
In an SHM, restoring force is F = -kx, where k is force constant, x is displacement and A is the amplitude of motion, then the total energy depends upon
A. k, A and M
B. k, x, M
C. k, A
D. k, x
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: We will consider the work done by the restoring force when bringing the particle back to the mean position from one of the extremes. Then we will find the total energy at the mean position and accordingly choose the option that has the variables that appear in the expression for total energy.
Complete step by step answer:
We will be assuming that the only force acting on the particle is the given restoring force. So, when the particle goes from one of the extreme positions to the mean position of the oscillatory motion, the work will be done by the restoring force to increase the velocity of the particle. At the extreme position we will observe that all of the energy of the particle will be stored as its potential energy as the kinetic energy will be zero because the particle will be at rest there and at the mean position we see that the force on the particle will be zero and so will be its potential energy. All the energy of the particle at the mean position will be its kinetic energy. And using the work energy theorem we can state that the work done by the restoring force will be the same as the kinetic energy.
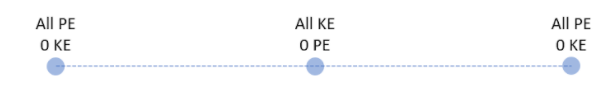
Let us now calculate the work done by the restoring force. Let us assume that the particle starts from the position of A or -A and goes to 0. The work done by the restoring force here for a small distance dx travelled by the particle as distance x away from the mean position will be given as

\[\begin{align}
& W=Fd \\
& dW=-kxdx \\
& \int{dW=\int\limits_{A}^{0}{-kxdx}}=\left[ \dfrac{-k{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right]_{A}^{0}=\left[ \dfrac{-k{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{-k{{\left( A \right)}^{2}}}{2} \right]=\dfrac{k{{A}^{2}}}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
We only need the amplitude and the force constant for total energy. Hence, the correct option will be C, i.e. k, A.
Note:
We can take either of the extreme position and will get the same answer as in the calculation we will need to take the square of that value and that will give the same result for both A and -A. Alternatively we can calculate the potential energy of the particle by using the formula that $F=\dfrac{-dU}{dx}$at the extreme position and we will get the value of potential energy, U at the extreme. Both the expressions will be the same.
Complete step by step answer:
We will be assuming that the only force acting on the particle is the given restoring force. So, when the particle goes from one of the extreme positions to the mean position of the oscillatory motion, the work will be done by the restoring force to increase the velocity of the particle. At the extreme position we will observe that all of the energy of the particle will be stored as its potential energy as the kinetic energy will be zero because the particle will be at rest there and at the mean position we see that the force on the particle will be zero and so will be its potential energy. All the energy of the particle at the mean position will be its kinetic energy. And using the work energy theorem we can state that the work done by the restoring force will be the same as the kinetic energy.

Let us now calculate the work done by the restoring force. Let us assume that the particle starts from the position of A or -A and goes to 0. The work done by the restoring force here for a small distance dx travelled by the particle as distance x away from the mean position will be given as

\[\begin{align}
& W=Fd \\
& dW=-kxdx \\
& \int{dW=\int\limits_{A}^{0}{-kxdx}}=\left[ \dfrac{-k{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right]_{A}^{0}=\left[ \dfrac{-k{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{-k{{\left( A \right)}^{2}}}{2} \right]=\dfrac{k{{A}^{2}}}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
We only need the amplitude and the force constant for total energy. Hence, the correct option will be C, i.e. k, A.
Note:
We can take either of the extreme position and will get the same answer as in the calculation we will need to take the square of that value and that will give the same result for both A and -A. Alternatively we can calculate the potential energy of the particle by using the formula that $F=\dfrac{-dU}{dx}$at the extreme position and we will get the value of potential energy, U at the extreme. Both the expressions will be the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




