
In figure block 1 has one fourth mass and one fourth length of block 2 (mass $4m$ and length $l$. No friction exists between block 2 and the surface on which it rests. Coefficient of friction is ${{\mu }_{k}}$ between 1 and 2. The distance block 2 moves when only half of block 1 is still on block 2 is $\dfrac{n{{\mu }_{k}}l}{8\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}$. Then find the value of $n$.


Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: First of all, the forces should be equated by considering the forces of friction, gravitation force and tension also. Then we have to calculate the relative acceleration between the blocks. From that the time taken to move should be calculated and finally the distance travelled is found using this, and the comparison will give the value of $n$ as the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
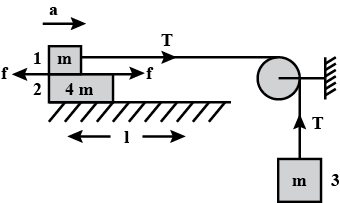
Let us consider the block 1 first,
$T-F=ma$………………………. (1)
Consider the block 3,
$mg-T=ma$……………………… (2)
From this two equation, equation (1) and (2),
\[mg-F=2ma\]
As we know
\[F={{\mu }_{k}}mg\]
Substituting it in this equation,
\[mg-{{\mu }_{k}}mg=2ma\]
From this after rearranging, we can write that,
\[a=\dfrac{g\left( 1-{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}{2}\]
Now let us consider the block 2,
\[F=4m{{a}_{2}}\]
After rearranging we can write that,
\[{{a}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}mg}{4m}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4}\]
Therefore we can write that, the relative acceleration between block 1 and 2 is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{a}_{r}}=a-{{a}_{2}}=\dfrac{g\left( 1-{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}{2}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4} \\
& =\dfrac{2g-3{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4} \\
& =\dfrac{g\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
Now the time taken to move \[\left( \dfrac{l}{2} \right)\] distance is\[t\],
Therefore the distance moved by the block 2 is\[x\],
\[\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{1}{2}{{a}_{2}}{{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4}\times \dfrac{4l}{g\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)} \\
& =\dfrac{4l{{\mu }_{k}}}{8\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)} \\
\end{align}\]
Compare this equation with the equation given in the question will be,
$\dfrac{n{{\mu }_{k}}l}{8\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}$
$=\dfrac{4{{\mu }_{k}}l}{8\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}$
Therefore it is understood that
$n=4$
Therefore the value of $n$ is determined.
Note:
Friction is the force which prevents the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are so many types of friction. Dry friction is a force that prevents the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact.
Complete step by step answer:

Let us consider the block 1 first,
$T-F=ma$………………………. (1)
Consider the block 3,
$mg-T=ma$……………………… (2)
From this two equation, equation (1) and (2),
\[mg-F=2ma\]
As we know
\[F={{\mu }_{k}}mg\]
Substituting it in this equation,
\[mg-{{\mu }_{k}}mg=2ma\]
From this after rearranging, we can write that,
\[a=\dfrac{g\left( 1-{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}{2}\]
Now let us consider the block 2,
\[F=4m{{a}_{2}}\]
After rearranging we can write that,
\[{{a}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}mg}{4m}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4}\]
Therefore we can write that, the relative acceleration between block 1 and 2 is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{a}_{r}}=a-{{a}_{2}}=\dfrac{g\left( 1-{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}{2}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4} \\
& =\dfrac{2g-3{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4} \\
& =\dfrac{g\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
Now the time taken to move \[\left( \dfrac{l}{2} \right)\] distance is\[t\],
Therefore the distance moved by the block 2 is\[x\],
\[\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{1}{2}{{a}_{2}}{{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{\mu }_{k}}g}{4}\times \dfrac{4l}{g\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)} \\
& =\dfrac{4l{{\mu }_{k}}}{8\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)} \\
\end{align}\]
Compare this equation with the equation given in the question will be,
$\dfrac{n{{\mu }_{k}}l}{8\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}$
$=\dfrac{4{{\mu }_{k}}l}{8\left( 2-3{{\mu }_{k}} \right)}$
Therefore it is understood that
$n=4$
Therefore the value of $n$ is determined.
Note:
Friction is the force which prevents the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are so many types of friction. Dry friction is a force that prevents the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




