
In a medullated nerve fibre, the conduction of Impulse is faster due to the presence of ________.
A. Pericytes
B. Endoneurium and epineurium
C. Myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier
D. Nissil’s granules
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Neurons are the fundamental unit of function in the central nervous system. They possess all metabolic machinery common to other somatic cells, except the bioelectrical properties. The protoplasmic extensions of neurons are covered with an insulating sheath which allows faster impulse conduction through neurons.
Complete answer: A general neuron consists of three main parts called the soma or cell body, the dendrites and the axon. The cell body consists of mitochondria, the nucleus, and other cell organelles. The dendrites are the thin hair-like extensions of the soma. These are responsible for receiving the nerve impulse from presynaptic neurons. The axons are the protoplasmic extension of the cell body and they are cylindrical in shape. The neuron that receives and conducts signals is called a presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives a signal from the presynaptic neuron is called the postsynaptic neuron. The space between the two neurons is called a synapse through which chemical conduction of signal occurs. For this chemical conduction, there is a need for an electrical impulse that stimulates the release of signalling chemicals called neurotransmitters.
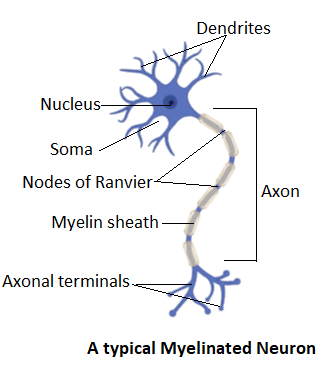
The electrical impulses occur through the axon of the neurons. The glial cells such as oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells make an insulating covering around the axons which are called the myelin sheath. The myelin sheath is a thick covering made of myelin protein which insulates the neuron from neighbouring neurons' electrical impulses. Myelin sheath is not present in a continuous way. It is present with minute gaps called Nodes of Ranvier. These nodes help in the concentration of ion channels and ion pumps that are necessary for electrical signalling in axons. Also, the myelin sheath decreases the leakiness of the axon membrane.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells both make the myelin sheath. But the oligodendrocytes are found only in the brain and spinal cord. The Schwann cells form myelination on nerve fibres of the body except for CNS or central nervous system. Myelin is important as it aids in the smooth propagation of neural signals along myelinated axons.
Complete answer: A general neuron consists of three main parts called the soma or cell body, the dendrites and the axon. The cell body consists of mitochondria, the nucleus, and other cell organelles. The dendrites are the thin hair-like extensions of the soma. These are responsible for receiving the nerve impulse from presynaptic neurons. The axons are the protoplasmic extension of the cell body and they are cylindrical in shape. The neuron that receives and conducts signals is called a presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives a signal from the presynaptic neuron is called the postsynaptic neuron. The space between the two neurons is called a synapse through which chemical conduction of signal occurs. For this chemical conduction, there is a need for an electrical impulse that stimulates the release of signalling chemicals called neurotransmitters.

The electrical impulses occur through the axon of the neurons. The glial cells such as oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells make an insulating covering around the axons which are called the myelin sheath. The myelin sheath is a thick covering made of myelin protein which insulates the neuron from neighbouring neurons' electrical impulses. Myelin sheath is not present in a continuous way. It is present with minute gaps called Nodes of Ranvier. These nodes help in the concentration of ion channels and ion pumps that are necessary for electrical signalling in axons. Also, the myelin sheath decreases the leakiness of the axon membrane.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells both make the myelin sheath. But the oligodendrocytes are found only in the brain and spinal cord. The Schwann cells form myelination on nerve fibres of the body except for CNS or central nervous system. Myelin is important as it aids in the smooth propagation of neural signals along myelinated axons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




