
In the diagram of lateral view of human brain , parts are indicated by alphabets.Choose the answer to which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts they indicate
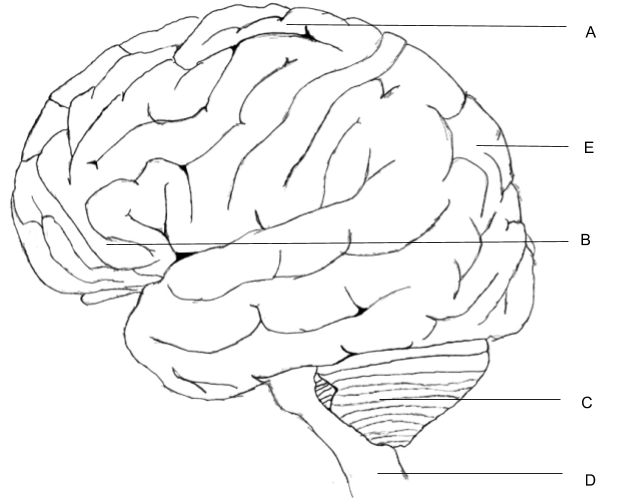
A = Temporal lobe, B = Parietal lobe, C = Cerebrum, D = Medulla oblongata, E = Frontal lobe
A = Frontal lobe, B = Temporal lobe, C = Cerebellum, D - Medulla oblongata, E = Parietal lobe
A = Temporal lobe, B = Parietal lobe, C = Cerebellum, D = Medulla oblongata, E = Frontal lobe
A = Frontal lobe, B = Temporal lobe, C = Cerebrum, D = Medulla oblongata, E = Occipital lobe.

Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: The lateral view of the brain shows the brain, cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem in three main sections. There are many anatomical landmarks on these structures observed from the lateral aspect, that carry great functional importance.
Complete answer:
There are three main components of the lateral vision of the human brain, which are the cerebellum, cerebrum and brainstem.
Cerebrum: A portion of the forebrain that forms the main part of the brain is the cerebrum. A deep cleft divides Cerebrum longitudinally into two halves. These two separated sections are called hemispheres of the cerebrum.
Cerebellum: In the cerebellum, there is a rather convoluted surface that helps to provide several more neurons with additional room.
Brain stem: The brainstem is created by the midbrain and hindbrain. The cerebellum portion of the hindbrain is not involved in the development of the stem of the brain.
For simpler localization of structures, the large structures of the brain are each divided into subparts or regions, such as the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, while the cerebrum is divisible into lobes.
While there are surfaces in the cerebral cortex, they are not smooth due to their embryonic development. The elevations or folds called gyri and depressions or grooves called sulci are distinguished by these surfaces.
Every gyrus is defined by these sulci, while the large sulci and fissures define the cerebral cortex and demarcate it into four major subdivisions called lobes, which are:
1.Frontal lobe
2.Parietal lobe
3.Temporal lobe
4.Occipital lobe
These lobes are named due to their links to the skull's bones. Therefore the frontal lobe is the part just below the frontal bone, the parietal lobe is right next to the parietal bone, the temporal lobe is the temporal bone, and the occipital lobe is situated in relation to the cranium's occipital bone.
The main portion of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which regulates posture, balance, orientation.
Pons varolli consists of a nerve fibre that forms a bridge between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum.
The medulla oblongata is most posterior and starts with the spinal cord. Involuntary processes such as heartbeats, breathing, etc are regulated
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: There is a forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain in the brain.
Cerebrum, diencephalon, thalami, and hypothalamus form the forebrain. The cerebrum is divided into a cerebral hemisphere that is divided into four frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes.
The posterior-most area of the brain is the hindbrain. Cerebellum, pons varolli, and medulla oblongata are included.
Complete answer:
There are three main components of the lateral vision of the human brain, which are the cerebellum, cerebrum and brainstem.
Cerebrum: A portion of the forebrain that forms the main part of the brain is the cerebrum. A deep cleft divides Cerebrum longitudinally into two halves. These two separated sections are called hemispheres of the cerebrum.
Cerebellum: In the cerebellum, there is a rather convoluted surface that helps to provide several more neurons with additional room.
Brain stem: The brainstem is created by the midbrain and hindbrain. The cerebellum portion of the hindbrain is not involved in the development of the stem of the brain.
For simpler localization of structures, the large structures of the brain are each divided into subparts or regions, such as the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, while the cerebrum is divisible into lobes.
While there are surfaces in the cerebral cortex, they are not smooth due to their embryonic development. The elevations or folds called gyri and depressions or grooves called sulci are distinguished by these surfaces.
Every gyrus is defined by these sulci, while the large sulci and fissures define the cerebral cortex and demarcate it into four major subdivisions called lobes, which are:
1.Frontal lobe
2.Parietal lobe
3.Temporal lobe
4.Occipital lobe
These lobes are named due to their links to the skull's bones. Therefore the frontal lobe is the part just below the frontal bone, the parietal lobe is right next to the parietal bone, the temporal lobe is the temporal bone, and the occipital lobe is situated in relation to the cranium's occipital bone.
The main portion of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which regulates posture, balance, orientation.
Pons varolli consists of a nerve fibre that forms a bridge between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum.
The medulla oblongata is most posterior and starts with the spinal cord. Involuntary processes such as heartbeats, breathing, etc are regulated
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: There is a forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain in the brain.
Cerebrum, diencephalon, thalami, and hypothalamus form the forebrain. The cerebrum is divided into a cerebral hemisphere that is divided into four frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes.
The posterior-most area of the brain is the hindbrain. Cerebellum, pons varolli, and medulla oblongata are included.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




