
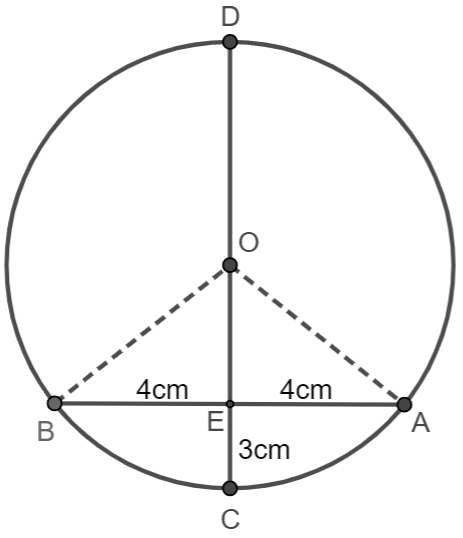
In the figure given below, CD is the diameter which meets the chord AB in E such that AE = BE = 4cm. If CE = 3cm, find the radius of the circle.

Answer
521.7k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we are given that CD is the diameter which meets the chord AB in E such that AE = BE = 4cm and if CE = 3cm, we have to find the radius of the circle. We can see in the given diagram that OB = OC = r and OE = r-3, we can find the radius of the triangle using the Pythagorean formula for the right triangle OBE.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here we are given that CD is the diameter which meets the chord AB in E such that AE = BE = 4cm.
If CE = 3cm, we have to find the radius of the circle.
We can see in the diagram that,
OB = OC = r.
Where, OE = r-3.
We can now use the Pythagorean formula, to find the radius of the right triangle OBE.
\[\Rightarrow O{{B}^{2}}=B{{E}^{2}}+O{{E}^{2}}\]
We can now substitute the required values in the above formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}={{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( r-3 \right)}^{2}}\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=16+{{r}^{2}}-6r+9 \\
& \Rightarrow 6r=25 \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{25}{6}=4.16cm \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of radius is 4.16 cm.
Note: We should always remember that, to solve a right triangle, we can use the Pythagoras theorem, from which we can find the unknown value of the required part. We should know that Pythagora's theorem is the square of the hypotenuse equal to the sum of the square of opposite and the adjacent side.
Complete step-by-step solution:
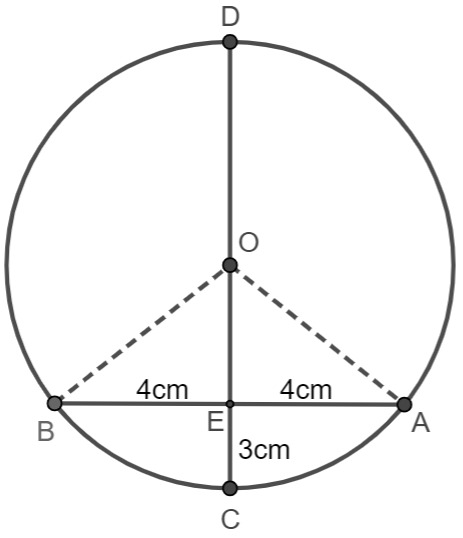
Here we are given that CD is the diameter which meets the chord AB in E such that AE = BE = 4cm.
If CE = 3cm, we have to find the radius of the circle.

We can see in the diagram that,
OB = OC = r.
Where, OE = r-3.
We can now use the Pythagorean formula, to find the radius of the right triangle OBE.
\[\Rightarrow O{{B}^{2}}=B{{E}^{2}}+O{{E}^{2}}\]
We can now substitute the required values in the above formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}={{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( r-3 \right)}^{2}}\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=16+{{r}^{2}}-6r+9 \\
& \Rightarrow 6r=25 \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{25}{6}=4.16cm \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of radius is 4.16 cm.
Note: We should always remember that, to solve a right triangle, we can use the Pythagoras theorem, from which we can find the unknown value of the required part. We should know that Pythagora's theorem is the square of the hypotenuse equal to the sum of the square of opposite and the adjacent side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




