is equal to ${{90}^{\circ }}$. Thus, we have $\angle GDE=\angle DEF={{90}^{\circ }}$.
We observe that $\angle GDE$ and $\angle BDG$ form a linear pair. Thus, we have $\angle GDE+\angle BDG={{180}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle BDG={{180}^{\circ }}\Rightarrow \angle BDG={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }}$
Similarly, we observe that $\angle DEF$ and $\angle CEF$ form a linear pair. Thus, we have $\angle DEF+\angle CEF={{180}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle CEF={{180}^{\circ }}\Rightarrow \angle CEF={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }}$
Thus, we have $\angle CEF=\angle BDG={{90}^{\circ }}.....\left( 1 \right)$.
Let’s assume that $\angle DBG=x$.
We know that the sum of all interior angles of a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
In $\Delta BDG$, we have $\angle BDG+\angle DGB+\angle GBD={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting the values $\angle GBD=x,\angle BDG={{90}^{\circ }}$ in the above equation, we have $x+{{90}^{\circ }}+\angle DGB={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle DGB={{180}^{\circ }}-x-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }}-x$.
We know that $\angle DGF={{90}^{\circ }}$ as all the angles of a square measure ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
As BA is a straight line, we have $\angle BGD+\angle DGF+\angle FGA={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting $\angle DGF={{90}^{\circ }},\angle BGD={{90}^{\circ }}-x$ in the above equation, we have ${{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x+\angle FGA={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle FGA={{180}^{\circ }}-\left( {{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x \right)=x$.
We know that sum of all interior angles of a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle GAF={{90}^{\circ }}$ as $\Delta GAF$ is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at A.
Thus, we have $\angle FGA+\angle GAF+\angle AFG={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting $\angle FGA=x,\angle GAF={{90}^{\circ }}$ in the above equation, we have $x+{{90}^{\circ }}+\angle AFG={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle AFG={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}-x={{90}^{\circ }}-x$.
We know that $\angle GFE={{90}^{\circ }}$ as all the angles of a square measure ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
As AC is a straight line, we have $\angle AFG+\angle GFE+\angle EFC={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting $\angle GFE={{90}^{\circ }},\angle AFG={{90}^{\circ }}-x$ in the above equation, we have ${{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x+\angle EFC={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle EFC={{180}^{\circ }}-\left( {{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x \right)=x$.
Thus, we observe that $\angle DBG=\angle EFC=x.....\left( 2 \right)$.
Using equation (1) and (2), we observe that two angles of the triangles $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta FEC$ are equal.
Thus, using AA (Angle – Angle) Property, we observe that $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta FEC$ are similar.
We know that the ratio of corresponding sides of similar triangles is equal.
Thus, we have $\dfrac{BD}{FE}=\dfrac{DG}{EC}=\dfrac{BG}{FC}.....\left( 3 \right)$.
As DEFG is a square, the length of all of its sides is equal. Thus, we have $DE=EF=FG=GD.....\left( 4 \right)$.
Substituting equation (4) in equation (3), we have $\dfrac{BD}{DE}=\dfrac{DE}{EC}$.
Cross multiplying the terms of the above equation, we have $BD\times EC={{\left( DE \right)}^{2}}$.
Hence, we have proved that $BD\times EC={{\left( DE \right)}^{2}}$.
Note: We can also solve this question by proving that $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta GAF$ are similar. Also, prove that $\Delta GAF$ is similar to $\Delta FEC$ and thus $\Delta BDG$ is similar to $\Delta FEC$. We can also prove that the two triangles are similar using AAA Property.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We have $\Delta ABC$ with a square DEFG inscribed in it such that \[\angle BAC={{90}^{\circ }}\]. We have to prove that \[D{{E}^{2}}=BD\times EC\].

We will prove that $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta ECF$ are similar.
As DEFG is a square, each angle is equal to ${{90}^{\circ }}$. Thus, we have $\angle GDE=\angle DEF={{90}^{\circ }}$.
We observe that $\angle GDE$ and $\angle BDG$ form a linear pair. Thus, we have $\angle GDE+\angle BDG={{180}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle BDG={{180}^{\circ }}\Rightarrow \angle BDG={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }}$
Similarly, we observe that $\angle DEF$ and $\angle CEF$ form a linear pair. Thus, we have $\angle DEF+\angle CEF={{180}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle CEF={{180}^{\circ }}\Rightarrow \angle CEF={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }}$
Thus, we have $\angle CEF=\angle BDG={{90}^{\circ }}.....\left( 1 \right)$.
Let’s assume that $\angle DBG=x$.
We know that the sum of all interior angles of a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
In $\Delta BDG$, we have $\angle BDG+\angle DGB+\angle GBD={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting the values $\angle GBD=x,\angle BDG={{90}^{\circ }}$ in the above equation, we have $x+{{90}^{\circ }}+\angle DGB={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle DGB={{180}^{\circ }}-x-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }}-x$.
We know that $\angle DGF={{90}^{\circ }}$ as all the angles of a square measure ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
As BA is a straight line, we have $\angle BGD+\angle DGF+\angle FGA={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting $\angle DGF={{90}^{\circ }},\angle BGD={{90}^{\circ }}-x$ in the above equation, we have ${{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x+\angle FGA={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle FGA={{180}^{\circ }}-\left( {{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x \right)=x$.
We know that sum of all interior angles of a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle GAF={{90}^{\circ }}$ as $\Delta GAF$ is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at A.
Thus, we have $\angle FGA+\angle GAF+\angle AFG={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting $\angle FGA=x,\angle GAF={{90}^{\circ }}$ in the above equation, we have $x+{{90}^{\circ }}+\angle AFG={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle AFG={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}-x={{90}^{\circ }}-x$.
We know that $\angle GFE={{90}^{\circ }}$ as all the angles of a square measure ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
As AC is a straight line, we have $\angle AFG+\angle GFE+\angle EFC={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Substituting $\angle GFE={{90}^{\circ }},\angle AFG={{90}^{\circ }}-x$ in the above equation, we have ${{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x+\angle EFC={{180}^{\circ }}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $\angle EFC={{180}^{\circ }}-\left( {{90}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}-x \right)=x$.
Thus, we observe that $\angle DBG=\angle EFC=x.....\left( 2 \right)$.
Using equation (1) and (2), we observe that two angles of the triangles $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta FEC$ are equal.
Thus, using AA (Angle – Angle) Property, we observe that $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta FEC$ are similar.
We know that the ratio of corresponding sides of similar triangles is equal.
Thus, we have $\dfrac{BD}{FE}=\dfrac{DG}{EC}=\dfrac{BG}{FC}.....\left( 3 \right)$.
As DEFG is a square, the length of all of its sides is equal. Thus, we have $DE=EF=FG=GD.....\left( 4 \right)$.
Substituting equation (4) in equation (3), we have $\dfrac{BD}{DE}=\dfrac{DE}{EC}$.
Cross multiplying the terms of the above equation, we have $BD\times EC={{\left( DE \right)}^{2}}$.
Hence, we have proved that $BD\times EC={{\left( DE \right)}^{2}}$.
Note: We can also solve this question by proving that $\Delta BDG$ and $\Delta GAF$ are similar. Also, prove that $\Delta GAF$ is similar to $\Delta FEC$ and thus $\Delta BDG$ is similar to $\Delta FEC$. We can also prove that the two triangles are similar using AAA Property.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




