
In mitochondria, ATP synthesis occurs
(a)At the outer membrane
(b)At the Cristae
(c)In the Matrix
(d)In the Intra-cristal space
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: The ATP synthesis occurs within the fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The passage of energy-rich electrons among cytochromes and coenzymes drains the energy from the electrons to make ATP from ADP and phosphate ions. The particular formation of ATP molecules requires a complex process called chemiosmosis.
Complete answer:
Mitochondria is a double membrane-bound structure; the outer and inner mitochondrial membrane.
The inner mitochondrial membrane is folded multiple times to make cristae and has F0-F1 particles that are the particles for the electron transport system. The inner membrane is also loaded with proteins that are involved within the ATP synthesis and this is often an area where the formation of ATP takes place.
Additional Information: ATP synthesis in mitochondria
To understand the mechanism by which the energy released during respiration is conserved as ATP, it's necessary to understand the structural features of mitochondria. These are organelles in animal and plant cells during which oxidative phosphorylation takes place. There are many mitochondria in animal tissues for instance, in heart and striated muscle, which require large amounts of energy for mechanical work, and within the pancreas, where there's biosynthesis, and within the kidney, where the method of excretion begins. Mitochondria have an outer membrane, which allows the passage of most small molecules and ions, and a highly folded inner membrane (crista), which doesn't even allow the passage of small ions then maintains a closed space within the cell. The electron-transferring molecules of the respiratory chain and therefore the enzymes responsible for ATP synthesis are located in and on this inner membrane, while space inside (matrix) contains the enzymes of the TCA cycle. The enzyme systems primarily liable for the discharge and subsequent oxidation of reducing equivalents are thus closely related so that the reduced coenzymes formed during catabolism (NADH + H+ and FADH2) are available as substrates for respiration. The movement of most charged metabolites into the matrix space is mediated by special carrier proteins within the crista that catalyzes exchange-diffusion (i.e., a one-for-one exchange).
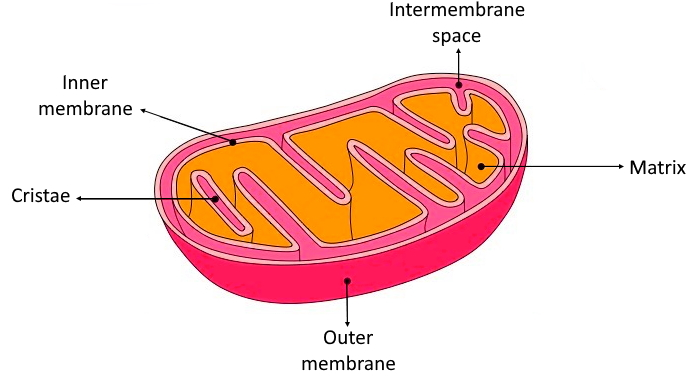
So, the correct answer is,” At the cristae.”
Note: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency for cellular processes. ATP provides the energy for both energy-consuming endergonic reactions and energy-releasing exergonic reactions, which require a small input of energy.
Complete answer:
Mitochondria is a double membrane-bound structure; the outer and inner mitochondrial membrane.
The inner mitochondrial membrane is folded multiple times to make cristae and has F0-F1 particles that are the particles for the electron transport system. The inner membrane is also loaded with proteins that are involved within the ATP synthesis and this is often an area where the formation of ATP takes place.
Additional Information: ATP synthesis in mitochondria
To understand the mechanism by which the energy released during respiration is conserved as ATP, it's necessary to understand the structural features of mitochondria. These are organelles in animal and plant cells during which oxidative phosphorylation takes place. There are many mitochondria in animal tissues for instance, in heart and striated muscle, which require large amounts of energy for mechanical work, and within the pancreas, where there's biosynthesis, and within the kidney, where the method of excretion begins. Mitochondria have an outer membrane, which allows the passage of most small molecules and ions, and a highly folded inner membrane (crista), which doesn't even allow the passage of small ions then maintains a closed space within the cell. The electron-transferring molecules of the respiratory chain and therefore the enzymes responsible for ATP synthesis are located in and on this inner membrane, while space inside (matrix) contains the enzymes of the TCA cycle. The enzyme systems primarily liable for the discharge and subsequent oxidation of reducing equivalents are thus closely related so that the reduced coenzymes formed during catabolism (NADH + H+ and FADH2) are available as substrates for respiration. The movement of most charged metabolites into the matrix space is mediated by special carrier proteins within the crista that catalyzes exchange-diffusion (i.e., a one-for-one exchange).

So, the correct answer is,” At the cristae.”
Note: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency for cellular processes. ATP provides the energy for both energy-consuming endergonic reactions and energy-releasing exergonic reactions, which require a small input of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




