
In the figure given below, what does P represent?
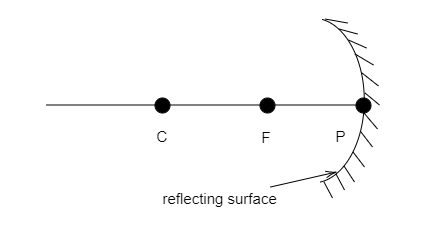
A) Principal focus
B) Principal axis
C) Pole
D) None of the above

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: The given figure represents a concave mirror. Pole of a mirror refers to the centre of the mirror. In the figure, the point P lies on a line passing through the centre of the mirror and its centre of curvature C.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch the diagram and explain the different points represented.
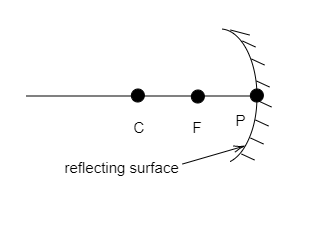
The above figure represents a concave mirror. The points marked as P, F and C represent the pole, principal focus and centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
The principal axis is a line passing through the geometric centre of the reflecting surface of the mirror. It also passes through the centre of curvature of the mirror. Here, the line on which the points P, F and C are marked is the principal axis. The object whose image is to be obtained can be placed anywhere along the principal axis.
In the above figure, the point P is positioned at the centre of the reflecting surface. Thus it represents the pole of the mirror. The pole of a mirror represents the geometric centre of the reflecting surface. It lies on the principal axis.
Therefore, the correct option is c.
Additional Information: A concave mirror is a spherical mirror with the reflecting surface on its inside. Concave mirrors are called converging mirrors as the light on striking the reflecting surface of the concave mirror will get reflected back and converge at a point.
When light rays parallel to the principal axis fall on the mirror, they get reflected and meet or converge at a particular point on the principal axis. This particular point on the principal axis is called the principal focus. It is denoted by F. The distance between the pole of the concave mirror (P) and its principal focus (F) is called the focal length of the concave mirror.
The point C in the figure represents the centre of curvature of the concave mirror. It refers to the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part of. The centre of curvature lies in front of the reflecting surface for a concave mirror. The distance between the pole of the mirror and the centre of curvature gives the radius of curvature R.
Note: The object can be placed anywhere along the principal axis except at the pole of the mirror. The pole is essentially a point inside the mirror. So to place an object at the pole you would have to break the mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch the diagram and explain the different points represented.
Representation of a Concave Mirror

The above figure represents a concave mirror. The points marked as P, F and C represent the pole, principal focus and centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
The principal axis is a line passing through the geometric centre of the reflecting surface of the mirror. It also passes through the centre of curvature of the mirror. Here, the line on which the points P, F and C are marked is the principal axis. The object whose image is to be obtained can be placed anywhere along the principal axis.
In the above figure, the point P is positioned at the centre of the reflecting surface. Thus it represents the pole of the mirror. The pole of a mirror represents the geometric centre of the reflecting surface. It lies on the principal axis.
Therefore, the correct option is c.
Additional Information: A concave mirror is a spherical mirror with the reflecting surface on its inside. Concave mirrors are called converging mirrors as the light on striking the reflecting surface of the concave mirror will get reflected back and converge at a point.
When light rays parallel to the principal axis fall on the mirror, they get reflected and meet or converge at a particular point on the principal axis. This particular point on the principal axis is called the principal focus. It is denoted by F. The distance between the pole of the concave mirror (P) and its principal focus (F) is called the focal length of the concave mirror.
The point C in the figure represents the centre of curvature of the concave mirror. It refers to the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part of. The centre of curvature lies in front of the reflecting surface for a concave mirror. The distance between the pole of the mirror and the centre of curvature gives the radius of curvature R.
Note: The object can be placed anywhere along the principal axis except at the pole of the mirror. The pole is essentially a point inside the mirror. So to place an object at the pole you would have to break the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




