
In the accompanied diagram, the ideal behavior of a solution is shown by the line/s
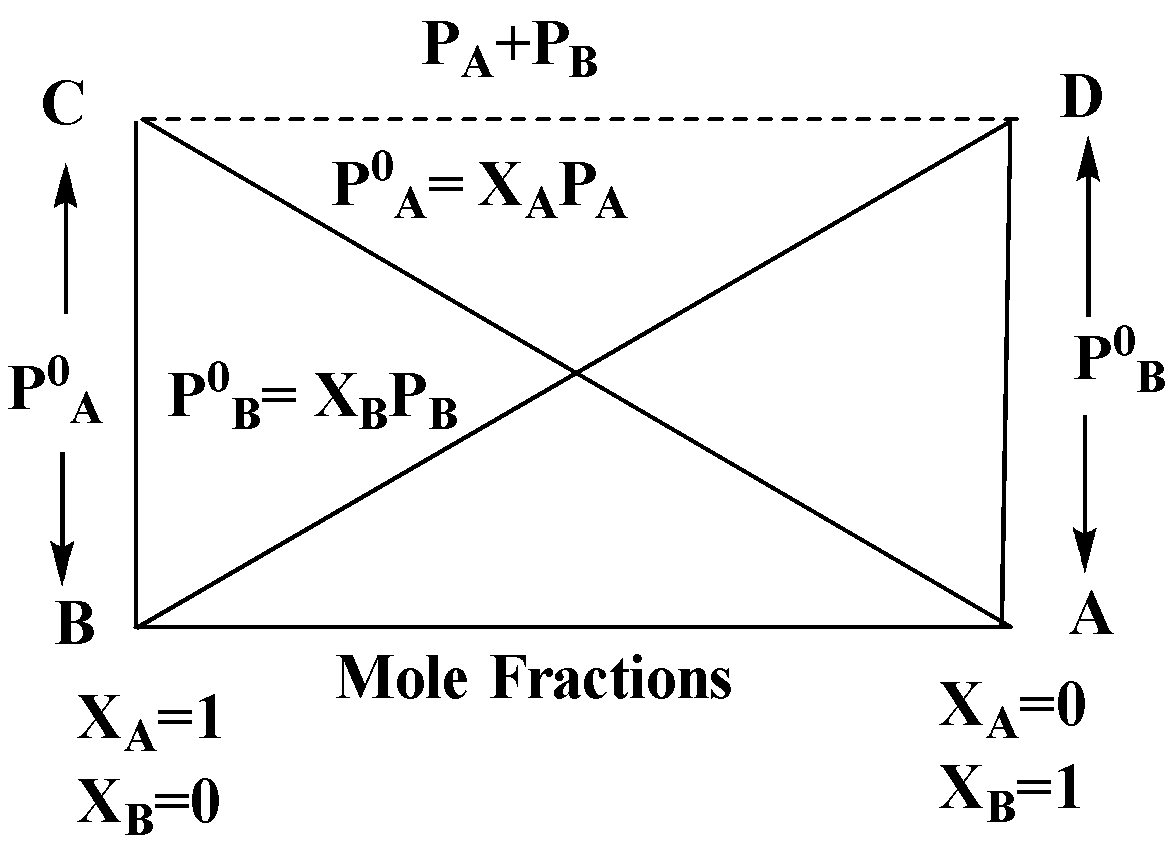
A) AD
B) CB
C) BD
D) AD, CB

Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: We know that for a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapor pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution. ${{\text{P}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{\alpha }}{{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{P}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}$ , where ${{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}$ is the vapor pressure of pure solvent and ${{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}$ is the mole fraction of A. This is called Raoult's law. The ideal solution obeys Raoult's law. When a solution does not obey Raoult's law, it is called a non-ideal solution.
Complete step by step answer:
Considering a binary solution with 2 volatile liquids A and B that would evaporate and an equilibrium will be established between the liquid phase and vapor phase.
As mentioned above, based on Raoult's law, ${{\text{P}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}$ and ${{\text{P}}_{\text{B}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{B}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$
We know what mole fraction is.
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{n}}_{\text{A}}}}}{{{{\text{n}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{n}}_{\text{B}}}}}$ .
We know from Dalton’s law that the total pressure of the solution in a container is the sum of the partial pressure of each component. ${{\text{P}}_{{\text{total}}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{B}}}$
Hence, ${{\text{P}}_{{\text{total}}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{B}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$ ( from Raoult's law)
We know that ${{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}{\text{ = 1}}$ , so ${{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = 1 - }}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$
Therefore, ${{\text{P}}_{{\text{total}}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{\text{(1 - }}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}{\text{) + }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{B}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$
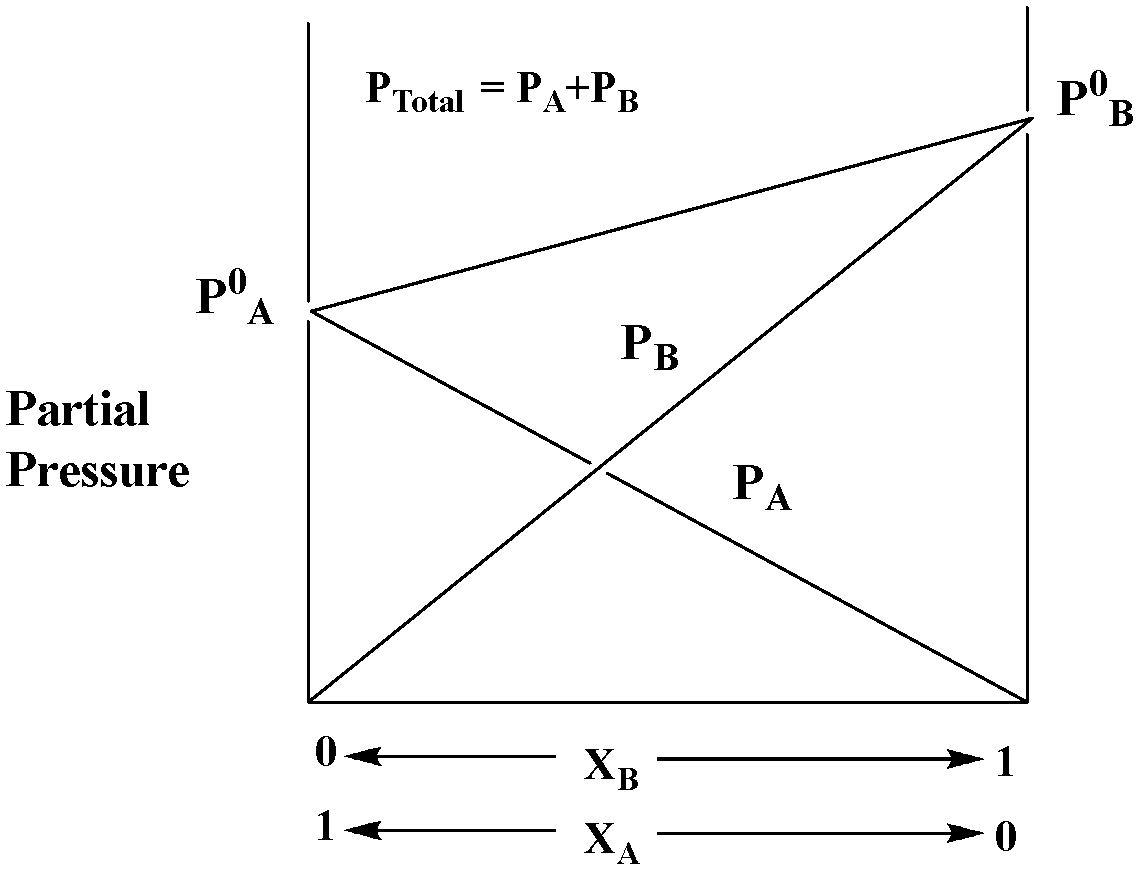
This is the case for the ideal behavior of the solution.
From the figure given in the question, line AD and CB shows ideal behaviors as it is the expression for Raoult's law.
The correct answer is option (D) .
Note:
When a solution does not obey Raoult's law, it is called a non-ideal solution. It may show deviations from the ideal behavior. The vapor pressure of such a non-ideal solution is either higher or lower than that which is predicted by Raoult's law. Thus, it can show a positive or negative deviation.
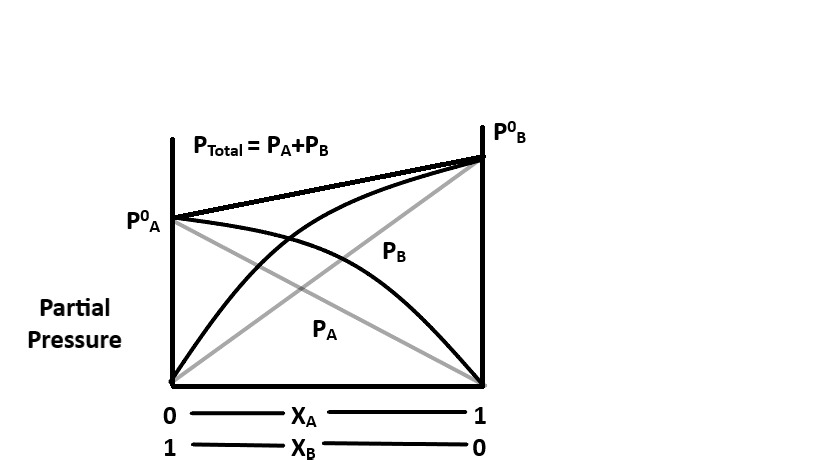
This is a non-ideal solution that shows a positive deviation.
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{P}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}$ , where ${{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}$ is the vapor pressure of pure solvent and ${{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}$ is the mole fraction of A. This is called Raoult's law. The ideal solution obeys Raoult's law. When a solution does not obey Raoult's law, it is called a non-ideal solution.
Complete step by step answer:
Considering a binary solution with 2 volatile liquids A and B that would evaporate and an equilibrium will be established between the liquid phase and vapor phase.
As mentioned above, based on Raoult's law, ${{\text{P}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}$ and ${{\text{P}}_{\text{B}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{B}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$
We know what mole fraction is.
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{n}}_{\text{A}}}}}{{{{\text{n}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{n}}_{\text{B}}}}}$ .
We know from Dalton’s law that the total pressure of the solution in a container is the sum of the partial pressure of each component. ${{\text{P}}_{{\text{total}}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{B}}}$
Hence, ${{\text{P}}_{{\text{total}}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{B}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$ ( from Raoult's law)
We know that ${{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}{\text{ = 1}}$ , so ${{\text{X}}_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = 1 - }}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$
Therefore, ${{\text{P}}_{{\text{total}}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{A}}{\text{(1 - }}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}{\text{) + }}{{\text{P}}^{\text{0}}}_{\text{B}}{{\text{X}}_{\text{B}}}$

This is the case for the ideal behavior of the solution.
From the figure given in the question, line AD and CB shows ideal behaviors as it is the expression for Raoult's law.
The correct answer is option (D) .
Note:
When a solution does not obey Raoult's law, it is called a non-ideal solution. It may show deviations from the ideal behavior. The vapor pressure of such a non-ideal solution is either higher or lower than that which is predicted by Raoult's law. Thus, it can show a positive or negative deviation.

This is a non-ideal solution that shows a positive deviation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




