
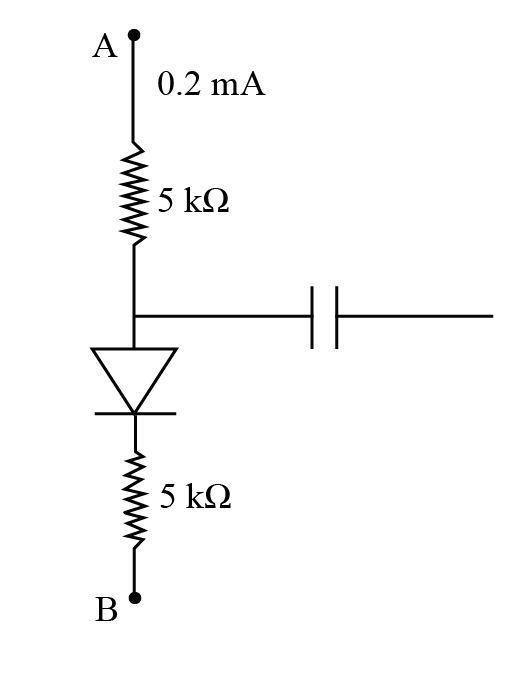
- In the figure shown, if the diode forward voltage drops is 0.2V, the voltage difference between A and B is
A. $1.3\;{\rm{V}}$
B. $2.2\;{\rm{V}}$
C. $0.5\;{\rm{V}}$
D. $0$

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the Diode. So, we have to know the term diode. Diode is an electronic device that is used to provide an electric current to move in forward direction, and it blocks in the reverse direction. We have to also know the term potential difference. The potential difference is the difference in potential between two points that show the work associated or the energy liberated in transferring a unit amount of electricity from one to another point. By applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law, we can calculate the potential difference between two points A and B.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: The voltage drop across the diode is ${V_d} = 0.2\;{\rm{V}}$, the current in the circuit is $0.2\;{\rm{mA}}$ and resistance of the resistor is $R = \;5\;{\rm{k\Omega }}$.
To calculate the potential difference between two points, we have to use the following method.
${V_{AB}} = IR + {V_d} + IR$
Since, there are two resistances so we write $IR$ two times.
Now, in a given circuit there are two resistances and a battery.
So, the potential between the two points A and B is,
$
{V_{AB}} = IR + {V_d} + IR\\
\implies {V_{AB}} = \left( {0.2 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right)\left( {5 \times {{10}^3}} \right) + 0.2 + (0.2 \times {10^{ - 3}})(5 \times {10^3})\\
\implies {V_{AB}} = 2.2\;{\rm{Volts}}
$
Therefore, the potential between the two points A and B is $2.2\;{\rm{Volts}}$.
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note:
In this question, the students must have the knowledge of potential difference and knowledge of the term diode. This question can alternatively be solved by Kirchhoff's voltage law. Kirchhoff’s gives two laws, first current law and voltage law. Kirchhoff’s current law states that the summation of all the current in the circuit is equal to zero. And Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that the summation of all the voltage in the circuit is equal to zero.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: The voltage drop across the diode is ${V_d} = 0.2\;{\rm{V}}$, the current in the circuit is $0.2\;{\rm{mA}}$ and resistance of the resistor is $R = \;5\;{\rm{k\Omega }}$.
To calculate the potential difference between two points, we have to use the following method.
${V_{AB}} = IR + {V_d} + IR$
Since, there are two resistances so we write $IR$ two times.
Now, in a given circuit there are two resistances and a battery.
So, the potential between the two points A and B is,
$
{V_{AB}} = IR + {V_d} + IR\\
\implies {V_{AB}} = \left( {0.2 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right)\left( {5 \times {{10}^3}} \right) + 0.2 + (0.2 \times {10^{ - 3}})(5 \times {10^3})\\
\implies {V_{AB}} = 2.2\;{\rm{Volts}}
$
Therefore, the potential between the two points A and B is $2.2\;{\rm{Volts}}$.
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note:
In this question, the students must have the knowledge of potential difference and knowledge of the term diode. This question can alternatively be solved by Kirchhoff's voltage law. Kirchhoff’s gives two laws, first current law and voltage law. Kirchhoff’s current law states that the summation of all the current in the circuit is equal to zero. And Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that the summation of all the voltage in the circuit is equal to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




