
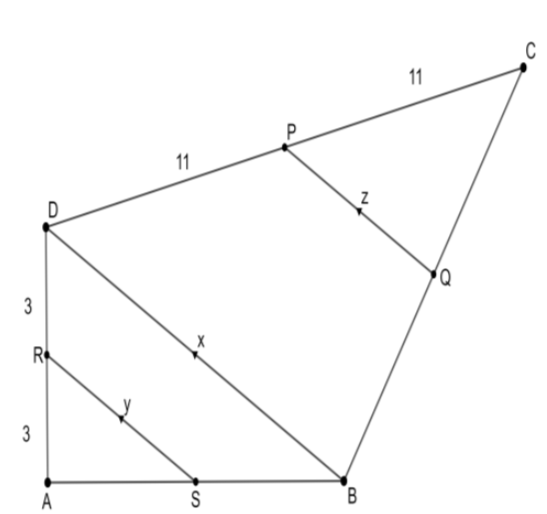
In the figure, $RS\parallel DB\parallel PQ$. If $CP=PD=11$ cm and $DR=RA=3$ cm. Then the values of $x$, $y$ and $z$ can be:

Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have a figure that includes three parallel line segments joining midpoints of sides of triangles. From this information, we can make use of the basic proportionality theorem. The basic proportionality theorem states that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. There is a corollary of the basic proportionality theorem which states that a line segment that is parallel to a side in a triangle defines a new smaller triangle that is similar to the original triangle. Using these two results, we can find the possible values of $x$, $y$, and $z$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that $DR=RA=3$ cm. Hence, R is the midpoint of AD. Similarly, since $CP=PD=11$ cm, we can conclude that P is the midpoint of CD. From the corollary of the basic proportionality theorem, we have $\Delta ARS\sim \Delta ADB$ and $\Delta CPQ\sim \Delta CDB$. We know the length of sides $AR=3$and $AD=AR+RD=3+3=6$. Now, we take the ratio of similar sides from the similar triangles $\Delta ARS$ and $\Delta ADB$. We have the following equation,
\[\dfrac{AR}{AD}=\dfrac{RS}{DB}\]
Substituting the values, we get
\[\dfrac{3}{6}=\dfrac{y}{x}\]
So we have $3x=6y$. Therefore, $x=2y$.
Now, considering the other pair of similar triangles, $\Delta CPQ\sim \Delta CDB$, we will take the ratio of similar sides as follows,
\[\dfrac{CP}{CD}=\dfrac{PQ}{DB}\]
Substituting the values, we get
\[\dfrac{11}{22}=\dfrac{z}{x}\]
So we get the following equation, $11x=22z$. Therefore, $x=2z$.
So, the possible values of $x$, $y$ and $z$ will satisfy $x=2y=2z$.
Note: Analyzing the figure is important in this type of question. The statements of the basic proportionality theorem, its converse, and its corollary are very useful to derive the desired answer in such questions. Having similar triangles in a figure naturally suggests the use of ratios of similar sides or similar angles.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that $DR=RA=3$ cm. Hence, R is the midpoint of AD. Similarly, since $CP=PD=11$ cm, we can conclude that P is the midpoint of CD. From the corollary of the basic proportionality theorem, we have $\Delta ARS\sim \Delta ADB$ and $\Delta CPQ\sim \Delta CDB$. We know the length of sides $AR=3$and $AD=AR+RD=3+3=6$. Now, we take the ratio of similar sides from the similar triangles $\Delta ARS$ and $\Delta ADB$. We have the following equation,
\[\dfrac{AR}{AD}=\dfrac{RS}{DB}\]
Substituting the values, we get
\[\dfrac{3}{6}=\dfrac{y}{x}\]
So we have $3x=6y$. Therefore, $x=2y$.
Now, considering the other pair of similar triangles, $\Delta CPQ\sim \Delta CDB$, we will take the ratio of similar sides as follows,
\[\dfrac{CP}{CD}=\dfrac{PQ}{DB}\]
Substituting the values, we get
\[\dfrac{11}{22}=\dfrac{z}{x}\]
So we get the following equation, $11x=22z$. Therefore, $x=2z$.
So, the possible values of $x$, $y$ and $z$ will satisfy $x=2y=2z$.
Note: Analyzing the figure is important in this type of question. The statements of the basic proportionality theorem, its converse, and its corollary are very useful to derive the desired answer in such questions. Having similar triangles in a figure naturally suggests the use of ratios of similar sides or similar angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




