
In the esterification reaction, the correct order of reactivity of alcohols is
(A) $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ > $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ > ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHOH$
(B) $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ > ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHOH$ > $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$
(C) $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ > ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHOH$ > $C{{H}_{3}}OH$
(D) ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHOH$ > $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ > $C{{H}_{3}}OH$
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Reactivity of alcohols decreases as the bulk of attached groups to the longest chain increases.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first go through the esterification reactions and the reactivities of alcohol groups in that.
Esterification-
This is the chemical reaction in which alcohols and acids react with each other to form products as esters. Hence, the name esterification.
Here, the organic acid group reacts with alcohol to form stable ester and water.
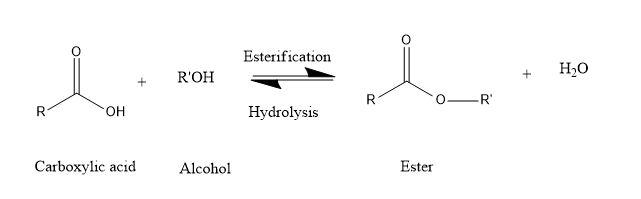
Mechanism-
Primary alcohol in the presence of sulphuric acid, is treated with carboxylic acid. Steps involved are;
1. Formation of cations takes place.
2. Protonation of carbonyl oxygen to give delocalised carbocation (electrophile).
3. Formation of a good leaving group through proton transfer to hydroxyl group.
4. Elimination of water group. A pi-bond is formed as oxygen (of resulting water) donates a pair of electrons to carbon atoms.
5. Formation of product i.e. ester.
Hence, the O-H bond of alcohol cleaves to form ester. The reactivity for this cleavage goes down from primary to tertiary alcohol as the bulk of the substitutes on alcohol increases.
The alcohol acts as nucleophile here and also the steric effects support the reactivity order. Thus, tertiary alcohol is the least reactive than primary and secondary.
Thus,
Primary alcohol > Secondary alcohol > Tertiary alcohol.
i.e. $C{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{-}}>C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}{{O}^{-}}>{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CH{{O}^{-}}$ (according to nucleophilicity order)
Therefore, the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in esterification is, $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ > $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ > ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHOH$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Steric effects and the nucleophilicity order is responsible for the reactivities of alcohol during esterification. Do note that always primary alcohol is more reactive than the substituted ones.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first go through the esterification reactions and the reactivities of alcohol groups in that.
Esterification-
This is the chemical reaction in which alcohols and acids react with each other to form products as esters. Hence, the name esterification.
Here, the organic acid group reacts with alcohol to form stable ester and water.

Mechanism-
Primary alcohol in the presence of sulphuric acid, is treated with carboxylic acid. Steps involved are;
1. Formation of cations takes place.
2. Protonation of carbonyl oxygen to give delocalised carbocation (electrophile).
3. Formation of a good leaving group through proton transfer to hydroxyl group.
4. Elimination of water group. A pi-bond is formed as oxygen (of resulting water) donates a pair of electrons to carbon atoms.
5. Formation of product i.e. ester.
Hence, the O-H bond of alcohol cleaves to form ester. The reactivity for this cleavage goes down from primary to tertiary alcohol as the bulk of the substitutes on alcohol increases.
The alcohol acts as nucleophile here and also the steric effects support the reactivity order. Thus, tertiary alcohol is the least reactive than primary and secondary.
Thus,
Primary alcohol > Secondary alcohol > Tertiary alcohol.
i.e. $C{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{-}}>C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}{{O}^{-}}>{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CH{{O}^{-}}$ (according to nucleophilicity order)
Therefore, the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in esterification is, $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ > $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ > ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHOH$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Steric effects and the nucleophilicity order is responsible for the reactivities of alcohol during esterification. Do note that always primary alcohol is more reactive than the substituted ones.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




