
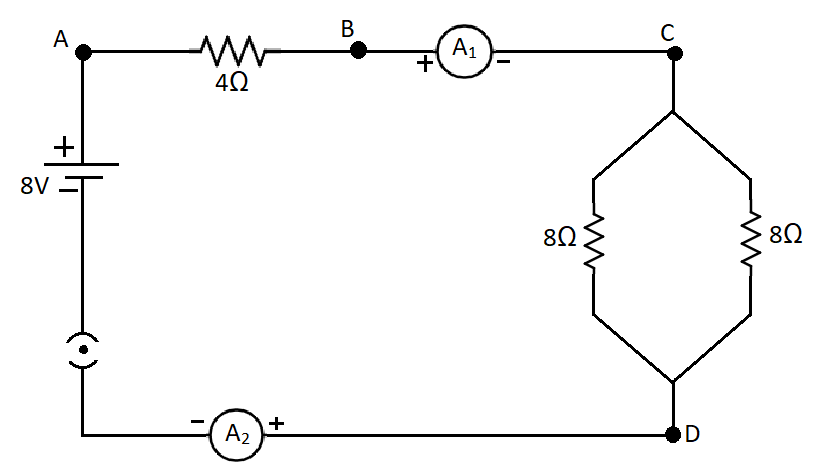
In the electric circuit shown in figure, current flowing through $4\Omega $ resistor is :
(A) $3A$
(B) $2A$
(C) $1A$
(D) $4A$

Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint
In the given circuit, to find the current through the $4\Omega $ resistor, we need to first find the equivalent resistance in the circuit. Then by dividing the potential with the equivalent resistance we will get the current in the circuit.
In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in series.
And $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in a parallel circuit.
and $V = IR$ where $V$ is the potential across the battery, $I$ is the current, $R$ is the resistance.
Complete step by step answer
To find the current in the circuit, we need to first calculate the equivalent resistance in the circuit. From the diagram we can see that two resistances of $8\Omega $ each are connected in parallel and with the equivalent of those two resistances we have a $4\Omega $ resistor in series. So we need to first find the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistances,
It is given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$
Where we have ${R_1} = {R_2} = 8\Omega $
Therefore we can write,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{8} + \dfrac{1}{8}$
Therefore, by taking the LCM as 8,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{1 + 1}}{8} = \dfrac{2}{8}$
Hence we can cancel the 2 from numerator and denominator and then get the equivalent resistance by taking the inverse as,
$\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = 4\Omega $
In the circuit diagram, we have a $4\Omega $ resistor in series with the parallel resistances, therefore, the equivalent resistance in the whole circuit can found by,
$\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$
By substituting \[{R_1} = {R_2} = 4\Omega \], we have
$\Rightarrow R = \left( {4 + 4} \right)\Omega $
Therefore the total resistance is, $R = 8\Omega $
Now in the diagram, the potential across the cell is given as $8V$.
So from the Ohm’s law, the current will be given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
So substituting the values, $I = \dfrac{8}{8}A$
Therefore we get, $\Rightarrow I = 1A$
This is the current that is flowing through the $4\Omega $ resistor. So the answer will be $\Rightarrow 1A$.
Therefore, the correct option will be (C).
Note
The current that will be coming from the cell will flow through the $4\Omega $ resistor. But when it reaches the $8\Omega $ resistances, the current will get divided into two paths and hence the current in each of the wires will be proportional to the resistances in them. Since the resistances are equal so the current in each wire will be $0.5A$ each.
In the given circuit, to find the current through the $4\Omega $ resistor, we need to first find the equivalent resistance in the circuit. Then by dividing the potential with the equivalent resistance we will get the current in the circuit.
In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in series.
And $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in a parallel circuit.
and $V = IR$ where $V$ is the potential across the battery, $I$ is the current, $R$ is the resistance.
Complete step by step answer
To find the current in the circuit, we need to first calculate the equivalent resistance in the circuit. From the diagram we can see that two resistances of $8\Omega $ each are connected in parallel and with the equivalent of those two resistances we have a $4\Omega $ resistor in series. So we need to first find the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistances,
It is given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$
Where we have ${R_1} = {R_2} = 8\Omega $
Therefore we can write,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{8} + \dfrac{1}{8}$
Therefore, by taking the LCM as 8,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{1 + 1}}{8} = \dfrac{2}{8}$
Hence we can cancel the 2 from numerator and denominator and then get the equivalent resistance by taking the inverse as,
$\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = 4\Omega $
In the circuit diagram, we have a $4\Omega $ resistor in series with the parallel resistances, therefore, the equivalent resistance in the whole circuit can found by,
$\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$
By substituting \[{R_1} = {R_2} = 4\Omega \], we have
$\Rightarrow R = \left( {4 + 4} \right)\Omega $
Therefore the total resistance is, $R = 8\Omega $
Now in the diagram, the potential across the cell is given as $8V$.
So from the Ohm’s law, the current will be given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
So substituting the values, $I = \dfrac{8}{8}A$
Therefore we get, $\Rightarrow I = 1A$
This is the current that is flowing through the $4\Omega $ resistor. So the answer will be $\Rightarrow 1A$.
Therefore, the correct option will be (C).
Note
The current that will be coming from the cell will flow through the $4\Omega $ resistor. But when it reaches the $8\Omega $ resistances, the current will get divided into two paths and hence the current in each of the wires will be proportional to the resistances in them. Since the resistances are equal so the current in each wire will be $0.5A$ each.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




