
In Dianthus, placentation is
(a)Basal
(b)Free central
(c)Axile
(d)marginal
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The arrangement of ovules within the ovary is called placentation. There are different types of placentation namely marginal, axile, parietal, basal, and free central. In dianthus and primrose, the ovules are born on the central axis without septa.
Complete answer:
A plant ovary contains one or more ovules attached to a flattened,cushion-like structure called the placenta.
In free central placentation, the ovules are borne on the central axis without septa.
Therefore, the type of placentation in dianthus is free central.
Additional Information: There are different types of placentation namely,
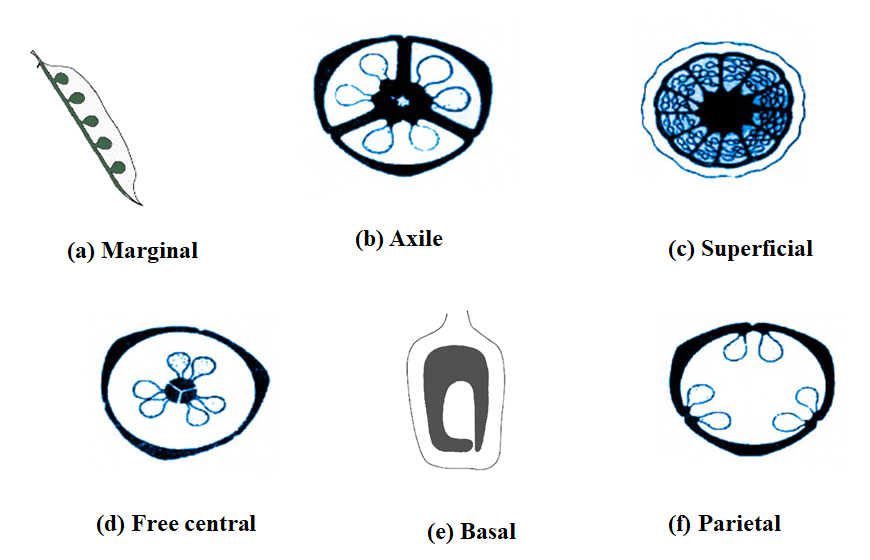
-Marginal type of placentation, wherein the placenta forms a ridge seen at the ventral suture of the ovary. The ovules are attached to this ridge in two rows.
-Axile placentation, where the placenta is present at the center with ovules attached to it and the ovary is multilocular.
-Parietal placentation, where the ovules are attached to the wall of the ovary that is parietally. The ovary is originally unilocular but due to the formation of a false septum becomes two-chambered.
-Free central placentation wherein the ovules are present at the center and the ovary is unilocular.
-Basal type of placentation where as the name suggests a single ovule is present at the basal part of the unilocular ovary.
Examples of different types of placentation are
Marginal: pea
Axile: rose,tomato,lemon
Parietal: mustard, agremone
Free central: dianthus, primrose
Basal: sunflower, marigold
So, the correct answer is ‘free central’.
Note: Placentation is referred to as the arrangement of ovules inside the ovary.
Another type of placentation that is lesser known is the superficial placentation as seen in a multicarpellary ovary. Here the ovules are seen developing on the inner surface of the carpels. Ex: Nymphaeaceae.
Complete answer:
A plant ovary contains one or more ovules attached to a flattened,cushion-like structure called the placenta.
In free central placentation, the ovules are borne on the central axis without septa.
Therefore, the type of placentation in dianthus is free central.
Additional Information: There are different types of placentation namely,
-Marginal type of placentation, wherein the placenta forms a ridge seen at the ventral suture of the ovary. The ovules are attached to this ridge in two rows.
-Axile placentation, where the placenta is present at the center with ovules attached to it and the ovary is multilocular.
-Parietal placentation, where the ovules are attached to the wall of the ovary that is parietally. The ovary is originally unilocular but due to the formation of a false septum becomes two-chambered.
-Free central placentation wherein the ovules are present at the center and the ovary is unilocular.
-Basal type of placentation where as the name suggests a single ovule is present at the basal part of the unilocular ovary.
Examples of different types of placentation are
Marginal: pea
Axile: rose,tomato,lemon
Parietal: mustard, agremone
Free central: dianthus, primrose
Basal: sunflower, marigold
So, the correct answer is ‘free central’.
Note: Placentation is referred to as the arrangement of ovules inside the ovary.
Another type of placentation that is lesser known is the superficial placentation as seen in a multicarpellary ovary. Here the ovules are seen developing on the inner surface of the carpels. Ex: Nymphaeaceae.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




