
In protein synthesis, the polymerization of amino acids involves three steps. Which of the following is not involved in protein synthesis?
A.Elongation
B.Transcription
C.Termination
D.Initiation
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Polypeptides synthesis means the formation of amide bonds between the amino acid monomers. These amide bonds are formed through a condensation reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid. For the synthesis of the amide bond, it requires chemical activation of the carboxyl group and followed by an attack on the free amine group nucleophile.
Complete answer:Initiation- mRNA chain has a 5’ end which is an initiator or the start codon, AUG which signals the start of polypeptide chain formation. This start codon lies very close to the P site of the ribosome. Formyl-methionine amino acid initiates the process. tRNA with UAC anticodon will carry out the process by bonding to the AUG initiator codon of mRNA through hydrogen bonds.
Elongation- In protein synthesis, the elongation cycle begins with the insertion of an aminoacyl tRNA onto the empty A site of the ribosome. The type of tRNA species that has to be inserted depends upon the codon present on the mRNA A site. The aminoacyl tRNA complementary is transferred to the A site by a non-ribosomal specific protein which is called the elongation factor T (EF-T) which binds to the aminoacyl tRNA.
Termination- For the termination of protein synthesis two conditions are required. One is the presence of the stop codon which signals the chain elongation to be terminated and the other signal being the presence of the RF factors (RF) which will recognize the termination of the chain. The termination codon or UGA, UAA, and UAG for which the tRNA does not exist.
Transcription- Transcription is the process in which the information of the DNA strand is copied into the new molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA stably and safely stores the genetic information in the nucleus of the cell.
Hence the correct answer is option B, Transcription.
Below is the picture of polypeptide formation.
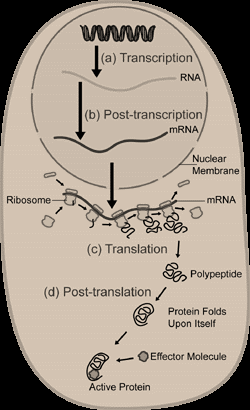
Note: Translation or the protein synthesis starts with the process known as the pre-initiation, the mRNA template, tRNA, and initiator factors come together. During elongation and translocation of the ribosome moves down the mRNA, which brings the tRNA to the A site and then removes the uncharged tRNA to the E site. When the ribosome is reached to the termination codon the translation stops.
Complete answer:Initiation- mRNA chain has a 5’ end which is an initiator or the start codon, AUG which signals the start of polypeptide chain formation. This start codon lies very close to the P site of the ribosome. Formyl-methionine amino acid initiates the process. tRNA with UAC anticodon will carry out the process by bonding to the AUG initiator codon of mRNA through hydrogen bonds.
Elongation- In protein synthesis, the elongation cycle begins with the insertion of an aminoacyl tRNA onto the empty A site of the ribosome. The type of tRNA species that has to be inserted depends upon the codon present on the mRNA A site. The aminoacyl tRNA complementary is transferred to the A site by a non-ribosomal specific protein which is called the elongation factor T (EF-T) which binds to the aminoacyl tRNA.
Termination- For the termination of protein synthesis two conditions are required. One is the presence of the stop codon which signals the chain elongation to be terminated and the other signal being the presence of the RF factors (RF) which will recognize the termination of the chain. The termination codon or UGA, UAA, and UAG for which the tRNA does not exist.
Transcription- Transcription is the process in which the information of the DNA strand is copied into the new molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA stably and safely stores the genetic information in the nucleus of the cell.
Hence the correct answer is option B, Transcription.
Below is the picture of polypeptide formation.

Note: Translation or the protein synthesis starts with the process known as the pre-initiation, the mRNA template, tRNA, and initiator factors come together. During elongation and translocation of the ribosome moves down the mRNA, which brings the tRNA to the A site and then removes the uncharged tRNA to the E site. When the ribosome is reached to the termination codon the translation stops.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




