
In $OF_2$ oxygen has hybridisation of :-
A.$\mathop {sp}\nolimits^3 $
B.$\mathop {sp}\nolimits^2 $
C.$sp$
D.None of these
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Hybridisation is defined as a combination of atomic orbitals to form a new set of equivalent orbitals which are known as hybrid orbitals. When 3 of the p orbitals combine and one s orbital combines it forms sp3 hybridisation. When two p orbitals and one s orbital combines it forms sp2 orbital. When one p and one s orbital combine it forms sp orbital .
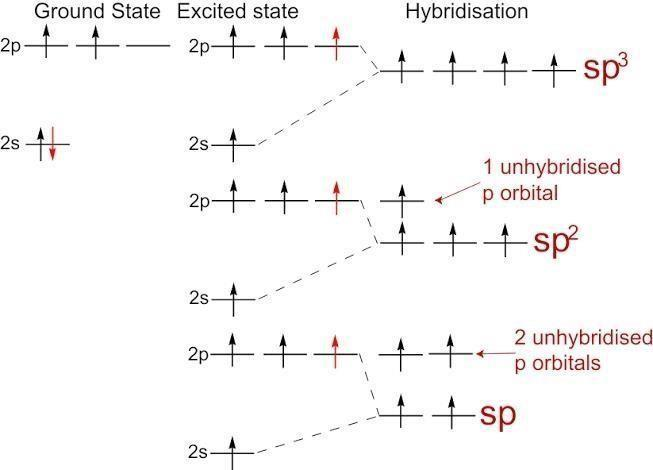
Complete step by step answer:
$\mathop {sp}\nolimits^3 $:- oxygen has 6 electrons in its valence shell due to its atomic number 8 and electronic configuration 2,6 . It forms 2 bonds with fluorine rest 4 electrons forms two lone pairs. We count lone pairs in hybridisation state . So total it has 4 bonds ( 2bond pair and 2 lone pair) thus it forms sp3 hybridisation . Hence this option is correct.
$\mathop {sp}\nolimits^2 $ :- oxygen forms four bonds but sp2 hybridisation means three bonds . It has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs. Hence this option is not correct.
$sp$ :- oxygen forms four bonds due its 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs . But sp hybridisation involves only two bonds. Hence this option is also not correct.
None of these :- as the first option is accurately correct so this option can’t be taken into consideration.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
Features of hybridisation:-
1.The number of hybrid orbitals is equal to the number of atomic orbitals that get hybridised.
2.The hybridised orbitals are always equivalent in energy and shape
3.The hybrid orbitals are more effective in forming stable bonds than in pure atomic orbitals.
4.Type of hybridisation indicates the geometry of molecule
Conditions for hybridisation:-
1.The orbitals present in the valence shell of the atom are hybridised.
2.The orbitals taking part in hybridisation must have only a small difference of energies.
3.Promotion of electron is not essential condition prior to hybridisation
4.It is not necessary that only half filled orbitals participate in hybridisation.

Complete step by step answer:
$\mathop {sp}\nolimits^3 $:- oxygen has 6 electrons in its valence shell due to its atomic number 8 and electronic configuration 2,6 . It forms 2 bonds with fluorine rest 4 electrons forms two lone pairs. We count lone pairs in hybridisation state . So total it has 4 bonds ( 2bond pair and 2 lone pair) thus it forms sp3 hybridisation . Hence this option is correct.
$\mathop {sp}\nolimits^2 $ :- oxygen forms four bonds but sp2 hybridisation means three bonds . It has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs. Hence this option is not correct.
$sp$ :- oxygen forms four bonds due its 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs . But sp hybridisation involves only two bonds. Hence this option is also not correct.
None of these :- as the first option is accurately correct so this option can’t be taken into consideration.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
Features of hybridisation:-
1.The number of hybrid orbitals is equal to the number of atomic orbitals that get hybridised.
2.The hybridised orbitals are always equivalent in energy and shape
3.The hybrid orbitals are more effective in forming stable bonds than in pure atomic orbitals.
4.Type of hybridisation indicates the geometry of molecule
Conditions for hybridisation:-
1.The orbitals present in the valence shell of the atom are hybridised.
2.The orbitals taking part in hybridisation must have only a small difference of energies.
3.Promotion of electron is not essential condition prior to hybridisation
4.It is not necessary that only half filled orbitals participate in hybridisation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




