
In the figure, two circular flower beds have been shown on two sides of a square lawn ABCD of side 56 m. If the center of each circular flower bed is the point of intersection of O of the diagonals of the square lawn, find the sum of the areas of the lawn and the flower bed.
Answer
617.7k+ views
Hint: Total area of the figure given can be found by taking the area of lawn and the two flower beds, i.e. area of square and the area of 2 segments formed. Here the 2 flower beds are of the same area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
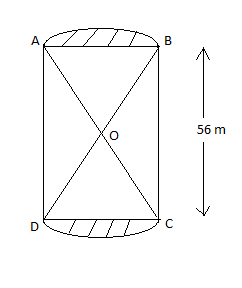
It is said that 2 circular flower beds are shown on 2 sides of the square lawn ABCD.
Thus to get the total area, it is the sum of the area of lawn and area of flower bed.
\[\therefore \]Total area = Area of lawn + Area of flower bed.
We can find the area of lawn ABCD, which is a square of side 56 m.
\[\therefore \]Area of lawn = Area of square \[={{\left( side \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 56 \right)}^{2}}=3136{{m}^{2}}.\]
\[\therefore \]Hence we got the area of the lawn \[=3136{{m}^{2}}.\]
Now we need to find the area of the flower beds AB and CD.
Area of flower bed AB = area of segment AB = Area of sector OAB – Area of \[\Delta OAB.\]
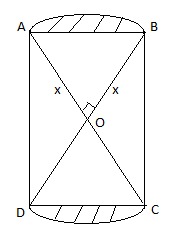
First let us find the length of OA and OB.
We know that the diagonals of a square bisect at right angles are equal.
\[\therefore \angle AOB={{90}^{\circ }}\] and OA = OB.
Let us put OA = OB = x.
Now, let us consider \[\Delta OAB.\]
By Pythagoras theorem,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( height \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( base \right)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore A{{B}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+O{{B}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that \[AB=56m\].
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore {{\left( 56 \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}} \\
& \therefore 2{{x}^{2}}={{\left( 56 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{x}^{2}}=56\times 28...........(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We know the area of sector \[=\dfrac{\theta }{360}\times \pi {{r}^{2}}.\]
\[\therefore \]Area of sector OAB, with \[\theta ={{90}^{\circ }}\] and r = x.
\[\therefore \]Area of sector OAB
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{90}{360}\times \pi {{x}^{2}} \\
& =\dfrac{90}{360}\pi \left( 56\times 28 \right) \\
& =\dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 56\times 28 \\
& =22\times 56 \\
& =1232{{m}^{2.}} \\
\end{align}\] \[\begin{align}
& \left[ \because {{x}^{2}}=56\times 28 \right] \\
& \left[ Take:\pi ={}^{22}/{}_{7} \right] \\
\end{align}\]
Let us find the area of \[\Delta OAB.\]
The diagonals of a square divide the square into congruent triangles.
\[\therefore \Delta AOB\cong \Delta BOC\cong \Delta COD\cong \Delta AOD.\]
Thus all triangles are similar, i.e. congruent triangles have the same area.
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta AOB \right)=ar\left( \Delta BOC \right)=ar\left( \Delta AOD \right).\]
which is equal to \[{{{}^{1}/{}_{4}}^{th}}\]of the area of square ABCD.
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore 4ar\left( AOB \right)=ar\left( ABCD \right) \\
& ar\left( AOB \right)=\dfrac{1}{4}ar\left( ABCD \right) \\
& \therefore ar\left( AOB \right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\times 3136=784{{m}^{2}}. \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \]Area of \[\Delta AOB=784{{m}^{2}}.\]
\[\therefore \]Area of flower bed = Area of sector AOB – Area of \[\Delta AOB=1232-784=448{{m}^{2}}.\]
Similarly by symmetry we can say that the area of flower bed CD is the same as area of flower bed AB \[=448{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \]Area of lawn + Area of flower bed
\[=3136+(448+448)=4032{{m}^{2}}\].
