
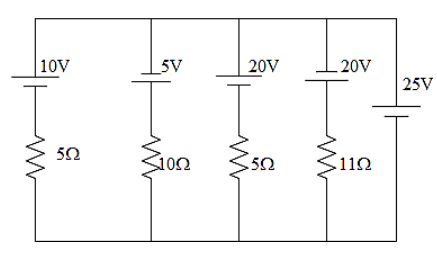
In the circuit shown in the figure, the current flowing through $25V$ cell will be given as,
$\begin{align}
& A.7.2A \\
& B.10A \\
& C.12A \\
& D.14.2A \\
\end{align}$

Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: First of all let us find out the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Then find the electric potential should be found out by taking the product of current through the circuit and the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Use Kirchhoff's law for the second loop in the figure. And find the current through the cell. Hope these will help you in answering this question.
Complete answer:
It has been given that the voltage of the cells in the circuit is given as,
$\begin{align}
& {{E}_{1}}=10V \\
& {{E}_{2}}=5V \\
& {{E}_{3}}=20V \\
& {{E}_{4}}=20V \\
\end{align}$
The value of the resistances of the resistors given in the circuit can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& {{r}_{1}}=5\Omega \\
& {{r}_{2}}=10\Omega \\
& {{r}_{3}}=5\Omega \\
& {{r}_{4}}=11\Omega \\
\end{align}$
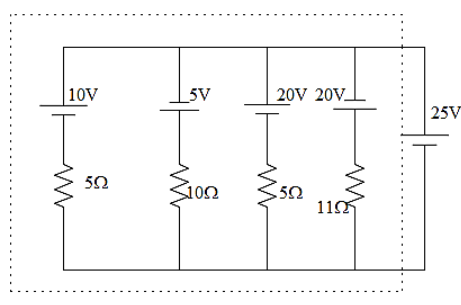
This is equivalent to,
As the resistors are connected parallel in the circuit will give,
The equivalent resistance can be calculated as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{3}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{4}}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{11}$
Let us simplify the obtained equation now,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2}{5}+\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}=\dfrac{4}{10}+\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11} \\
& \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{65}{110} \\
& {{r}_{eq}}=1.69\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the value of the equivalent resistance is obtained.
The equivalent voltage can be calculated now. The electric potential should be found out by taking the product of current through the circuit and the equivalent resistance of the circuit. That is,
The current through each of the component is given as,
$I=\dfrac{E}{r}$
The equivalent voltage of the circuit will be given as,
${{E}_{eq}}=I{{r}_{eq}}$
That is,
${{E}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{r}_{1}}}+\dfrac{-{{E}_{2}}}{{{r}_{2}}}+\dfrac{{{E}_{3}}}{{{r}_{3}}}+\dfrac{{{E}_{4}}}{{{r}_{4}}} \right){{r}_{eq}}$
The negative sign for some of the terms are due to the opposite way off connection of the cell.
Substituting the values in it will give,
${{E}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{10}{5}+\dfrac{-5}{10}+\dfrac{20}{5}+\dfrac{-20}{11} \right)\times 1.69$
Simplifying the equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& {{E}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{30}{5}+\dfrac{-5}{10}+\dfrac{-20}{11} \right)\times 1.69 \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{eq}}=\left( 6+-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{-20}{11} \right)\times 1.69 \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{eq}}=3.682\times 1.69=6.222V \\
\end{align}\]
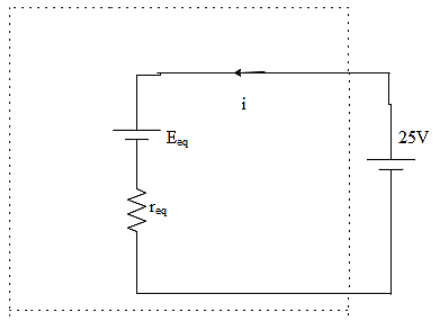
Use Kirchhoff's law for the second loop now. That is,
\[-25+6.222+i\left( 1.69 \right)=0\]
Rearranging the equation will give the current through the $25V$cell. That is,
\[i=\dfrac{18.777}{1.69}=11.11V\]
The approximate value can be taken as \[12V\].
Hence the answer is mentioned as option C.
Note:
There are two laws in Kirchhoff’s law. One is the current law in which the current entering the junction will be equivalent to the current leaving the junction. The voltage law is the other one which says that the algebraic sum of the voltages in a closed loop will be zero.
Complete answer:
It has been given that the voltage of the cells in the circuit is given as,
$\begin{align}
& {{E}_{1}}=10V \\
& {{E}_{2}}=5V \\
& {{E}_{3}}=20V \\
& {{E}_{4}}=20V \\
\end{align}$
The value of the resistances of the resistors given in the circuit can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& {{r}_{1}}=5\Omega \\
& {{r}_{2}}=10\Omega \\
& {{r}_{3}}=5\Omega \\
& {{r}_{4}}=11\Omega \\
\end{align}$

This is equivalent to,

As the resistors are connected parallel in the circuit will give,
The equivalent resistance can be calculated as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{3}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{4}}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{11}$
Let us simplify the obtained equation now,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2}{5}+\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}=\dfrac{4}{10}+\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11} \\
& \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{65}{110} \\
& {{r}_{eq}}=1.69\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the value of the equivalent resistance is obtained.
The equivalent voltage can be calculated now. The electric potential should be found out by taking the product of current through the circuit and the equivalent resistance of the circuit. That is,
The current through each of the component is given as,
$I=\dfrac{E}{r}$
The equivalent voltage of the circuit will be given as,
${{E}_{eq}}=I{{r}_{eq}}$
That is,
${{E}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{r}_{1}}}+\dfrac{-{{E}_{2}}}{{{r}_{2}}}+\dfrac{{{E}_{3}}}{{{r}_{3}}}+\dfrac{{{E}_{4}}}{{{r}_{4}}} \right){{r}_{eq}}$
The negative sign for some of the terms are due to the opposite way off connection of the cell.
Substituting the values in it will give,
${{E}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{10}{5}+\dfrac{-5}{10}+\dfrac{20}{5}+\dfrac{-20}{11} \right)\times 1.69$
Simplifying the equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& {{E}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{30}{5}+\dfrac{-5}{10}+\dfrac{-20}{11} \right)\times 1.69 \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{eq}}=\left( 6+-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{-20}{11} \right)\times 1.69 \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{eq}}=3.682\times 1.69=6.222V \\
\end{align}\]
Use Kirchhoff's law for the second loop now. That is,
\[-25+6.222+i\left( 1.69 \right)=0\]
Rearranging the equation will give the current through the $25V$cell. That is,
\[i=\dfrac{18.777}{1.69}=11.11V\]
The approximate value can be taken as \[12V\].
Hence the answer is mentioned as option C.
Note:
There are two laws in Kirchhoff’s law. One is the current law in which the current entering the junction will be equivalent to the current leaving the junction. The voltage law is the other one which says that the algebraic sum of the voltages in a closed loop will be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




