
In a lift, when will the apparent weight become twice the actual weight?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Before going to the question let us first know about apparent weight. The apparent weight of an object is a feature of items that relates to how heavy it is in physics. When the force of gravity acting on an object is not balanced by an equal but opposing normal force, the apparent weight of the object will differ from the weight of the object.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The elevator and the occupant are starting their journey on a lower floor in this example. The elevator, often known as a lift, moves upward. Because the person's inertia would prefer him to remain stationary, the elevator floor and scale must push up on him to propel him higher with the elevator. To stimulate the person's bulk upward, the scale must press upward with greater power on the person. This occurs when the scale and the human come into closer contact.
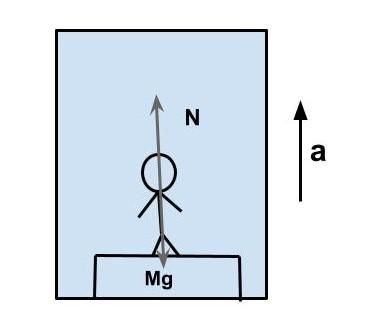
As a result, the Normal Force is stronger, and the reading on the scale is more than the genuine weight. \[F = ma\] operating on the person, according to Newton's 2nd Law.
The person's total acceleration is upward (with the elevator). As a result, the parameter \['ma'\] is positive (upward).
The force of gravity acting downward, \[ - W = - mg\] , and the supporting normal force are the only external forces acting on the person.
while the lift is travelling up with g acceleration.
\[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}m{\text{ }}\left( {g + a} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}m{\text{ }}\left( {g + g} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2mg\]
As a result, the perceived weight becomes twice the actual weight when climbing up and speeding up (acceleration and is positive).
Note:The weight you 'feel' is your apparent weight. When you're falling, you'll have a sense of weightlessness. As a result, the apparent weight is zero. When you're in an elevator that's speeding up, you'll notice that you're getting heavier. As a result, the apparent weight increases.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The elevator and the occupant are starting their journey on a lower floor in this example. The elevator, often known as a lift, moves upward. Because the person's inertia would prefer him to remain stationary, the elevator floor and scale must push up on him to propel him higher with the elevator. To stimulate the person's bulk upward, the scale must press upward with greater power on the person. This occurs when the scale and the human come into closer contact.

As a result, the Normal Force is stronger, and the reading on the scale is more than the genuine weight. \[F = ma\] operating on the person, according to Newton's 2nd Law.
The person's total acceleration is upward (with the elevator). As a result, the parameter \['ma'\] is positive (upward).
The force of gravity acting downward, \[ - W = - mg\] , and the supporting normal force are the only external forces acting on the person.
while the lift is travelling up with g acceleration.
\[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}m{\text{ }}\left( {g + a} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}m{\text{ }}\left( {g + g} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2mg\]
As a result, the perceived weight becomes twice the actual weight when climbing up and speeding up (acceleration and is positive).
Note:The weight you 'feel' is your apparent weight. When you're falling, you'll have a sense of weightlessness. As a result, the apparent weight is zero. When you're in an elevator that's speeding up, you'll notice that you're getting heavier. As a result, the apparent weight increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




