
In the figure, the diameter CD of a circle with center O is perpendicular to the chord AB. If AB = 12 cm and CE = 3 cm, the radius of the circle is:
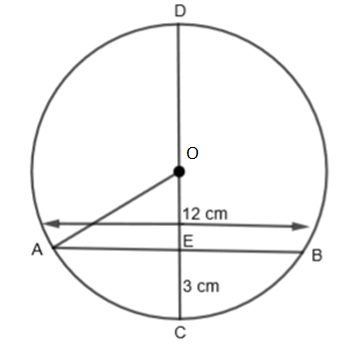
(a) 4.5 cm
(b) 9.5 cm
(c) 6.5 cm
(d) 7.5 cm

Answer
612.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will first prove that AE = EB. After proving this, we will derive the relations between OA, OE, and EC. After this, we will apply Pythagoras theorem in OAE and we will find the hypotenuse of the triangle which is equal to the radius of the given circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will find the lengths AE and EB. For this, we will join the points O and B as shown:
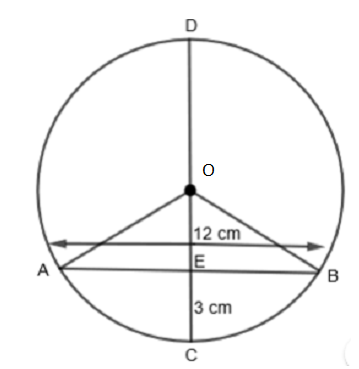
Here, we can say that OA = OB because they are radii of the circle. Also, \[\angle OEA=\angle OEB={{90}^{o}}\] because OC is the perpendicular to chord AB. Now, in the triangles OAE and OBE, we have,
OA = OB = radius (H)
\[\angle OEA=\angle OEB={{90}^{o}}\left( R \right)\]
OE = OE (Common Side) (S)
Thus the triangles OAE and OBE are congruent by RHS (Right – Angle – Hypotenuse – Side) rule. Thus, if two triangles are congruent, then we can say that AE = EB. It is also given that AB = 12 cm. Thus, we have:
AB = AE + EB
12 = AE + AE
2 AE = 12 cm
AE = 6 cm
Now, we know that OA and OC are both radii of the circle. Thus, we can say that,
OA = OC = r
OA = r…..(i)
OC = r
r = OE + EC
r = OE + 3
OE = r – 3……(ii)
Now, we will apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle OAE. According to Pythagoras theorem, we have,
\[{{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}\]
where H is the hypotenuse of the triangle. In our case, it is equal to radius OA. P is the perpendicular of the triangle. In this case, it is equal to the length OE. B is the base of the triangle. In our case, it is equal to length AE. Thus, we have:
\[{{\left( OA \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OE \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AE \right)}^{2}}.....\left( iii \right)\]
Now, we will substitute the value of OA and OE from (ii) and (i) to (iii). After doing this, we will get:
\[{{\left( r \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[{{r}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}-6r+9+36\]
\[6r=45\]
\[r=\dfrac{45}{6}\]
\[r=7.5cm\]
Hence, option (d) is the right answer.
Note: We can also prove the equality of AE and EB from the chords of the circle theorem. According to this theorem if a radius is perpendicular to the chord then that radius will be the perpendicular bisector of that chord. Thus, if the radius bisects the chord then AE = EB.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will find the lengths AE and EB. For this, we will join the points O and B as shown:

Here, we can say that OA = OB because they are radii of the circle. Also, \[\angle OEA=\angle OEB={{90}^{o}}\] because OC is the perpendicular to chord AB. Now, in the triangles OAE and OBE, we have,
OA = OB = radius (H)
\[\angle OEA=\angle OEB={{90}^{o}}\left( R \right)\]
OE = OE (Common Side) (S)
Thus the triangles OAE and OBE are congruent by RHS (Right – Angle – Hypotenuse – Side) rule. Thus, if two triangles are congruent, then we can say that AE = EB. It is also given that AB = 12 cm. Thus, we have:
AB = AE + EB
12 = AE + AE
2 AE = 12 cm
AE = 6 cm
Now, we know that OA and OC are both radii of the circle. Thus, we can say that,
OA = OC = r
OA = r…..(i)
OC = r
r = OE + EC
r = OE + 3
OE = r – 3……(ii)
Now, we will apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle OAE. According to Pythagoras theorem, we have,
\[{{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}\]
where H is the hypotenuse of the triangle. In our case, it is equal to radius OA. P is the perpendicular of the triangle. In this case, it is equal to the length OE. B is the base of the triangle. In our case, it is equal to length AE. Thus, we have:
\[{{\left( OA \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OE \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AE \right)}^{2}}.....\left( iii \right)\]
Now, we will substitute the value of OA and OE from (ii) and (i) to (iii). After doing this, we will get:
\[{{\left( r \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[{{r}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}-6r+9+36\]
\[6r=45\]
\[r=\dfrac{45}{6}\]
\[r=7.5cm\]
Hence, option (d) is the right answer.
Note: We can also prove the equality of AE and EB from the chords of the circle theorem. According to this theorem if a radius is perpendicular to the chord then that radius will be the perpendicular bisector of that chord. Thus, if the radius bisects the chord then AE = EB.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




