
In the diagram, the circle contains the vertices A, B, C of △ABC. Now \[\angle ABC=30{}^\circ \] and the length of AC is 5. The diameter of the circle is
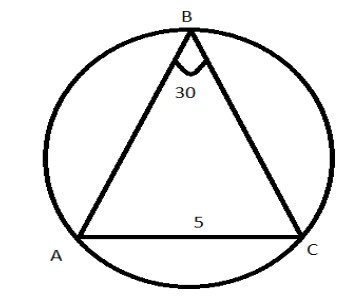
(a) $5\sqrt{3}$
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) $5\sqrt{5}$

Answer
611.1k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we are given a triangle inscribed in a circle having one side length as 5 and one angle as 30°. To calculate the diameter of the circle, we must try to evaluate the radius of the circle by using some construction and geometrical properties.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Considering O as the center of the circle, join OA and OC.
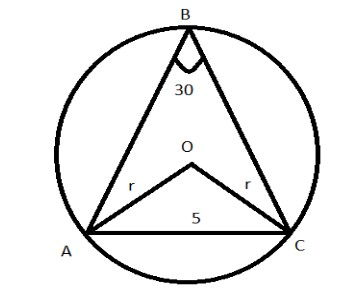
Using the theorem, “Angle subtended by the chord at the center is double the angle subtended at the circumference”. We can calculate the measurement of $\angle BAC$. Therefore, $\angle AOC= 2\angle BAC={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Now, we have to prove $\Delta AOC$ is an equilateral triangle. Length of $AC=5cm$ is given. Sides of the equilateral triangle are equal. The length of OA, OB and AC are equal.
The diameter of the circle is twice the radius.
In $\Delta ABC$, the angle ABC is 30 degrees.
Also, \[~\angle AOC=2\angle BAC={{60}^{\circ }}\].
In $\Delta OAC$,
OA = OC (radius of the circle). This implies that the respective angles must be equal.
$\therefore \angle OAC=\angle OCA$
Now, as we know that the sum total of all the angles of a triangle is 180 by angle sum property.
$\begin{align}
& \angle OAC+\angle OCA+\angle AOC=180{}^\circ \\
& \because \angle AOC=60{}^\circ ,\therefore \angle OAC=\angle OCA=60{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Hence, triangle OAC is equilateral.
Since, all the sides of an equilateral triangle are equal. Therefore, $OA=OC=AC=5$.
Thus, the diameter of the circle will be $2\times 5=10$.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Note: The key concept for solving this problem is the knowledge of equilateral triangles and basic properties of angle subtended in a circle. Once the constructed triangle is proved equilateral, then by using the properties of the equilateral triangle we obtain our solution without any error.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Considering O as the center of the circle, join OA and OC.

Using the theorem, “Angle subtended by the chord at the center is double the angle subtended at the circumference”. We can calculate the measurement of $\angle BAC$. Therefore, $\angle AOC= 2\angle BAC={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Now, we have to prove $\Delta AOC$ is an equilateral triangle. Length of $AC=5cm$ is given. Sides of the equilateral triangle are equal. The length of OA, OB and AC are equal.
The diameter of the circle is twice the radius.
In $\Delta ABC$, the angle ABC is 30 degrees.
Also, \[~\angle AOC=2\angle BAC={{60}^{\circ }}\].
In $\Delta OAC$,
OA = OC (radius of the circle). This implies that the respective angles must be equal.
$\therefore \angle OAC=\angle OCA$
Now, as we know that the sum total of all the angles of a triangle is 180 by angle sum property.
$\begin{align}
& \angle OAC+\angle OCA+\angle AOC=180{}^\circ \\
& \because \angle AOC=60{}^\circ ,\therefore \angle OAC=\angle OCA=60{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Hence, triangle OAC is equilateral.
Since, all the sides of an equilateral triangle are equal. Therefore, $OA=OC=AC=5$.
Thus, the diameter of the circle will be $2\times 5=10$.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Note: The key concept for solving this problem is the knowledge of equilateral triangles and basic properties of angle subtended in a circle. Once the constructed triangle is proved equilateral, then by using the properties of the equilateral triangle we obtain our solution without any error.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




