
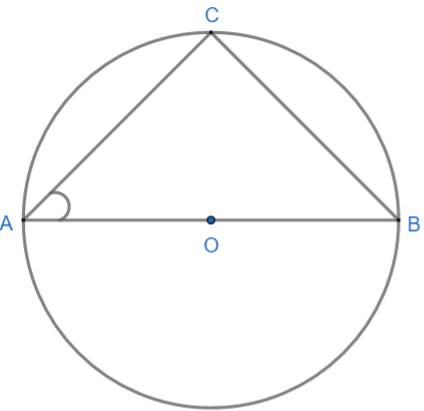
In the given figure AOB is a diameter of the circle and AC = BC. Then $\angle CAB$ is
\[\begin{align}
& A{{.30}^{\circ }} \\
& B{{.60}^{\circ }} \\
& C{{.45}^{\circ }} \\
& D{{.90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given a figure of a circle in which two chords of a circle are equal and $\Delta ABC$ is formed. We need to find the $\angle CAB$. For this, we will use the following properties,
(i) Angle inscribed by the diameter on any point on the circle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] or we can say angle inscribed in semicircle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
(ii) Isosceles triangle property: angles corresponding to the equal sides of the triangle are also equal.
(iii) Angle sum property: the sum of the angles of a triangle is equal to \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are given the figure as,
Here AOB is a diameter of the circle and AC is equal to BC. We need to find the angle $\angle CAB$.
As we know that, angle inscribed by the diameter on any point on the circle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] or we can say that angle inscribed in a semicircle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\]. So from the figure we can say that $\angle ACB$ is inscribed by the diameter AOB and therefore it must be \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
Hence $\angle ACB$ is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
Now in $\Delta ACB$ we are given that AC = BC. So $\Delta ACB$ is an isosceles triangle.
We know from isosceles triangle property that angles corresponding to the equal sides are also equal. So here, $\angle CAB\text{ and }\angle CBA$ are angles corresponding to the equal sides AC and BC.
Therefore, $\angle CAB=\angle CBA$.
We know that from the angle sum property that the sum of the angles in a triangle is equal to \[{{180}^{\circ }}\]. Therefore in $\Delta ACB$,
$\angle CAB+\angle CBA+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$
Putting in the values of $\angle CAB\text{ and }\angle ACB$ we get,
$\begin{align}
& \angle CAB+\angle CAB+{{90}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle CAB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle CAB={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by 2 we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle CAB=\dfrac{{{90}^{\circ }}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle CAB={{45}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the required value of $\angle CAB={{45}^{\circ }}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Students should keep in mind all the properties before solving this sum. Take care of the signs while solving this sum. Students should note that ${{90}^{\circ }}$ angle is formed if the angle is inscribed by diameter only.
(i) Angle inscribed by the diameter on any point on the circle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] or we can say angle inscribed in semicircle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
(ii) Isosceles triangle property: angles corresponding to the equal sides of the triangle are also equal.
(iii) Angle sum property: the sum of the angles of a triangle is equal to \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are given the figure as,

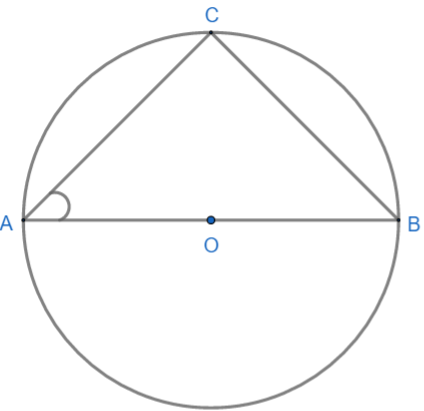
Here AOB is a diameter of the circle and AC is equal to BC. We need to find the angle $\angle CAB$.
As we know that, angle inscribed by the diameter on any point on the circle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] or we can say that angle inscribed in a semicircle is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\]. So from the figure we can say that $\angle ACB$ is inscribed by the diameter AOB and therefore it must be \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
Hence $\angle ACB$ is equal to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
Now in $\Delta ACB$ we are given that AC = BC. So $\Delta ACB$ is an isosceles triangle.
We know from isosceles triangle property that angles corresponding to the equal sides are also equal. So here, $\angle CAB\text{ and }\angle CBA$ are angles corresponding to the equal sides AC and BC.
Therefore, $\angle CAB=\angle CBA$.
We know that from the angle sum property that the sum of the angles in a triangle is equal to \[{{180}^{\circ }}\]. Therefore in $\Delta ACB$,
$\angle CAB+\angle CBA+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$
Putting in the values of $\angle CAB\text{ and }\angle ACB$ we get,
$\begin{align}
& \angle CAB+\angle CAB+{{90}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle CAB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle CAB={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by 2 we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle CAB=\dfrac{{{90}^{\circ }}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle CAB={{45}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the required value of $\angle CAB={{45}^{\circ }}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Students should keep in mind all the properties before solving this sum. Take care of the signs while solving this sum. Students should note that ${{90}^{\circ }}$ angle is formed if the angle is inscribed by diameter only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




