
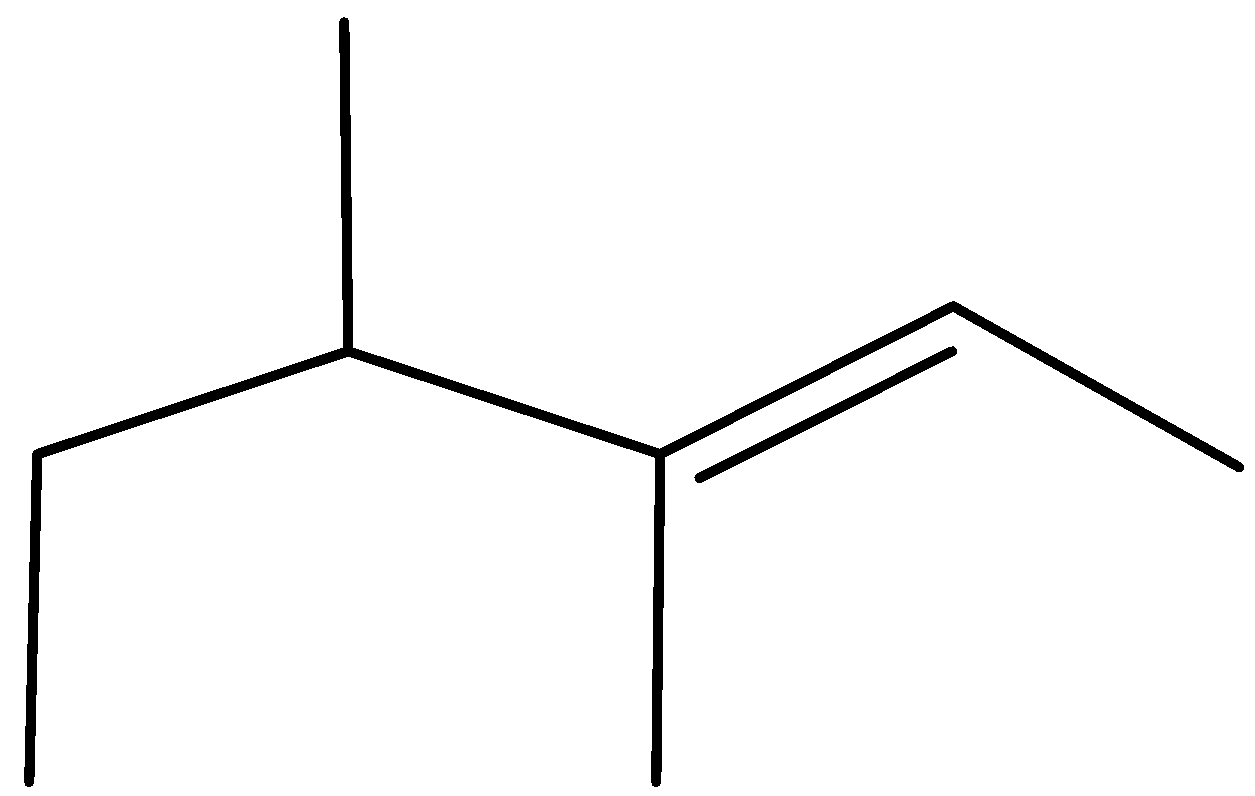
In acid catalyzed dehydration of alcohol which of the following alkene is formed.
The reaction may involve rearrangement.
