
In ECG, the P-R interval corresponds to
(a) Time delay in A-V node
(b) S-A nodal conduction time
(c) Increased ventricular contraction
(d) The time interval between the onset of ventricular contraction.
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: The ECG PR interval corresponds to a time lag of approximately 0.09 seconds. This delay in the cardiac impulse is extremely important as it shows that the Atria have ejected their blood into the ventricles first before the ventricles contract. This delay is seen in the part of the heart that connects the atria and ventricles electrically.
Complete answer:
In ECG, the P-R interval corresponds to the time delay in the A-V node. The record or graphical representation of the electrical activities of the heart which occur before the onset of mechanical activities is called an ‘electrocardiogram’ (ECG).
Now let's study the major complexes in a normal electrocardiogram in brief.
-’P’ wave which corresponds to the atrial complex.
-‘QRS’ complex, it is the initial ventricular complex.
-‘T’ wave, it corresponds to the final ventricular complex.
-‘QRST’ represents the ventricular complex in total.
The various intervals of ECG are:
‘PR’ interval:
-It shows the duration of conduction of impulses from the SA node to ventricles through atrial muscles and AV nodes.
-The normal duration of this interval is 0.18 seconds. It varies between 0.12 and 0.2 seconds. Sometimes it may be more than 0.2 seconds. Usually, this delay occurs in the AV node so it is called the AV nodal delay.
‘Q-T’ interval :
-It is the interval between the onset of Q wave and the end of the T wave.
-It signifies the electrical activity in ventricles and its duration is between 0.4 and 0.42 seconds.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Time delay in A-V node.’
Note: -‘Electrocardiography’ is the technique by which the electrical activities of the heart are studied.
-The instrument by which the electrical activities of the heart are recorded is called ‘electrocardiograph’ or the ECG machine.
-SA node pacemaker activity is indirectly estimated from ‘P’-waves generated by the atrial activity.
-Ventricular contraction can be checked from QRS Complex in the ECG.
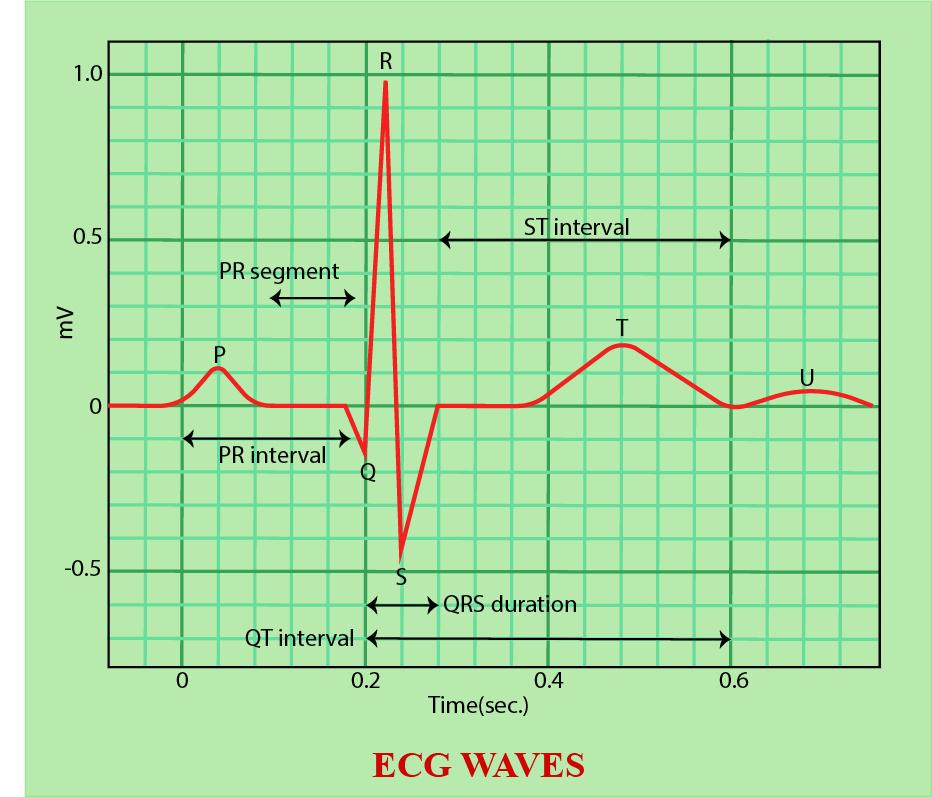
Complete answer:
In ECG, the P-R interval corresponds to the time delay in the A-V node. The record or graphical representation of the electrical activities of the heart which occur before the onset of mechanical activities is called an ‘electrocardiogram’ (ECG).
Now let's study the major complexes in a normal electrocardiogram in brief.
-’P’ wave which corresponds to the atrial complex.
-‘QRS’ complex, it is the initial ventricular complex.
-‘T’ wave, it corresponds to the final ventricular complex.
-‘QRST’ represents the ventricular complex in total.
The various intervals of ECG are:
‘PR’ interval:
-It shows the duration of conduction of impulses from the SA node to ventricles through atrial muscles and AV nodes.
-The normal duration of this interval is 0.18 seconds. It varies between 0.12 and 0.2 seconds. Sometimes it may be more than 0.2 seconds. Usually, this delay occurs in the AV node so it is called the AV nodal delay.
‘Q-T’ interval :
-It is the interval between the onset of Q wave and the end of the T wave.
-It signifies the electrical activity in ventricles and its duration is between 0.4 and 0.42 seconds.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Time delay in A-V node.’
Note: -‘Electrocardiography’ is the technique by which the electrical activities of the heart are studied.
-The instrument by which the electrical activities of the heart are recorded is called ‘electrocardiograph’ or the ECG machine.
-SA node pacemaker activity is indirectly estimated from ‘P’-waves generated by the atrial activity.
-Ventricular contraction can be checked from QRS Complex in the ECG.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




