
In the following figure, which of the following is the value of $\csc \theta $?
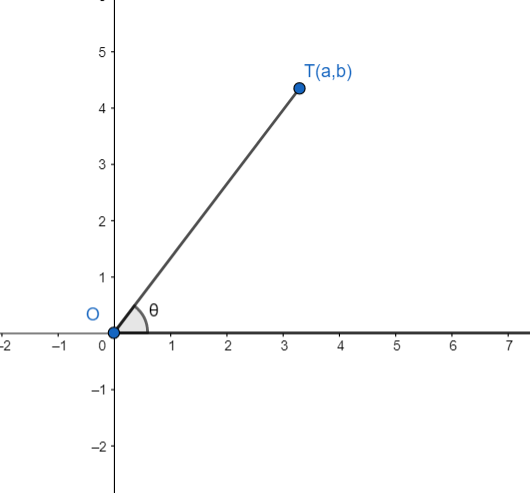
[a] $\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
[b] $\dfrac{b}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
[c] $\dfrac{b}{a}$
[d] $\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{a}$
[e] $\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{b}$

Answer
614.7k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that $\tan \theta $ is the slope of the line OT. Hence find the value of $\tan \theta $. Using the Pythagorean identity ${{\sec }^{2}}\theta =1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta $, find the value of $\sec \theta $ and hence find the value of $\cos \theta $.
Using the fact that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$, find the value of $\sin \theta $ and hence find the value of $\csc \theta $. Hence find which of the options is correct.
Complete step-by-step answer:
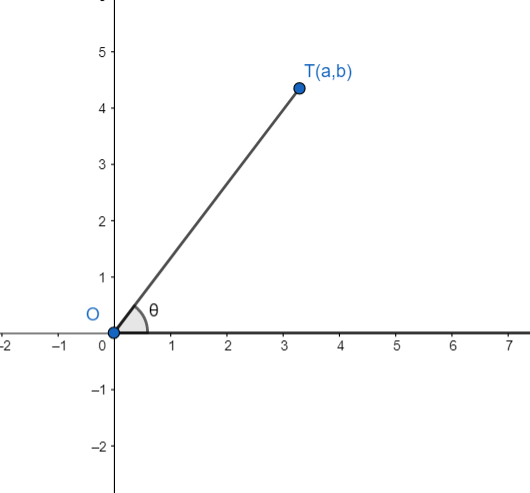
We know that the tangent of the angle made by a line with the positive direction of x-axis is the slope of the line.
Hence, we have
Slope of the line OT $=\tan \theta $
Now, we know that the slope of the line joining the poits $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$
Hence, we have
Slope of the line OT $=\dfrac{b-0}{a-0}=\dfrac{b}{a}$
Hence, we have $\tan \theta =\dfrac{b}{a}$
We know that ${{\sec }^{2}}\theta =1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta $
Hence, we have
${{\sec }^{2}}\theta =1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}$
Hence, we have
$\sec \theta =\pm \dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{a}$
Since $\theta $ lies in the first quadrant, we have $\sec \theta >0$
Hence, we have
$\sec \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{a}$
We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sec \theta }$
Substituting the value of $\sec \theta $, we get
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
Now, we know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$
Substituting the values of $\tan \theta $ and $\cos \theta $, we get
$\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}}$
Multiplying both sides by $\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$, we get
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{b}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
We know that $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$
Substituting the value of $\sin \theta $, we get
$\csc \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{b}$
Hence option [e] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution:
Draw perpendicular TA and TB on the x-axis and the y-axis, respectively.
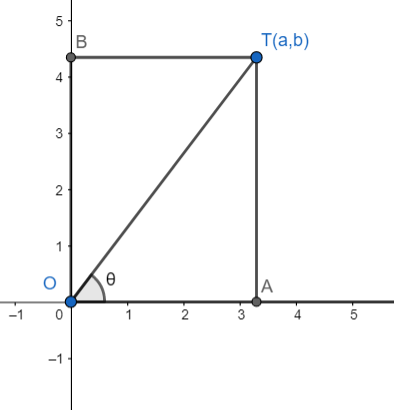
Hence, we have OA = a and OB = b.
Now, in triangle OAT, by Pythagoras theorem, we have
$O{{T}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\Rightarrow OT=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
We know that cosecant of an angle is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the opposite side.
Hence, we have
$\csc \theta =\dfrac{OT}{AT}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{b}$, which is the same as obtained above
Hence option [e] is correct.
Using the fact that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$, find the value of $\sin \theta $ and hence find the value of $\csc \theta $. Hence find which of the options is correct.
Complete step-by-step answer:

We know that the tangent of the angle made by a line with the positive direction of x-axis is the slope of the line.
Hence, we have
Slope of the line OT $=\tan \theta $
Now, we know that the slope of the line joining the poits $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$
Hence, we have
Slope of the line OT $=\dfrac{b-0}{a-0}=\dfrac{b}{a}$
Hence, we have $\tan \theta =\dfrac{b}{a}$
We know that ${{\sec }^{2}}\theta =1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta $
Hence, we have
${{\sec }^{2}}\theta =1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}$
Hence, we have
$\sec \theta =\pm \dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{a}$
Since $\theta $ lies in the first quadrant, we have $\sec \theta >0$
Hence, we have
$\sec \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{a}$
We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sec \theta }$
Substituting the value of $\sec \theta $, we get
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
Now, we know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$
Substituting the values of $\tan \theta $ and $\cos \theta $, we get
$\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}}$
Multiplying both sides by $\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$, we get
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{b}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
We know that $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$
Substituting the value of $\sin \theta $, we get
$\csc \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{b}$
Hence option [e] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution:
Draw perpendicular TA and TB on the x-axis and the y-axis, respectively.

Hence, we have OA = a and OB = b.
Now, in triangle OAT, by Pythagoras theorem, we have
$O{{T}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\Rightarrow OT=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
We know that cosecant of an angle is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the opposite side.
Hence, we have
$\csc \theta =\dfrac{OT}{AT}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}{b}$, which is the same as obtained above
Hence option [e] is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