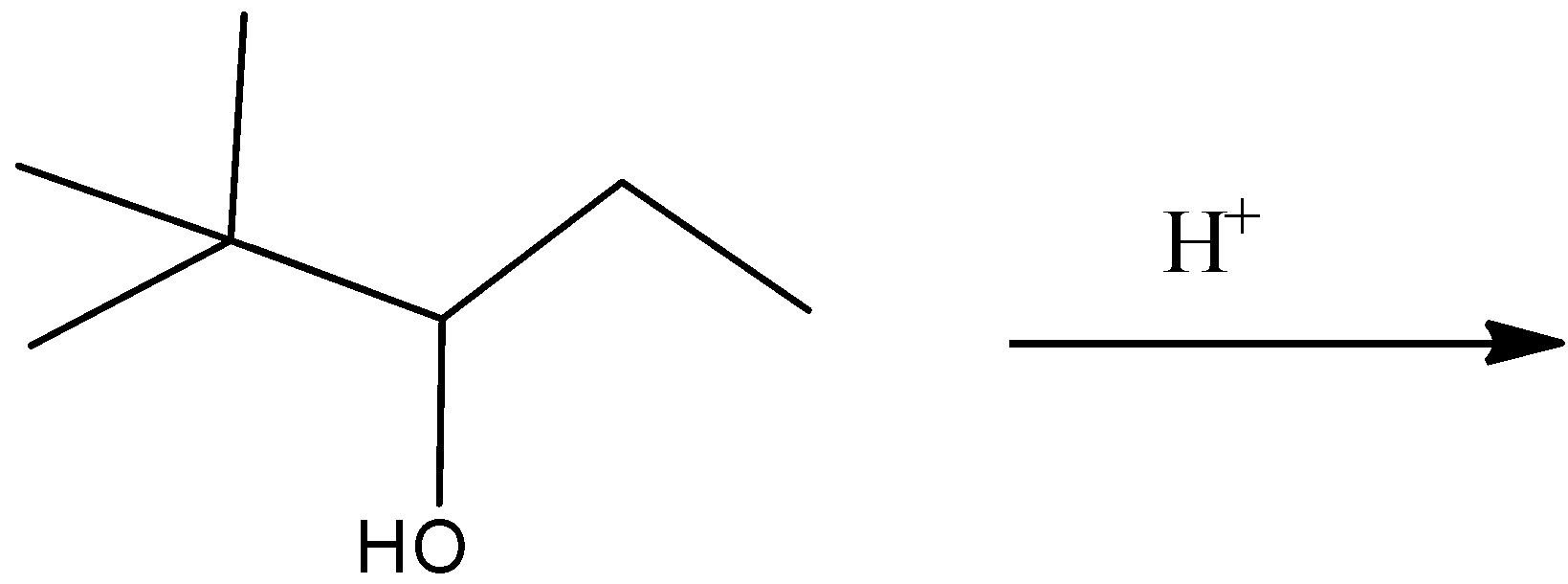
A)
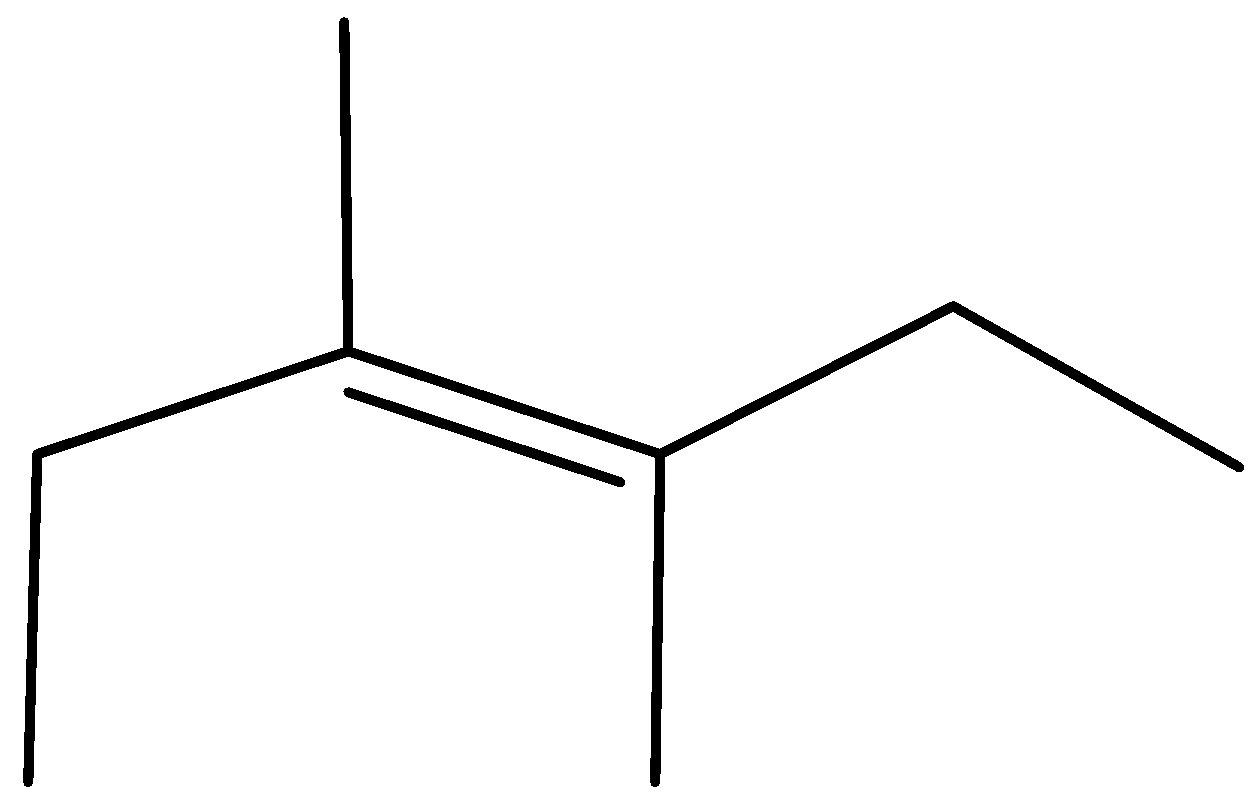
B)
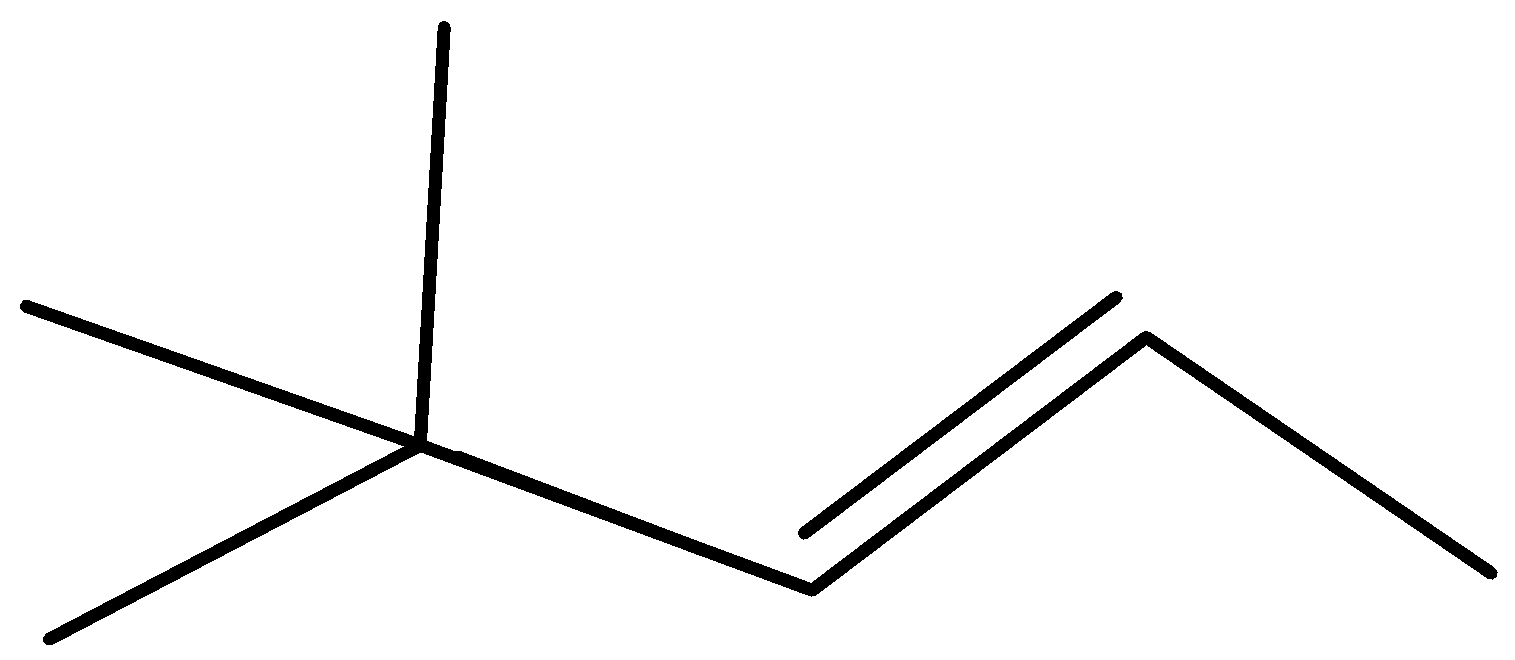
C)
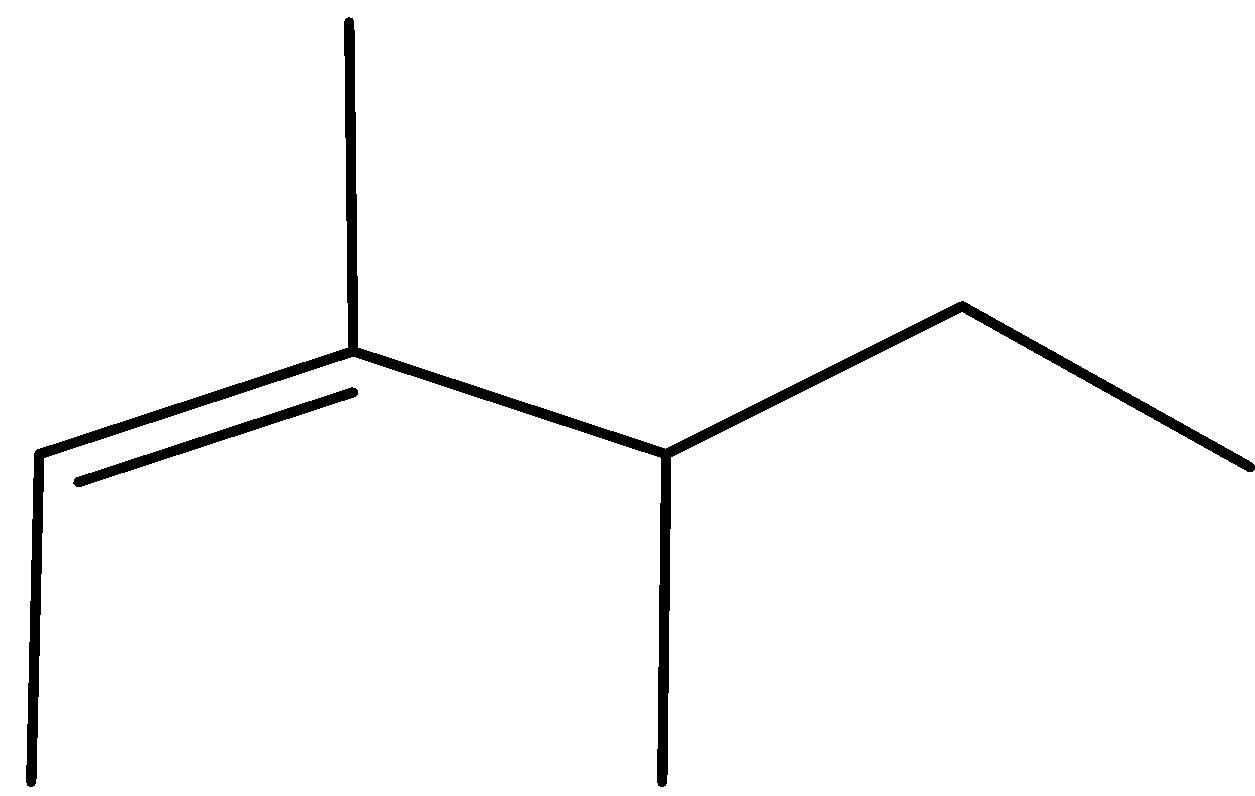
D)





Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: We must remember that the dehydration of alcohols is a way to synthesize alkenes is by dehydration of alcohols, a process during which alcohols undergo \[E_1{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}E_2\] mechanisms to lose water and form a covalent bond. The dehydration reaction of alcohols to get alkene proceeds by heating the alcohols within the presence of a robust acid, like sulfuric or ortho phosphoric acid, at high temperatures.
Complete step by step answer:As we know that the \[{H^ + }\] attach to OH group due to the presence of lone pair of electron and form \[OH{2^ + }\] which may be a good leaving group so removal of water takes place and carbocation is made and then methyl shift takes place because tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation and eventually removal of \[{H^ + }\] ion happen and formation of most stable alkene takes place stability of alkene is