
In an isothermal change of an ideal gas, $\Delta {\text{U = 0}}$. The change in the heat energy $\Delta {\text{Q}}$is equal to
A) \[0.5{\text{ }}W\]
B) $W$
C) $1.5W$
D) $2W$
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint-Ideal gas It is a theoretical gas that obeys ideal gas law. It comprises randomly moving point particles which are not participating in interparticle interactions. Ideal gas models fail at lower temperatures and high pressure. It also fails for heavy gases.
Formula used:
${\text{dQ = dU + W}}$ where,
${\text{dQ = }}$Heat supplied to the system by the surroundings,
${\text{dU = }}$Change in internal energy,
$W$= system’s work done on the surroundings
Complete step by step solution:
According to the First law of thermodynamics, if some heat is supplied to the system, then the quantity of heat absorbed by the system will be equal to the sum of the increase in its internal energy and the external work done by the system on the surroundings.
Ideal gas explores both in classical mechanics and quantum mechanics.
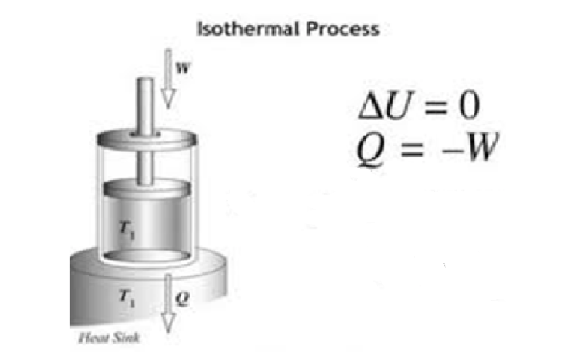
An isothermal process is one in which the pressure and volume of the system change but the temperature remains the same. Therefore, using the formula
${\text{dQ = dU + W}}$,
for an isothermal condition,${\text{dU = 0}}$
Substituting the values, we get, ${\text{dQ = W}}$
Hence the heat supplied to the system by the surroundings is equal to the system’s work done on the surroundings.
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
Note: The essential conditions for an isothermal process:
-The walls of the container are perfectly conducting to allow the free exchange of heat between the system and the surroundings.
-The process of compression and expansion should be very slow, to provide sufficient time for the exchange of heat energy.
-The internal energy of the isothermal process remains constant. The transfer of heat in or out of the system happens very slowly that the system maintains equilibrium.
Formula used:
${\text{dQ = dU + W}}$ where,
${\text{dQ = }}$Heat supplied to the system by the surroundings,
${\text{dU = }}$Change in internal energy,
$W$= system’s work done on the surroundings
Complete step by step solution:
According to the First law of thermodynamics, if some heat is supplied to the system, then the quantity of heat absorbed by the system will be equal to the sum of the increase in its internal energy and the external work done by the system on the surroundings.
Ideal gas explores both in classical mechanics and quantum mechanics.

An isothermal process is one in which the pressure and volume of the system change but the temperature remains the same. Therefore, using the formula
${\text{dQ = dU + W}}$,
for an isothermal condition,${\text{dU = 0}}$
Substituting the values, we get, ${\text{dQ = W}}$
Hence the heat supplied to the system by the surroundings is equal to the system’s work done on the surroundings.
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
Note: The essential conditions for an isothermal process:
-The walls of the container are perfectly conducting to allow the free exchange of heat between the system and the surroundings.
-The process of compression and expansion should be very slow, to provide sufficient time for the exchange of heat energy.
-The internal energy of the isothermal process remains constant. The transfer of heat in or out of the system happens very slowly that the system maintains equilibrium.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




