
In frog heart, there are cardiac muscles, which consists of fibres, called as
(a) Purkinje fibres
(b) Myonemes
(c) Telodendria
(d) Columnae carneae
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: The fibres in the heart of frog's cardiac muscles are also called subendocardial branches. They are a special cardiac end-organ. It is a special conductive fibre located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just below the endocardium, in a space called subendocardium.
Complete step by step answer:
The epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium form the heart wall of the frog. The myocardium consists of branched and striated yet involuntary cardiac muscles that contract and relax rhythmically at a constant rate. The fibres of the heart's self-exciting and conductive muscle are of three forms, namely nodal fibres, transitional fibres and Purkinje fibres. Purkinje fibres bear the contraction impulse to the ventricle myocardium from both the left and right branches of the bundle. Purkinje fibres enable synchronised contractions of its ventricles to be produced by the heart's conduction system and are therefore important for maintaining steady heart rhythm.
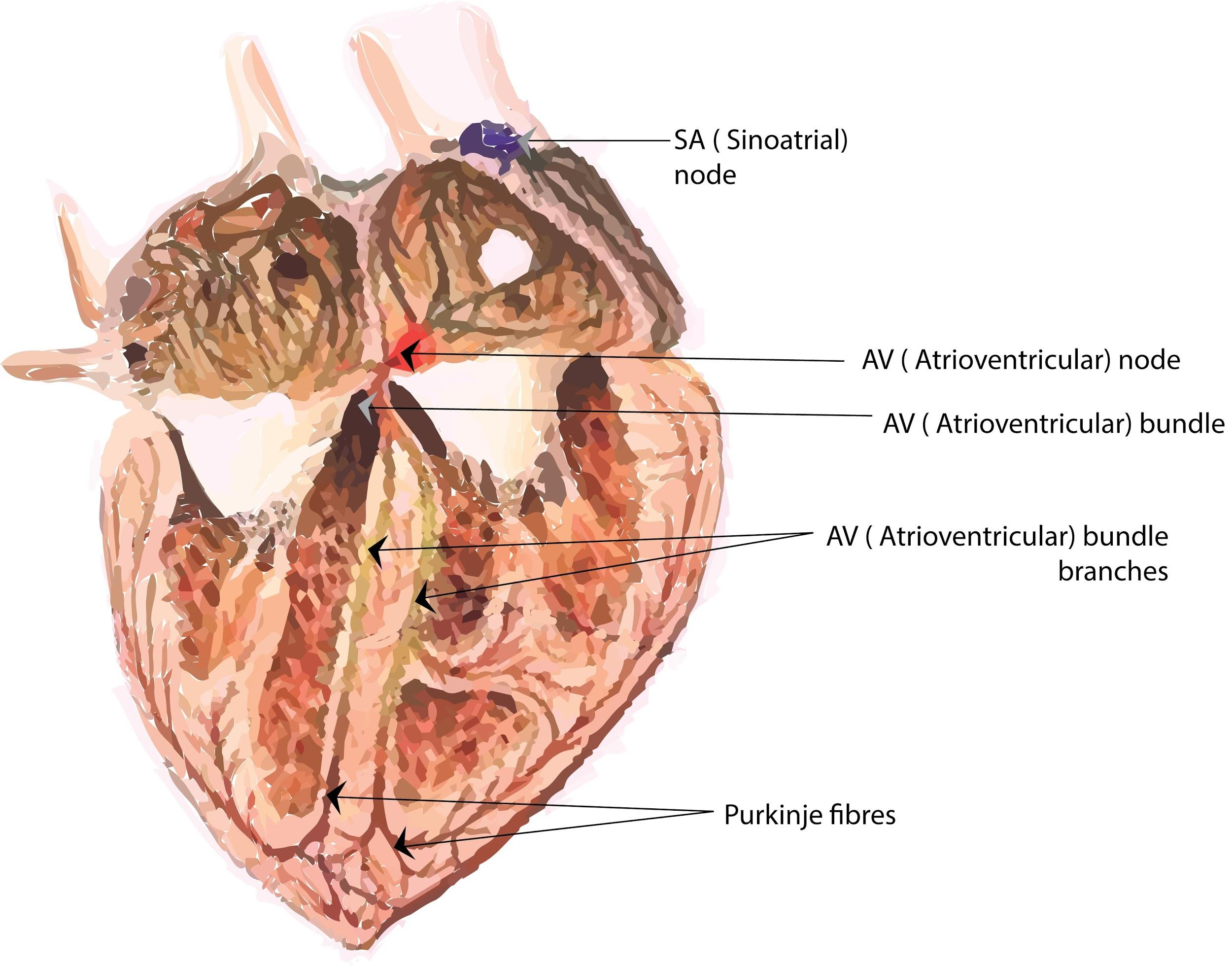
Myonemes are contractile fibrils of some protozoans located in the cytoplasm. Telodendria is known as the terminal branches of axons which contain neurotransmitters. A number of muscular ridges called columnae carneae were projected into its cavity from the ventricle wall in the frog heart, separating the peripheral portion of the cavity into a number of pockets. Columnae carneae are muscles found in the heart ventricles which aid in the heart's pumping action.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Purkinje fibres’.
Note: The heart of the frog is composed of three chambers, a ventricle and two atria. The Purkinje fibres are special conducting fibres consisting mainly of electrically excitable cells that are larger than cardiomyocytes with less myofibril and more mitochondria and that perform cardiac action potentials faster and more effectively than any other heart cells.
Complete step by step answer:
The epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium form the heart wall of the frog. The myocardium consists of branched and striated yet involuntary cardiac muscles that contract and relax rhythmically at a constant rate. The fibres of the heart's self-exciting and conductive muscle are of three forms, namely nodal fibres, transitional fibres and Purkinje fibres. Purkinje fibres bear the contraction impulse to the ventricle myocardium from both the left and right branches of the bundle. Purkinje fibres enable synchronised contractions of its ventricles to be produced by the heart's conduction system and are therefore important for maintaining steady heart rhythm.

Myonemes are contractile fibrils of some protozoans located in the cytoplasm. Telodendria is known as the terminal branches of axons which contain neurotransmitters. A number of muscular ridges called columnae carneae were projected into its cavity from the ventricle wall in the frog heart, separating the peripheral portion of the cavity into a number of pockets. Columnae carneae are muscles found in the heart ventricles which aid in the heart's pumping action.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Purkinje fibres’.
Note: The heart of the frog is composed of three chambers, a ventricle and two atria. The Purkinje fibres are special conducting fibres consisting mainly of electrically excitable cells that are larger than cardiomyocytes with less myofibril and more mitochondria and that perform cardiac action potentials faster and more effectively than any other heart cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




