
In a projectile motion, KE varies with time as in graph: (\[\theta \ne 0^\circ ,180^\circ \] with vertical)
A.
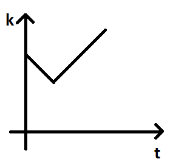
B.

C.
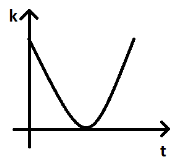
D.
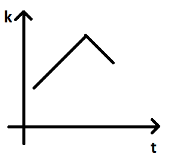




Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint:To solve this problem, we need to know the changes taking place in the kinetic energy of a projectile with respect to time when it is projected with a certain velocity. We will also use the fact that the total energy of the projectile is the sum of its kinetic energy and potential energy. According to this, we will eliminate the wrong options one by one and finally get the final answer.
Formulas used:
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$,
where, $KE$ is kinetic energy, $m$ is mass and $v$ is velocity.
$PE = mgh$, where, $PE$ is potential energy, $m$ is mass, $g$ is gravitational acceleration and $h$ is height.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the kinetic energy of the body decreases and the potential energy increases when the body is projected with some velocity. Here, in option D it is shown that initially the kinetic energy increases with time which is not correct. Thus, option D cannot be our answer.
When the body is projected with the velocity $v$, the minimum velocity is $v\cos \theta $ which is the horizontal component of velocity. This is not equal to zero. Therefore, kinetic energy will never be zero. Thus, option C cannot be our answer.
Now, we know that total energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy.
\[
Total{\text{ }}energy = KE + PE \\
\Rightarrow KE = Total{\text{ }}energy - PE \\
\]
Here, we know that total energy of the body remains constant.
And potential energy $PE = mgh$
Where, $h = v\sin \theta \cdot t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$.
Thus potential energy is a quadratic function of time and hence the kinetic energy also changes quadratically with respect to time.In option A, it is shown that kinetic energy varies linearly with respect to time which is incorrect. Thus, option A cannot be our answer.
Hence, option B is the right answer.
Note:We have seen how kinetic energy changes with respect to time in a projectile motion. We have considered two important facts here. First is that the minimum velocity of the projectile in motion is equal to the horizontal component of the velocity and not zero. Another important thing is that the potential energy is the quadratic function of time which makes the same for the kinetic energy.
Formulas used:
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$,
where, $KE$ is kinetic energy, $m$ is mass and $v$ is velocity.
$PE = mgh$, where, $PE$ is potential energy, $m$ is mass, $g$ is gravitational acceleration and $h$ is height.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the kinetic energy of the body decreases and the potential energy increases when the body is projected with some velocity. Here, in option D it is shown that initially the kinetic energy increases with time which is not correct. Thus, option D cannot be our answer.
When the body is projected with the velocity $v$, the minimum velocity is $v\cos \theta $ which is the horizontal component of velocity. This is not equal to zero. Therefore, kinetic energy will never be zero. Thus, option C cannot be our answer.
Now, we know that total energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy.
\[
Total{\text{ }}energy = KE + PE \\
\Rightarrow KE = Total{\text{ }}energy - PE \\
\]
Here, we know that total energy of the body remains constant.
And potential energy $PE = mgh$
Where, $h = v\sin \theta \cdot t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$.
Thus potential energy is a quadratic function of time and hence the kinetic energy also changes quadratically with respect to time.In option A, it is shown that kinetic energy varies linearly with respect to time which is incorrect. Thus, option A cannot be our answer.
Hence, option B is the right answer.
Note:We have seen how kinetic energy changes with respect to time in a projectile motion. We have considered two important facts here. First is that the minimum velocity of the projectile in motion is equal to the horizontal component of the velocity and not zero. Another important thing is that the potential energy is the quadratic function of time which makes the same for the kinetic energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




