
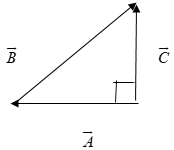
In the adjoining vector diagram, what is the angle between $\overrightarrow{A}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$?
(Given: $C=\dfrac{B}{2}$)
A. ${{30}^{\circ }}$
B. ${{60}^{\circ }}$
C. ${{120}^{\circ }}$
D. ${{150}^{\circ }}$

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint:
When we’re given that the magnitude of the sum of two vectors is equal to half the magnitude of one of the vectors, the angle between the two vectors can be determined only if the ratio of the magnitudes of these two vectors is known.
We’re given a right triangle. Hence, we can use the basic trigonometric formulas to find the solution. In the given vector diagram, A is the base, B is the hypotenuse and C is the height. Note that A,B, and C are vectors and their direction should also be considered during calculation.
Formula used:
$sin\theta =\dfrac{C}{B}$, that is $\dfrac{opp.side}{hypotenuse}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let $\theta $ be the angle between $\overrightarrow{A}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$.
From figure, $sin\theta =\dfrac{C}{B}$
We are given that, $C=\dfrac{B}{2}$
Hence, $sin\theta =\dfrac{(\dfrac{B}{2})}{B}$
$sin\theta =\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{1}{2})={{30}^{\circ }}$
Considering the direction of $\overrightarrow{A}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$, an obtuse angle is generated.
Hence, the angle between $\overrightarrow{A}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$ is ${{180}^{\circ }}-{{30}^{\circ }}={{150}^{\circ }}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Most students tend to choose ${{30}^{\circ }}$ as the answer as they consider it as a triangle and not a triangle composed of vectors. The direction is to be considered and the vectors are to be expanded along with the direction, so as to deduce the actual value of angles.
When we’re given that the magnitude of the sum of two vectors is equal to half the magnitude of one of the vectors, the angle between the two vectors can be determined only if the ratio of the magnitudes of these two vectors is known.
We’re given a right triangle. Hence, we can use the basic trigonometric formulas to find the solution. In the given vector diagram, A is the base, B is the hypotenuse and C is the height. Note that A,B, and C are vectors and their direction should also be considered during calculation.
Formula used:
$sin\theta =\dfrac{C}{B}$, that is $\dfrac{opp.side}{hypotenuse}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let $\theta $ be the angle between $\overrightarrow{A}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$.
From figure, $sin\theta =\dfrac{C}{B}$
We are given that, $C=\dfrac{B}{2}$
Hence, $sin\theta =\dfrac{(\dfrac{B}{2})}{B}$
$sin\theta =\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{1}{2})={{30}^{\circ }}$
Considering the direction of $\overrightarrow{A}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$, an obtuse angle is generated.
Hence, the angle between $\overrightarrow{A}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$ is ${{180}^{\circ }}-{{30}^{\circ }}={{150}^{\circ }}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Most students tend to choose ${{30}^{\circ }}$ as the answer as they consider it as a triangle and not a triangle composed of vectors. The direction is to be considered and the vectors are to be expanded along with the direction, so as to deduce the actual value of angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