defined by the amount of alpha hydrogen present; more the amount of alpha hydrogen more are going to be the stability so the merchandise formed have \[11{\text{ }}\alpha \] hydrogen and hence most stable.
Therefore, Option (A) is correct.
Note:Now we discuss about the nature of carbocation as,
Carbocation:
An ion in which the carbon carries a positive charge is called carbocation and they are formed by the heterolytic cleavage.
Stability of the carbocation:
The stability of the allylic carbocation depends on the inductive effect of the alkyl group attached to the carbocation. The stability of the carbocation increases with an increase in the number of alkyl groups.
The stability order of carbocation is given below,
${{\text{3}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ > }}{{\text{2}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ > }}{{\text{1}}^{\text{o}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:As we know that the \[{H^ + }\] attach to OH group due to the presence of lone pair of electron and form \[OH{2^ + }\] which may be a good leaving group so removal of water takes place and carbocation is made and then methyl shift takes place because tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation and eventually removal of \[{H^ + }\] ion happen and formation of most stable alkene takes place stability of alkene is defined by the amount of alpha hydrogen present; more the amount of alpha hydrogen more are going to be the stability so the merchandise formed have \[11{\text{ }}\alpha \] hydrogen and hence most stable.
Therefore, Option (A) is correct.
Note:Now we discuss about the nature of carbocation as,
Carbocation:
An ion in which the carbon carries a positive charge is called carbocation and they are formed by the heterolytic cleavage.
Stability of the carbocation:
The stability of the allylic carbocation depends on the inductive effect of the alkyl group attached to the carbocation. The stability of the carbocation increases with an increase in the number of alkyl groups.
The stability order of carbocation is given below,
${{\text{3}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ > }}{{\text{2}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ > }}{{\text{1}}^{\text{o}}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




