
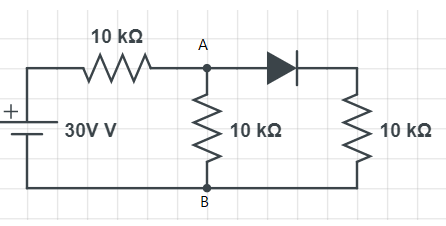
In the given circuit, the potential difference between A to B is:
\[\begin{align}
& A.0V \\
& B.5V \\
& C.10V \\
& D.15V \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: Here, we have a combination of resistances and a diode with an input source. To calculate the potential difference between the points A and B we need first identify the basing of the diode and then find the resultant resistance of the circuit.
Formula used:
$V=IR$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that a diode is a two-terminal electronic component. The terminals are made of P or N junction. Where impurities are added to the semiconductor to increase the charge carriers. We know that an increase in positive charge carries, results in N type semiconductor, whereas, increase in negative charge carries, results in P type semiconductor. Due to the biasing property of the p-n junction semiconductor, they are used as a diode.
Here, in the circuit given, the diode is forward biased. Since the two resistance is in parallel circuit, then the net resistance is given as $\dfrac{1}{R_{p}}=\dfrac{1}{R_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{R_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{10k}=\dfrac{1}{5k}$
Thus, the net resistance is $R_{p}=5K\omega$
Since the resistance is now in series connection, then the $R_{s}=R_{p}+10k=15K\omega$. Then, the current in the circuit is given as, $i=\dfrac{V}{R_{s}}$
$\implies, i=\dfrac{30}{15K}=2mA$
Now, the potential drop at AB is given as $V_{ab}=10K\times 2m=10V$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We know that in forward bias, the p-terminal is connected to the positive terminal of the source and the n-type is connected to the negative terminal. Then the majority charge carriers flow through the semiconductor, causing current in the circuit. Similarly, for the reverse bias, the p-terminal is connected to the negative terminal of the source and the n-type is connected to the positive terminal. Then the potential barrier between the p-n junction increases, thus there is no current in the circuit.
Formula used:
$V=IR$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that a diode is a two-terminal electronic component. The terminals are made of P or N junction. Where impurities are added to the semiconductor to increase the charge carriers. We know that an increase in positive charge carries, results in N type semiconductor, whereas, increase in negative charge carries, results in P type semiconductor. Due to the biasing property of the p-n junction semiconductor, they are used as a diode.
Here, in the circuit given, the diode is forward biased. Since the two resistance is in parallel circuit, then the net resistance is given as $\dfrac{1}{R_{p}}=\dfrac{1}{R_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{R_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{10k}=\dfrac{1}{5k}$
Thus, the net resistance is $R_{p}=5K\omega$
Since the resistance is now in series connection, then the $R_{s}=R_{p}+10k=15K\omega$. Then, the current in the circuit is given as, $i=\dfrac{V}{R_{s}}$
$\implies, i=\dfrac{30}{15K}=2mA$
Now, the potential drop at AB is given as $V_{ab}=10K\times 2m=10V$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We know that in forward bias, the p-terminal is connected to the positive terminal of the source and the n-type is connected to the negative terminal. Then the majority charge carriers flow through the semiconductor, causing current in the circuit. Similarly, for the reverse bias, the p-terminal is connected to the negative terminal of the source and the n-type is connected to the positive terminal. Then the potential barrier between the p-n junction increases, thus there is no current in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




