
In one Krebs’ cycle, decarboxylation takes place at _______ steps.
(a) Five
(b) Four
(c) Three
(d) Two
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Decarboxylation is the process of removal of the carboxyl group from a compound with the release of a carbon dioxide molecule. So, the number of steps in which a ${C}{O}_{2}$ molecule is released after removal of a carboxyl from a compound is the number of decarboxylation reactions in one Krebs’ cycle.
Complete answer:
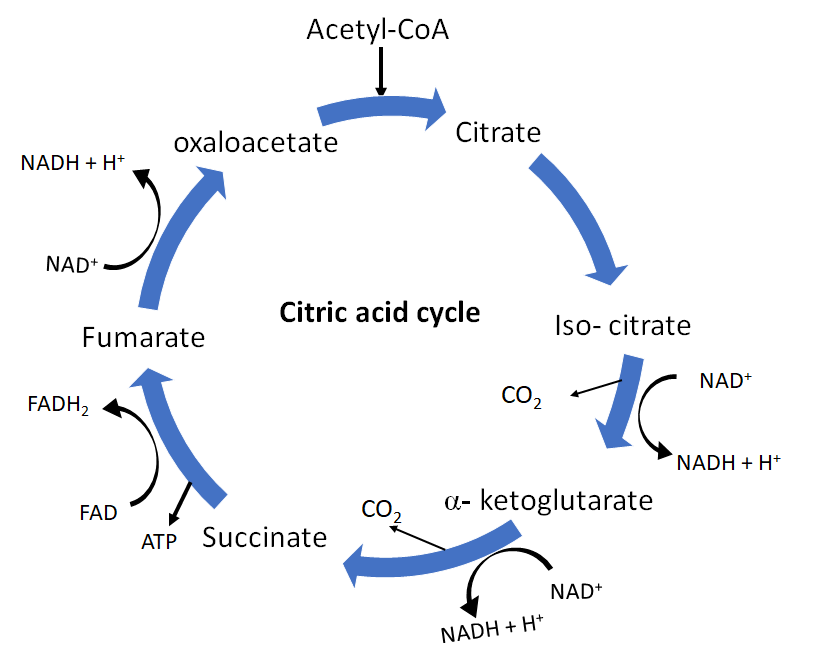
Krebs’ cycle is the central pathway for the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It begins with a citric acid molecule which is a 6- carbon compound and ends at Oxaloacetate which is a 4-carbon compound which indicates the removal of two carboxyl groups.
These carboxyl groups are removed with the release of a ${C}{O}_{2}$ molecule in two different steps.
- The first oxidative decarboxylation takes place at the fourth step of the TCA cycle where isocitrate is converted to 5-carbon α-ketoglutarate, with the release of a pair of hydrogen atoms and a molecule of carbon dioxide.
- The second oxidative decarboxylation occurs at the fifth step of the Krebs’ cycle where a molecule of coenzyme-A reacts with the α-ketoglutarate to form a 4-carbon compound succinyl- coenzyme A and releasing carbon dioxide and a pair of hydrogen atoms.
So, the answer is, “Two”.
Note:Decarboxylation is the reaction in which a carboxyl group is removed and it generally refers to the reactions of carboxylic acids. The reverse of this process in which there is an addition of a ${C}{O}_{2}$ molecule to a compound is called carboxylation and it is the first chemical step in photosynthesis.
Complete answer:
Krebs’ cycle is the central pathway for the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It begins with a citric acid molecule which is a 6- carbon compound and ends at Oxaloacetate which is a 4-carbon compound which indicates the removal of two carboxyl groups.
These carboxyl groups are removed with the release of a ${C}{O}_{2}$ molecule in two different steps.
- The first oxidative decarboxylation takes place at the fourth step of the TCA cycle where isocitrate is converted to 5-carbon α-ketoglutarate, with the release of a pair of hydrogen atoms and a molecule of carbon dioxide.
- The second oxidative decarboxylation occurs at the fifth step of the Krebs’ cycle where a molecule of coenzyme-A reacts with the α-ketoglutarate to form a 4-carbon compound succinyl- coenzyme A and releasing carbon dioxide and a pair of hydrogen atoms.

So, the answer is, “Two”.
Note:Decarboxylation is the reaction in which a carboxyl group is removed and it generally refers to the reactions of carboxylic acids. The reverse of this process in which there is an addition of a ${C}{O}_{2}$ molecule to a compound is called carboxylation and it is the first chemical step in photosynthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




