
In \[O{F_2}\] , oxygen has hybridization of:
A.sp
B.\[s{p^2}\]
C.\[s{p^3}\]
D.\[s{p^3}d\]
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: Hybridization can be understood as mixing of orbitals of a given chemical species to form new orbitals. These new orbitals are known as hybrid orbitals. These newly formed hybrid orbitals have different energy levels, shapes, etc. as compared to the original orbitals it is made from.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Hybridization is necessary to understand the types of bonds that the bonding atoms form. Hybridization translates into formation of hybrid orbitals with lower energy levels that the parent orbitals. This enables the bond to be more stable because of the low energy profile.
Now, we can determine the hybridization of a molecule on the basis of its Lewis structure. In
order to do that, we must follow these steps:
1.Select the atom we need to determine the hybridization for.
2.Count the number of atoms that are bonded to this atom.
3.Then count the number of lone pairs present on the given atom
4.Add these two values and cross check with the data below:
Moving to the question, the Lewis structure for \[O{F_2}\] can be given as:
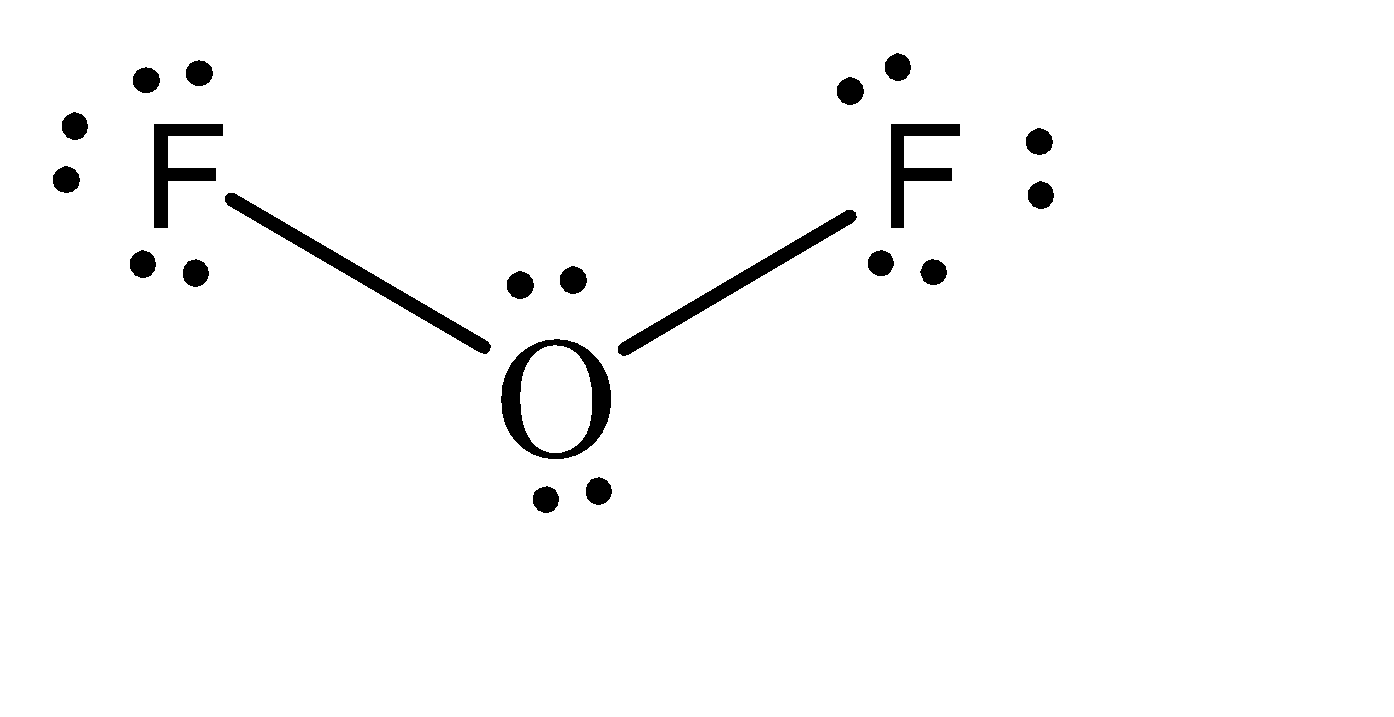
We can observe that there are 2 atoms attached to the oxygen atom. Also, there are 2 lone pairs present on the oxygen atom. If we add these numbers, the sum turns out to be 4. Hence, the hybridization of the oxygen atom in \[O{F_2}\] is \[s{p^3}\] .
Hence, Option C is the correct option
Note: Hybridization lets us explain the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory helps us to predict the geometrical structures of individual molecules on the basis of the number of pairs of electrons that surround the central atoms.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Hybridization is necessary to understand the types of bonds that the bonding atoms form. Hybridization translates into formation of hybrid orbitals with lower energy levels that the parent orbitals. This enables the bond to be more stable because of the low energy profile.
Now, we can determine the hybridization of a molecule on the basis of its Lewis structure. In
order to do that, we must follow these steps:
1.Select the atom we need to determine the hybridization for.
2.Count the number of atoms that are bonded to this atom.
3.Then count the number of lone pairs present on the given atom
4.Add these two values and cross check with the data below:
a.If the sum is 2, then the hybridization is sp.
b.If the sum is 3, then the hybridization is \[s{p^2}\]
c.If the sum is 4, then the hybridization is \[s{p^3}\]
Moving to the question, the Lewis structure for \[O{F_2}\] can be given as:

We can observe that there are 2 atoms attached to the oxygen atom. Also, there are 2 lone pairs present on the oxygen atom. If we add these numbers, the sum turns out to be 4. Hence, the hybridization of the oxygen atom in \[O{F_2}\] is \[s{p^3}\] .
Hence, Option C is the correct option
Note: Hybridization lets us explain the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory helps us to predict the geometrical structures of individual molecules on the basis of the number of pairs of electrons that surround the central atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




