
In the figure shown all contact surfaces are smooth. Acceleration of block B will be \[\left( {g = 10{\text{ }}m/{s^2}} \right)\]
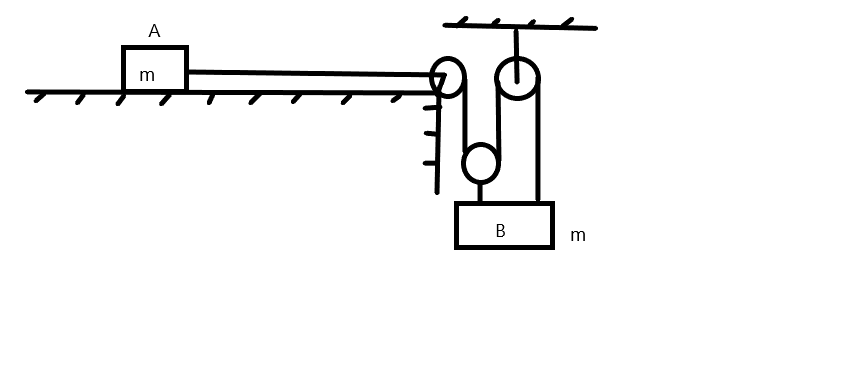
\[\left( {\text{A}} \right)\]\[1{\text{ }}m/{s^2}\]
\[\left( {\text{B}} \right)\]\[2{\text{ }}m/{s^2}\]
\[\left( {\text{C}} \right)\]\[3{\text{ }}m/{s^2}\]
\[\left( {\text{D}} \right)\] None of these

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: Friction: It is a force that comes into action when a body moves or tends to move over the surface of another body.
Acceleration: It is defined as the rate of change of velocity with the time period.
Tension: It is defined as the pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, cable, or chain.
Free body diagram (FBD): It is the diagrammatic representation used to show the relative magnitude and the direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation.
Work theorem: It states that the net work done by the forces on the object equals the change produced in its kinetic energy.
Formula used:
\[{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} - 3{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}} = 0\], here\[{{\;T}}\] is the tension of the string,\[\;{x_A}\] and \[{x_B}\] is the displacement due to the motion.
Complete step by step answer:
The free-body diagram is given below,
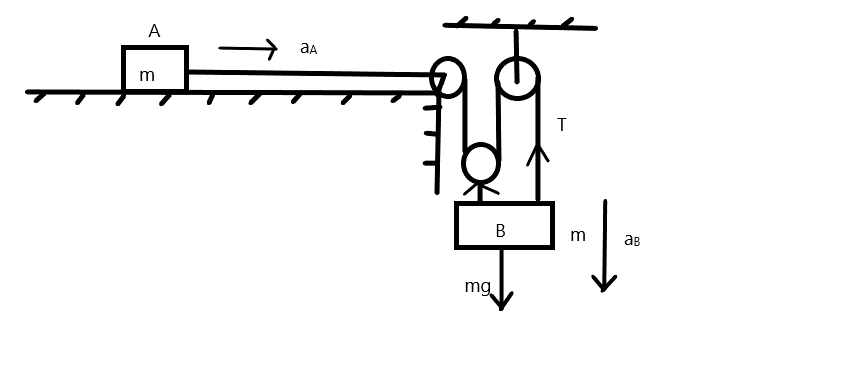
From the figure, we can say that the acceleration of the mass B is acting downward which is in equal magnitude with the weight of the body.
From the figure, we can write that \[{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} - 3{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}} = 0\]
Now we have to equate the terms we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}}$
Differentiating twice we get the values of acceleration, ${{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}}$
For block \[{\text{A}}\]: ${\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = {\text{T}}$
For block \[{\text{B}}\]:${\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 3T}}$
Replacing the value of \[{\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = {\text{T}}\] we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 3(m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}})$,
Substitute ${{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}}$ in the above equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow $${\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 3m(3}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}})$,
On multiplying the terms we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 9m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}}$
Taking the same terms in LHS and adding we get,
$ \Rightarrow 10{\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg}}$,
Substituting the value of \[g\]we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{10m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = 10{\text{m}}$
Cancel the same terms and we get,
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = 1{\text{ }}m/{s^2}$
Hence, the correct option is \[\left( {\text{A}} \right)\].
Note:
The force of attraction between the two surfaces at the point of actual contacts at nanoscales.
The tension means to stretch; it pulls only in parallel direction of the string length.
Forces are due to the interaction of at least two objects.
Force may change the state of motion of an object, the shape of the object.
Acceleration: It is defined as the rate of change of velocity with the time period.
Tension: It is defined as the pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, cable, or chain.
Free body diagram (FBD): It is the diagrammatic representation used to show the relative magnitude and the direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation.
Work theorem: It states that the net work done by the forces on the object equals the change produced in its kinetic energy.
Formula used:
\[{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} - 3{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}} = 0\], here\[{{\;T}}\] is the tension of the string,\[\;{x_A}\] and \[{x_B}\] is the displacement due to the motion.
Complete step by step answer:
The free-body diagram is given below,

From the figure, we can say that the acceleration of the mass B is acting downward which is in equal magnitude with the weight of the body.
From the figure, we can write that \[{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} - 3{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}} = 0\]
Now we have to equate the terms we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{\text{T}}{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{x}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{{\text{x}}_{\text{B}}}$
Differentiating twice we get the values of acceleration, ${{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}}$
For block \[{\text{A}}\]: ${\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = {\text{T}}$
For block \[{\text{B}}\]:${\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 3T}}$
Replacing the value of \[{\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = {\text{T}}\] we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 3(m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}})$,
Substitute ${{\text{a}}_{\text{A}}} = 3{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}}$ in the above equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow $${\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 3m(3}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}})$,
On multiplying the terms we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg - 9m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}}$
Taking the same terms in LHS and adding we get,
$ \Rightarrow 10{\text{m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = {\text{mg}}$,
Substituting the value of \[g\]we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{10m}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = 10{\text{m}}$
Cancel the same terms and we get,
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{a}}_{\text{B}}} = 1{\text{ }}m/{s^2}$
Hence, the correct option is \[\left( {\text{A}} \right)\].
Note:
The force of attraction between the two surfaces at the point of actual contacts at nanoscales.
The tension means to stretch; it pulls only in parallel direction of the string length.
Forces are due to the interaction of at least two objects.
Force may change the state of motion of an object, the shape of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




