
In an intrinsic semiconductor, if ${N_e}$ is the number of electrons in the conduction band and ${N_p}$ is the number of holes in the valence band then:
A) \[{N_e}\; > {N_p}\]
B) \[\;{N_e} = {N_p}\]
C) \[{N_e} < \;{N_p}\]
D) None of the above
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: In an intrinsic semiconductor how many electrons become free, the same number of holes are created. Here the number of electron density is $n$ and the number of hole density $p$ is equal.
Complete step by step answer:
A semiconductor is a material that has a conductivity between conductor and insulator. Two types of semiconductors are here, one is a pure(intrinsic) semiconductor and another is an impure(extrinsic) semiconductor. Pure semiconductors are silicon ($Si$), germanium ($Ge$), etc. The intrinsic semiconductor number density of electron-hole pair is ${n_i}$.
Let in a pure Silicon crystal the electron situated in the position of ‘$A$’ in the bond (fig-1) breaks the bond and goes to the position ‘$X$’. That means a valence electron becomes a conduction electron. In the meantime, in the position, ‘$A$’ there occurs a crisis of an electron, and then in the position, ‘A’ there generates a positive charge according to the corresponding electron clouds. This crisis of electrons in the bond is named Hole.
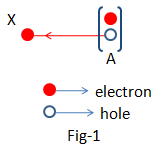
We can say, \[\;{N_e} = {N_p}\]
Hence, the right option is in option (B).
Additional information:
Conductor:
The materials that allow the electric current to flow through them easily are called Conductors. The human body is a good example of good conductors. This property is called Conductivity.
Insulators:
The materials that hinder the flow of electricity are known as the Insulators. Wood and plastic are good examples of insulators. This property is called Insulation.
Note:
The mass-action law states that In thermal equilibrium, the product of the number density of electron n and the number density of hole $p$ is constant. This constant is equal to the square of the number density of intrinsic semiconductor ${N_i}$.
That is, \[{N_e}{N_p} = {\left( {{\text{ }}{N_i}} \right)^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
A semiconductor is a material that has a conductivity between conductor and insulator. Two types of semiconductors are here, one is a pure(intrinsic) semiconductor and another is an impure(extrinsic) semiconductor. Pure semiconductors are silicon ($Si$), germanium ($Ge$), etc. The intrinsic semiconductor number density of electron-hole pair is ${n_i}$.
Let in a pure Silicon crystal the electron situated in the position of ‘$A$’ in the bond (fig-1) breaks the bond and goes to the position ‘$X$’. That means a valence electron becomes a conduction electron. In the meantime, in the position, ‘$A$’ there occurs a crisis of an electron, and then in the position, ‘A’ there generates a positive charge according to the corresponding electron clouds. This crisis of electrons in the bond is named Hole.

We can say, \[\;{N_e} = {N_p}\]
Hence, the right option is in option (B).
Additional information:
Conductor:
The materials that allow the electric current to flow through them easily are called Conductors. The human body is a good example of good conductors. This property is called Conductivity.
Insulators:
The materials that hinder the flow of electricity are known as the Insulators. Wood and plastic are good examples of insulators. This property is called Insulation.
Note:
The mass-action law states that In thermal equilibrium, the product of the number density of electron n and the number density of hole $p$ is constant. This constant is equal to the square of the number density of intrinsic semiconductor ${N_i}$.
That is, \[{N_e}{N_p} = {\left( {{\text{ }}{N_i}} \right)^2}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




