
In the adjoining circuit, the battery \[{E_1}\] has an E.M.F. of $12\,volts$ and zero internal resistance. While the battery ${E_2}$ has an E.M.F. of $2\,volts$ if the galvanometer $G$ reads zero than the value of the resistance $X$ in ohms is:
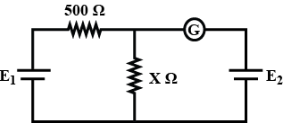
A. $10$
B. $100$
C. $14$
D. $200$

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: According to Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL), if you travel around any loop in a circuit, the voltages across the element add up to zero. That is in any closed path in a network, the algebraic sum of the $IR$ product is equal to the EMF in that path i.e, $\sum V = 0$. We will apply KVL in both the loops in order to get the desired result.
Complete step by step answer:
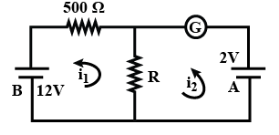
Let us consider the current flowing through loop (i) and (ii) be ${i_1}$ and ${i_2}$
Now the current flowing through the resistance $R$ well be $({i_1} - {i_2})$
Using Kirchhoff’s voltage law in loop (i) we get,
$
- 12 + X({i_1} - {i_2}) + 500{i_1} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow X{i_1} - X{i_2} + 500{i_1} = 12......(1) \\
$
Now applying KVL in loop (ii) we get,
$
2 + X({i_2} - {i_1}) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow X{i_1} - X{i_2} = 2......(2) \\
$
Since current flowing through galvanometer is zero therefore, we can say
${i_2} = 0......(3)$
Using (2) and (3) we get,
$X{i_1} = 2......(4)$
Now using (4) and (3) in (1) we get,
$
2 + 500{i_1} = 12 \\
\Rightarrow 500{i_1} = 10 \\
\Rightarrow{i_1} = \dfrac{{10}}{{500}} \\
\Rightarrow{i_1} = \dfrac{1}{{50}} \\ $
Now using above result in equation (4) we get,
$
X{i_1} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow X \times \dfrac{1}{{50}} = 2 \\
\therefore X = 100\Omega $
Hence the resistance of the resistor $R$ is $100\Omega $
Thus, option B is correct.
Note:While using KVL we have to keep in mind that the KVL equation is obtained by traversing a circuit loop in either direction and writing down unchanged the voltage of each element whose + terminal is entered first and writing down the negative of every element's voltage where the minus sign is first met. The loop must start and end at the same point.
Complete step by step answer:

Let us consider the current flowing through loop (i) and (ii) be ${i_1}$ and ${i_2}$
Now the current flowing through the resistance $R$ well be $({i_1} - {i_2})$
Using Kirchhoff’s voltage law in loop (i) we get,
$
- 12 + X({i_1} - {i_2}) + 500{i_1} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow X{i_1} - X{i_2} + 500{i_1} = 12......(1) \\
$
Now applying KVL in loop (ii) we get,
$
2 + X({i_2} - {i_1}) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow X{i_1} - X{i_2} = 2......(2) \\
$
Since current flowing through galvanometer is zero therefore, we can say
${i_2} = 0......(3)$
Using (2) and (3) we get,
$X{i_1} = 2......(4)$
Now using (4) and (3) in (1) we get,
$
2 + 500{i_1} = 12 \\
\Rightarrow 500{i_1} = 10 \\
\Rightarrow{i_1} = \dfrac{{10}}{{500}} \\
\Rightarrow{i_1} = \dfrac{1}{{50}} \\ $
Now using above result in equation (4) we get,
$
X{i_1} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow X \times \dfrac{1}{{50}} = 2 \\
\therefore X = 100\Omega $
Hence the resistance of the resistor $R$ is $100\Omega $
Thus, option B is correct.
Note:While using KVL we have to keep in mind that the KVL equation is obtained by traversing a circuit loop in either direction and writing down unchanged the voltage of each element whose + terminal is entered first and writing down the negative of every element's voltage where the minus sign is first met. The loop must start and end at the same point.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




