
In a triangle ABC, if AD is the median, then show that ${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2 (A}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2})$
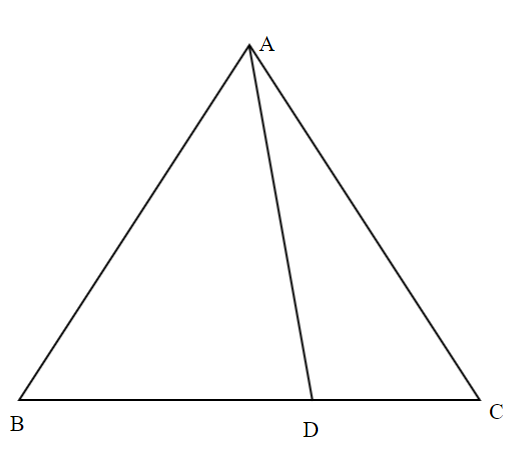

Answer
619.2k+ views
Hint: In this question we will do some construction and also apply the Pythagoras theorem to solve the given problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, to solve this problem we will construct a perpendicular from vertex A to base BC. Drawing AE perpendicular to BC.
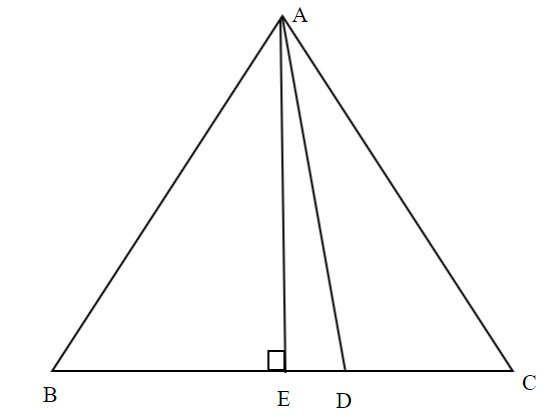
Now we will apply the Pythagorean theorem in right – angled triangles ABE and AEC.
Pythagorean theorem states that in a right – angled triangle the sum of square of base and perpendicular is equal to the square of hypotenuse on the largest side of the triangle. So, in a triangle ABC, right – angled at C,
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{C}}^2}$
Where AC is the perpendicular and BC is the base of the triangle ABC.
Now, applying Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABE, we get
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ = B}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{E}}^2}$ …… (1)
Applying Pythagoras theorem in triangle AEC,
${\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{C}}^2}$ ……. (2)
Now, adding equation (1) and (2),
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{E}}^2}$
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{C}}^2}$
BE = BD – ED and EC = ED + DC
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + (BD - ED}}{{\text{)}}^2}{\text{ + (ED + DC}}{{\text{)}}^2}$
Solving the above equation, we get
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ - 2BDED + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 2EDDC}}$
Now, AD is the median so, BD = DC
So,
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ - 2DCED + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 2EDDC}}$
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{C}}^2}$
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2(A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2})$ as BD = DC …. (3)
Now from triangle AED,
${\text{A}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}$
Putting this value in equation (3), we get
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2(A}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2})$
Hence proved.
Note: While solving such types of questions, you have to think how you can solve the given problem. By carefully seeing the figure given and understanding the question you can easily know which property you have to use to solve the question. Also, carefully apply the property you use to get the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, to solve this problem we will construct a perpendicular from vertex A to base BC. Drawing AE perpendicular to BC.

Now we will apply the Pythagorean theorem in right – angled triangles ABE and AEC.
Pythagorean theorem states that in a right – angled triangle the sum of square of base and perpendicular is equal to the square of hypotenuse on the largest side of the triangle. So, in a triangle ABC, right – angled at C,
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{C}}^2}$
Where AC is the perpendicular and BC is the base of the triangle ABC.
Now, applying Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABE, we get
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ = B}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{E}}^2}$ …… (1)
Applying Pythagoras theorem in triangle AEC,
${\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{C}}^2}$ ……. (2)
Now, adding equation (1) and (2),
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{E}}^2}$
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{C}}^2}$
BE = BD – ED and EC = ED + DC
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + (BD - ED}}{{\text{)}}^2}{\text{ + (ED + DC}}{{\text{)}}^2}$
Solving the above equation, we get
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ - 2BDED + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 2EDDC}}$
Now, AD is the median so, BD = DC
So,
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ - 2DCED + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 2EDDC}}$
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{C}}^2}$
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2(A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2})$ as BD = DC …. (3)
Now from triangle AED,
${\text{A}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ + E}}{{\text{D}}^2}$
Putting this value in equation (3), we get
${\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ = 2(A}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + B}}{{\text{D}}^2})$
Hence proved.
Note: While solving such types of questions, you have to think how you can solve the given problem. By carefully seeing the figure given and understanding the question you can easily know which property you have to use to solve the question. Also, carefully apply the property you use to get the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




