
In diborane, the banana bond is formed between:
A. 2 electrons. 3 atoms
B. 2 electrons. 1 atom
C. 1 electron. 2 atoms
D. 2 electrons. 2 atoms
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint:\[{B_2}{H_6}\] is commonly known as Diborane. It is a colorless, pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odor. It is also known as Bromoethane, boron hydride, and boron hexahydride. Banana Bonds are also known as Hydrogen Bridge Bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of \[{B_2}{H_6}\] the compound looks like the following:
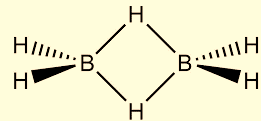
From this image, we can see that:
Four hydrogen atoms are present at the terminal position, while
Two hydrogen atoms are present as a bridge between the two central boron atoms.
The length of the terminal \[B - H\] bond is relatively small as compared to the bridge \[B - H\] bond. This indicates that the terminal \[B - H\] bonds are relatively weaker as compared to the bridge \[B - H\] bonds.
After using 2 electrons to bond with the terminal hydrogen atoms, the boron atom is left with one additional electron left for bonding. The bridging hydrogen atoms are then offering one electron each. The \[{B_2}{H_2}\] ring is held together by four electrons which are forming two 3-center 2-electron bonds. This type of bond is often referred to as a 'banana bond'.
Banana Bonds are otherwise known as Hydrogen Bridge Bonds. Hence, the two types of bonds present in \[{B_2}{H_6}\] are covalent and hydrogen bridge bonds.
So, the correct answer is A.
Note:
According to the Molecular Orbital Theory, the bonds between the Boron atoms and the terminal hydrogen atoms can be described as conventional 2-center, 2-electron covalent bonds. The bonding between the boron atoms and the bridging hydrogen atoms is, however, different from that in molecules such as hydrocarbons.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of \[{B_2}{H_6}\] the compound looks like the following:

From this image, we can see that:
Four hydrogen atoms are present at the terminal position, while
Two hydrogen atoms are present as a bridge between the two central boron atoms.
The length of the terminal \[B - H\] bond is relatively small as compared to the bridge \[B - H\] bond. This indicates that the terminal \[B - H\] bonds are relatively weaker as compared to the bridge \[B - H\] bonds.
After using 2 electrons to bond with the terminal hydrogen atoms, the boron atom is left with one additional electron left for bonding. The bridging hydrogen atoms are then offering one electron each. The \[{B_2}{H_2}\] ring is held together by four electrons which are forming two 3-center 2-electron bonds. This type of bond is often referred to as a 'banana bond'.
Banana Bonds are otherwise known as Hydrogen Bridge Bonds. Hence, the two types of bonds present in \[{B_2}{H_6}\] are covalent and hydrogen bridge bonds.
So, the correct answer is A.
Note:
According to the Molecular Orbital Theory, the bonds between the Boron atoms and the terminal hydrogen atoms can be described as conventional 2-center, 2-electron covalent bonds. The bonding between the boron atoms and the bridging hydrogen atoms is, however, different from that in molecules such as hydrocarbons.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




