
In a Young’s double slit experiment, (slit distance d) monochromatic light of wavelength \[\lambda \] is used and the figure pattern observed at a distance L from the slits. The angular position of the bright fringes is
\[\begin{align}
& A.\,\,{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{N\lambda }{d} \right) \\
& B.\,\,{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\left( N+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda }{d} \right) \\
& C.\,\,{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{N\lambda }{L} \right) \\
& D.\,\,{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\left( N+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda }{L} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
549.6k+ views
Hint: We will make use of the path difference formula of the constructive interference to compute the value of the angular position of the bright fringes. Then, we will equate this equation with the product of the wavelength of the light and the order of diffraction.
Formulae used:
\[\Delta =d\sin \theta \]
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
In a Young’s double slit experiment, (slit distance d) monochromatic light of wavelength \[\lambda \]is used and the figure pattern observed at a distance L from the slits.
The formulae that we will be using to compute the angular position of the bright fringes is given as follows.
We will be using the path difference formula to compute the same. Considering the constructive interference, we have,
\[\Delta =d\sin \theta \]
Where \[d\] is the slit distance and \[\theta \] is the angle between the plane and the fringe (the angle of diffraction).
The diagram of YDSE
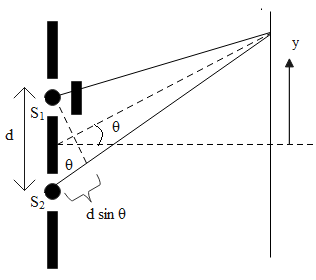
This value of the path difference equals the product of the wavelength of the monochromatic light and the order of diffraction.
\[d\sin \theta =N\lambda \]
Where \[N\] is the order of diffraction and \[\lambda \] is the wavelength of the monochromatic light.
Using this formula we will continue with the computation of the angular position of the bright fringes.
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{N\lambda }{d}\]
Now multiply both the sides by the inverse sine function.
\[\theta ={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{N\lambda }{d}\]
\[\therefore \] The expression of the angular position of the bright fringes, is \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{N\lambda }{d}\], thus, the option (A) is correct.
Note: We have considered the constructive interference to compute the expression of the angular position of the bright fringes. The relation between the angle of diffraction and the wavelength of the monochromatic light should be known.
Formulae used:
\[\Delta =d\sin \theta \]
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
In a Young’s double slit experiment, (slit distance d) monochromatic light of wavelength \[\lambda \]is used and the figure pattern observed at a distance L from the slits.
The formulae that we will be using to compute the angular position of the bright fringes is given as follows.
We will be using the path difference formula to compute the same. Considering the constructive interference, we have,
\[\Delta =d\sin \theta \]
Where \[d\] is the slit distance and \[\theta \] is the angle between the plane and the fringe (the angle of diffraction).
The diagram of YDSE

This value of the path difference equals the product of the wavelength of the monochromatic light and the order of diffraction.
\[d\sin \theta =N\lambda \]
Where \[N\] is the order of diffraction and \[\lambda \] is the wavelength of the monochromatic light.
Using this formula we will continue with the computation of the angular position of the bright fringes.
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{N\lambda }{d}\]
Now multiply both the sides by the inverse sine function.
\[\theta ={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{N\lambda }{d}\]
\[\therefore \] The expression of the angular position of the bright fringes, is \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{N\lambda }{d}\], thus, the option (A) is correct.
Note: We have considered the constructive interference to compute the expression of the angular position of the bright fringes. The relation between the angle of diffraction and the wavelength of the monochromatic light should be known.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




