
In a mRNA sequence of Nitrogen base is 5' AUG GUG CUC AAA 3’. What is the correct sequence of anticodons which recognizes codons of mRNA?
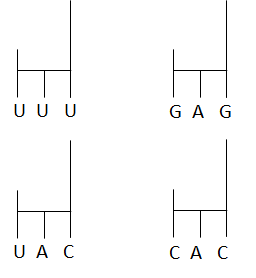
a) UUU
b) GAG
c) UAC
d)CAC

Answer
564k+ views
Hint: mRNA is converted to protein during translation. A sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA encodes a specific amino acid and is referred to as a codon. Each mRNA correlates to a specific amino acid sequence that shapes the resulting protein. The beginning and end of translation are signaled by two codons, called start and stop codons.
Complete answer:
A nucleic acid is a linear nucleotide polymer that forms an integral part of the information transfer system in cells. Nucleotides consist of a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group. In nucleotides, the sugar molecule can be either ribose or deoxyribose, and all sugars are in their pentagon or furanose form. An example of a nucleic acid produced by the polymerization of ribonucleotides is ribonucleic acid. It is a single-stranded chain of ribonucleotides generated by 7 to 12000. There is a ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base in this nucleic acid structure. Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Uracil ( U) are the nitrogenous bases in RNA. By the 'transcription' process, RNA is produced from DNA and is usually involved in protein synthesis. Types of RNA are – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), Transfer RNA (tRNA), and Messenger RNA ( mRNA). A is U complementary and G is C complimentary.
So the correct answer is option C.
Note: A codon is a DNA or RNA’s trinucleotide sequence that refers to a particular amino acid. The genetic code defines the relationship between a gene's sequence of DNA bases (A, C, G, and T) and the corresponding protein sequence it encodes. In groups of three bases, the cell reads the sequence of the gene. There are 64 different types of codons: 61 specify amino acids, while the remaining three are used as stop signs.
Complete answer:
A nucleic acid is a linear nucleotide polymer that forms an integral part of the information transfer system in cells. Nucleotides consist of a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group. In nucleotides, the sugar molecule can be either ribose or deoxyribose, and all sugars are in their pentagon or furanose form. An example of a nucleic acid produced by the polymerization of ribonucleotides is ribonucleic acid. It is a single-stranded chain of ribonucleotides generated by 7 to 12000. There is a ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base in this nucleic acid structure. Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Uracil ( U) are the nitrogenous bases in RNA. By the 'transcription' process, RNA is produced from DNA and is usually involved in protein synthesis. Types of RNA are – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), Transfer RNA (tRNA), and Messenger RNA ( mRNA). A is U complementary and G is C complimentary.
So the correct answer is option C.
Note: A codon is a DNA or RNA’s trinucleotide sequence that refers to a particular amino acid. The genetic code defines the relationship between a gene's sequence of DNA bases (A, C, G, and T) and the corresponding protein sequence it encodes. In groups of three bases, the cell reads the sequence of the gene. There are 64 different types of codons: 61 specify amino acids, while the remaining three are used as stop signs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