Thus we got the total area of the lawn and the flower beds as \[4032{{m}^{2}}\].
Note: We have used properties of squares to find the area of the triangles that are formed in the square, which will be of the same area and divide the square into 4 equal areas. Remember the formula for finding the area of a sector and prove that the angle formed between \[\angle AOB={{90}^{\circ }}\], so as to find the area of the sector.
Complete step-by-step answer:

It is said that 2 circular flower beds are shown on 2 sides of the square lawn ABCD.
Thus to get the total area, it is the sum of the area of lawn and area of flower bed.
\[\therefore \]Total area = Area of lawn + Area of flower bed.
We can find the area of lawn ABCD, which is a square of side 56 m.
\[\therefore \]Area of lawn = Area of square \[={{\left( side \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 56 \right)}^{2}}=3136{{m}^{2}}.\]
\[\therefore \]Hence we got the area of the lawn \[=3136{{m}^{2}}.\]
Now we need to find the area of the flower beds AB and CD.
Area of flower bed AB = area of segment AB = Area of sector OAB – Area of \[\Delta OAB.\]

First let us find the length of OA and OB.
We know that the diagonals of a square bisect at right angles are equal.
\[\therefore \angle AOB={{90}^{\circ }}\] and OA = OB.
Let us put OA = OB = x.
Now, let us consider \[\Delta OAB.\]
By Pythagoras theorem,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( height \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( base \right)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore A{{B}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+O{{B}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that \[AB=56m\].
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore {{\left( 56 \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}} \\
& \therefore 2{{x}^{2}}={{\left( 56 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{x}^{2}}=56\times 28...........(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We know the area of sector \[=\dfrac{\theta }{360}\times \pi {{r}^{2}}.\]
\[\therefore \]Area of sector OAB, with \[\theta ={{90}^{\circ }}\] and r = x.
\[\therefore \]Area of sector OAB
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{90}{360}\times \pi {{x}^{2}} \\
& =\dfrac{90}{360}\pi \left( 56\times 28 \right) \\
& =\dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 56\times 28 \\
& =22\times 56 \\
& =1232{{m}^{2.}} \\
\end{align}\] \[\begin{align}
& \left[ \because {{x}^{2}}=56\times 28 \right] \\
& \left[ Take:\pi ={}^{22}/{}_{7} \right] \\
\end{align}\]
Let us find the area of \[\Delta OAB.\]
The diagonals of a square divide the square into congruent triangles.
\[\therefore \Delta AOB\cong \Delta BOC\cong \Delta COD\cong \Delta AOD.\]
Thus all triangles are similar, i.e. congruent triangles have the same area.
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta AOB \right)=ar\left( \Delta BOC \right)=ar\left( \Delta AOD \right).\]
which is equal to \[{{{}^{1}/{}_{4}}^{th}}\]of the area of square ABCD.
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore 4ar\left( AOB \right)=ar\left( ABCD \right) \\
& ar\left( AOB \right)=\dfrac{1}{4}ar\left( ABCD \right) \\
& \therefore ar\left( AOB \right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\times 3136=784{{m}^{2}}. \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \]Area of \[\Delta AOB=784{{m}^{2}}.\]
\[\therefore \]Area of flower bed = Area of sector AOB – Area of \[\Delta AOB=1232-784=448{{m}^{2}}.\]
Similarly by symmetry we can say that the area of flower bed CD is the same as area of flower bed AB \[=448{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \]Area of lawn + Area of flower bed
\[=3136+(448+448)=4032{{m}^{2}}\].
Thus we got the total area of the lawn and the flower beds as \[4032{{m}^{2}}\].
Note: We have used properties of squares to find the area of the triangles that are formed in the square, which will be of the same area and divide the square into 4 equal areas. Remember the formula for finding the area of a sector and prove that the angle formed between \[\angle AOB={{90}^{\circ }}\], so as to find the area of the sector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




