
In a triangle $\Delta ABC$, the sum of exterior angles at $B$ and $C$ is equal to:
(a) ${{180}^{\circ }}-\angle BAC$
(b) ${{180}^{\circ }}+\angle BAC$
(c) ${{180}^{\circ }}-2\angle BAC$
(d) ${{180}^{\circ }}+2\angle BAC$

Answer
616.2k+ views
Hint: For solving this question, first we will understand some important properties related to triangles, especially exterior angle theorem. After that, we will write the sum of the exterior angles at $B$, $C$, and solve accordingly to get the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given:
We have a $\Delta ABC$, and we have to find the sum of exterior angles at $B$ and $C$ is equal to:
Now, we will see two important properties related to triangles one by one which will be used to solve this problem.
First property:
The Sum of interior angles of a triangle is always ${{180}^{0}}$. It is a very basic property but very useful and important.
Second property:
It is also known as the “Exterior Angle Theorem”. It states that if a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior angles. As shown in the figure below:
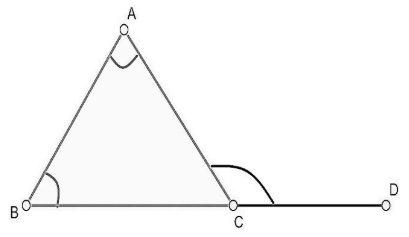
In the above figure, $\Delta ABC$ is shown in which side $BC$ is extended to $D$. Then, from the exterior angle theorem, we can write, $\angle DCA=\angle ABC+\angle CAB$.
Now, we come back to our problem in which we have the following figure:
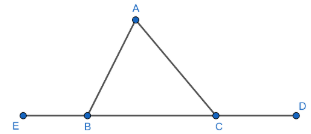
Now, as we know that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is always ${{180}^{0}}$ . Then,
$\angle BAC+\angle ABC+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}.............\left( 1 \right)$
Now, we will use the “Exterior Angle Theorem” for the exterior angles at $B$ and $C$ in the $\Delta ABC$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABE=\angle BAC+\angle ACB.........\left( 2 \right) \\
& \angle ACD=\angle BAC+\angle ABC.........\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will add the equation (2) and (3). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABE+\angle ACD=\left( \angle BAC+\angle ACB \right)+\left( \angle BAC+\angle ABC \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ABE+\angle ACD=\left( \angle BAC+\angle ACB+\angle ABC \right)+\angle BAC \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will write $\angle BAC+\angle ABC+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$ from equation (1) in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABE+\angle ACD=\left( \angle BAC+\angle ACB+\angle ABC \right)+\angle BAC \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ABE+\angle ACD={{180}^{\circ }}+\angle BAC \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the sum of exterior angles at $B$ and $C$ will be $\angle ABE+\angle ACD={{180}^{\circ }}+\angle BAC$.
Hence, (b) will be the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction. After that, we should apply the exterior angle theorem carefully stepwise and also use the property of the triangle correctly. Moreover, we could have solved this question by writing $\angle ABE+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}$, $\angle ACE+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$ as they are linear pairs and then we will add them. Then, substitute $\angle BAC+\angle ABC+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$ and solve to get the required result easily.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given:
We have a $\Delta ABC$, and we have to find the sum of exterior angles at $B$ and $C$ is equal to:

Now, we will see two important properties related to triangles one by one which will be used to solve this problem.
First property:
The Sum of interior angles of a triangle is always ${{180}^{0}}$. It is a very basic property but very useful and important.
Second property:
It is also known as the “Exterior Angle Theorem”. It states that if a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior angles. As shown in the figure below:

In the above figure, $\Delta ABC$ is shown in which side $BC$ is extended to $D$. Then, from the exterior angle theorem, we can write, $\angle DCA=\angle ABC+\angle CAB$.
Now, we come back to our problem in which we have the following figure:

Now, as we know that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is always ${{180}^{0}}$ . Then,
$\angle BAC+\angle ABC+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}.............\left( 1 \right)$
Now, we will use the “Exterior Angle Theorem” for the exterior angles at $B$ and $C$ in the $\Delta ABC$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABE=\angle BAC+\angle ACB.........\left( 2 \right) \\
& \angle ACD=\angle BAC+\angle ABC.........\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will add the equation (2) and (3). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABE+\angle ACD=\left( \angle BAC+\angle ACB \right)+\left( \angle BAC+\angle ABC \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ABE+\angle ACD=\left( \angle BAC+\angle ACB+\angle ABC \right)+\angle BAC \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will write $\angle BAC+\angle ABC+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$ from equation (1) in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABE+\angle ACD=\left( \angle BAC+\angle ACB+\angle ABC \right)+\angle BAC \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ABE+\angle ACD={{180}^{\circ }}+\angle BAC \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the sum of exterior angles at $B$ and $C$ will be $\angle ABE+\angle ACD={{180}^{\circ }}+\angle BAC$.
Hence, (b) will be the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction. After that, we should apply the exterior angle theorem carefully stepwise and also use the property of the triangle correctly. Moreover, we could have solved this question by writing $\angle ABE+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}$, $\angle ACE+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$ as they are linear pairs and then we will add them. Then, substitute $\angle BAC+\angle ABC+\angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}$ and solve to get the required result easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed




